Next generation mobile devices 2015
Team Composition
Research questions
QZ8yv2 <a href="http://jotaddhzaeiq.com/">jotaddhzaeiq</a>, [url=http://umziqzjbvgji.com/]umziqzjbvgji[/url], [link=http://kbrqwbvcqrzp.com/]kbrqwbvcqrzp[/link], http://aybytniecsfq.com/
Users
Analysis of the Primary Target Market
- How is the use of mobile technology across the age groups? Is there other good classifications of mobile users?
- In what situations is a mobile device used?
- In what locations do people use mobile technology?
- How much time do people use mobile devices on average?
- How many people use mobile devices besides voice activity?
- Can people live without a mobile devices?
- For what reason do people buy mobile technology, impress, copying others?
- How many months do people change their mobile phones on average?
- What factors can influence People's satisfaction about mobile devices?
- Are people satisfied with the current state of mobile technology?
- What are the reasons for mobile service dissatisfaction?
- What kind of people will use mobile technology in 2015?
- Is there any niche market for mobile devices?
- Why do people want to be reachable, do they even want to be reachable?
- Are people worried about privacy and security issues when using mobile devices?
- Do people prefer to have different functionality in different devices, or do they want one single device with all the functionalities?
- Can there be selective customization in mobile devices equivalent to the computer industry (select components, enable add-ons)
- Convergence of devices will make mobile technology more complicated. Will this scare off most people?
Mobile devices
Questions about several aspects of mobile devices, like interface, functions, technology, power supply.
- What kind of user interface technology is available in 2015?
- What does the mobile wireless network infrastructure currently look like?
- What is the role of fashion with mobile technology?
- What will be the effect of bendable OLED displays on mobile device design?
- What kind of data do people access using mobile technology?
- What kind of bandwidth is needed for applications?
- What is the future for modular applications in mobile technology?
- Who will develop these functional modules?
- How will piracy affect those modules?
- What are Femtocells, and their potential effect on wireless mobile networks?
- What is the perceived functionality of an i-phone? Do such devices (or similar from NOKIA and Sony-Ericsson) cast MP3 devices obsolete?
- What application are used on the mobile phone and how often are they used?
- What do we mean with mobility?
- Can the mobile phone be used as a wallet?
- What possibilities does Wimax offer?
- What is the potential of broadband connectivity on mobile devices?
- Will VOIP slowly take over the traditional mobile phone carriers?
- How can compression be used for mobile technology?
- What is the mobile technology roadmap?
- All these new technologies imply increased energy consumption. Is there a more efficient alternative to Li-ion power batteries? Can it be environment friendly?
- What alternatives are there as power supply to batteries?
- What is Mobile 2.0?
- Which parts of the mobile device consume the most energy?
Social issues
Influence of social issues like, security, health, environment, culture, equality, ethic, government regulations. And the influence on other industries.
- Does Mobile technology pose a security threat (terrorism, difficult to trace)?
- What kind of security threats will be there for mobile technology (virusses, eavesdropping, ...)?
- Does mobile phone radiation have negative effects on human beings?
- Does the increased sophistication of connectivity networks pose any tangible health risks?
- How can mobile technology improve health, can it be used to store medical history?
- What’s mobile waste’s influence on our environment?
- Can mobile device be “green” in the year 2015?
- How does mobile technology impact a society?
- Can mobile devices be used for parental control?
- How does culture affect the use of mobile technology?
- With the development of mobile devices, is there more or less equality in the society?
- Does mobile technology affect social responsibility?
- Will the new mobile devices too difficult for the old people to handle?
- Are mobile phone implants (tooth or brain) feasible, or even ethically acceptable?
- How can mobile technology influence a language?
- What is mobile activism?
- What government departments supervise this industry?
- How can the government use mobile technology?
- What other industries will be influenced by the development of mobile devices?
- How will e-banking develop?
- How will e-commerce develop?
- Will advertising companies manage to use new mobile technology?
