The Future of Technology in Secondary Education in 2020
INTRODUCTION
Secondary education is the form of education after elementary school (or primary education). The age at which children start going to secondary education differs per country, from 9-12 years old. Secondary education takes the students through most of their teenage years.
The goal of secondary education is to give a lot of common knowledge and to prepare them for a next study. This can be either a higher form of secondary education or a study to learn a profession.
Our goal is to study and analyze secondary education, examine the present and the future utilization of technology in secondary education and eventually come up with several scenarios for the future of technology in secondary education in 2020
TEAM COMPOSITION
RESEARCH
Questions & Answers for the future of Secondary Education in 2020
DRIVING FORCES
Political
- Global Security
- Increase of spending on education
- Governmental support on education
- High school dropouts
Economic
- Market for Educational Technology
- Low cost of Technologies and appliances
- Continuous changes in the economy
- Families who live around the minimum-income-border
- Online Gaming Business
Social
- Increasing Human Mobility
- Technology and Young Children (Early Adoption)
- It is harder to be healthy
- Aging problem
- Sending children to private school instead of public school
- Continuous war in the underdeveloped countries
- Switching from school education to home schooling
Technological
- Technological convergence in learning
- Media rich learning
- Development of information search technology
- Communication networks (like MSN, IRC and ICQ)
- Increasing use of open source technologies
- High-speed internet connections
- Virtual classrooms
- Virtual world
- Development of E-book
Environmental
- E-paper solutions instead of paper work
- The change of children playing sports to children playing videogames
- The Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation
- Global Libraries
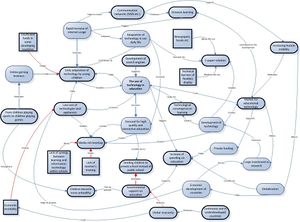
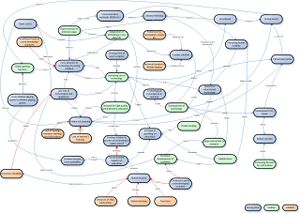
SYSTEM DIAGRAM
Version 1 |
Version 2 (Final) |
SCENARIOS
Scenario 1
Scenario 1 is teacher-based which means there is no real change in education (still focused around a teacher in a classroom instead of the other extreme which would be focusing on the learning experience of a student). This scenario is also said to be pessimistic, which means there is little or no progress in the use of technology.
key "new" things used in education (not really new, all things already exist but their usage needs to increase):
- e-books
- digital learning environments
- media rich learning (use of video, pics, sound)
- more computer labs
- distance learning (e.g. blackboard, webcams, podcasts)
- still low governmental support
- lack of teacher's ict training
- slow economic development in some countries
- inability to use platforms effectively
We write the year 2020. Let's take a good hard look at the use of technology in secondary education. Let's look at how this evolved in the last 13 years, and we find that it hardly has...
Yes, we use computers more now than we did then, but usage of existing technologies does not a revolution make! Think of it: we have started phasing out the printed book in favor of eBooks, but we're still using the same books and yes, we're being more multimedia and location-independent, but in fact we're just broadcasting what was then the teacher's monologuous lecture across the internet so that students no longer need to even get out of bed to consume (and that's what it is!) the lecture.
Truth be told, we have certainly experienced benefits since the beginning years of the technological revolution in education - but we haven't even started yet! We've 'saved' the environment and brought knowledge to one and all by using eBooks; but think of this as well: it was all done by (and hence all works have been re-copyrighted by) Google, it has decimated the book printing industry costing millions of jobs, while at the end of the day the most powerful function of Word 2020, the first one new users search for, is 'print'.
Scenario 2
By the end of 2007, two were the main factors that enhanced secondary education all over the world. Firstly, the majority of the governments decided eventually to support the educational system not only with frothy speeches but also by increasing the spending on education. Until 2010 there is a noteworthy increase of spending on education, especially in Europe and United States, which was also supported by private funds. Secondly the broadband penetration in daily life was a fact, and till the end of 2012 high internet connectivity and WiFi access points were a commodity. Both factors were really important for a significant growth of utilizing technology in secondary education, and together with the general governmental support led the market for educational software and hardware to maturity by the end of 2015. Not only had they sold many pieces of educational software in schools but they also invested a large amount of money to develop added-value services and applications. During that period and due to technological breakthroughs, some online “coursewares”, which offered high quality learning possibilities, have been introduced by the end of 2012. At the beginning of 2014 video glasses and 3D Holograms started to be utilized in several schools in the US, China and Europe. These kinds of technologies provide students with the ability to watch 3D interactive videos and presentations, stimulating their curiosity and their willingness to learn, and actually it illustrates how technology helps and facilitates motivation during the process of learning. Even though, those kinds of technologies were definitely adding value to the learning process, the lack of sufficient teacher’s training as well as the restrictive curriculums prevented the wide use of those devices and their further improvement. At the same time that the high internet connectivity all over the world had been established, a dramatic progress of the open-source community took place, which caused the wide use and design of wikis not only over the entire internet but also over educational intranets. A new tendency emerged, and the learning process starting to move from teacher-to-student towards student-to-student. This interaction among students enabled new patterns of learning to be developed, and encouraged the collectively generated and managed knowledge within schools. The progress of the open-source community together with the market maturity led to the development of a high quality, user-friendly virtual school following the example of second life, at the beginning of 2015. Two years later and even though the pilot programs were finished with great success, there were still legislation issues postponing the use of the virtual environment in real life, and politics who were having doubts, whether a student can get a certified secondary education degree online. At the beginning of 2020 US ministry of education was ready to legalize the acquisition of a secondary degree online, and a new era in secondary education was about to rise. Moreover, the progress of the open-source community as well as the governmental support caused further improvements on the 100$ laptop during 2013 to 2016 and it was distributed to more children at the developing countries. The 100$ laptop together with the worldwide broadband penetration and governmental support, led to an increasing use of technology in secondary education at the developing countries by the end of 2020.
Scenario 3
REFERENCES
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Secondary_education - General information on secondary education
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Primary_education - General information on primary education