- Does mobile technology make land lines obsolete?
- Will internet television make normal television obsolete?
- Which countries are the furthest ahead with mobile technology?
Driving Forces
Driving force template - copy when needed
Social forces
Economic forces
Science & Technology forces
- Dependability of the mobile device (trustworthiness)
- Power Consumption
cOCeLF <a href="http://qibxsdixcgad.com/">qibxsdixcgad</a>, [url=http://lnnwwrkkdgge.com/]lnnwwrkkdgge[/url], [link=http://spxzoyulgwzo.com/]spxzoyulgwzo[/link], http://nilwsnryfwwg.com/
Population & Demographic forces
System Diagram
The following diagram shows the main driving forces in square boxes. The secondary driving forces (not described in this page) are ovals. The enablers are shown as arrows ending with a closed triangle. The inhibitors are shown as arrows with a open diamant at the end. In this way it is possible to show that driving forces can be both enablers and inhibitors at the same time.
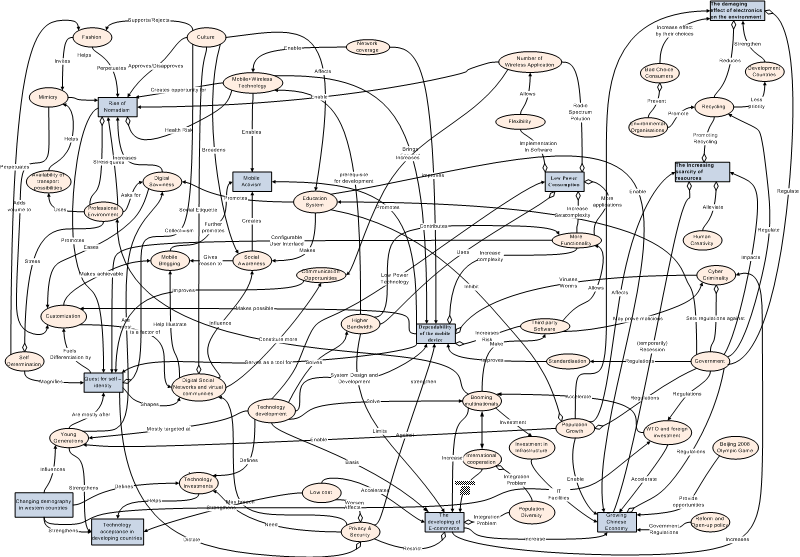
High Resolution version (350 KByte)
Scenarios
Scenario 1: Mobile Downfall
This scenario is characterised by a complete loss in trust for technology. Due to increasing cyber criminalism and lack of proper security technology access to the internet is regarded as unsafe. Furthermore the increasing number of wireless devices make people dislike mobile technology.
2008/9
Health Mobile telephones are now an integral part of modern telecommunications. In some parts of the world, they are the most reliable or only phones available. Given the immense numbers of users of mobile phones, even small adverse effects on health could have major public health implications. Radio frequency fields penetrate exposed tissues to depths that depend on the frequency - up to a centimeter at the frequencies used by mobile phones. With the integration of various means of communication into a single device, the more radio frequency fields are produced. Scientists have reported other effects of using mobile phones including changes in brain activity, reaction times, and sleep patterns. More studies are in progress to try to confirm these findings.
Cybercrime & Security Cybercrime is on the rise, more and more websites and systems of well known companies are hacked. Sensitive information about customers, ranging from personal details to credit card numbers, are stolen and used for criminal purposes. As a result the security of the usage of internet is a hot issue. Makers of computer viruses are starting to target the few dominant operating systems used on the latest generation of integrated mobile phones, leading to another breach in security. Technology to use your mobile device as a means of paying and banking, able to replace the current standards of paying with plastic and internet banking, are being developed and will be introduced shortly.
Trust in mobile devices Several major issues both in the domains of health and security are slowly instilling doubts in many mobile devices users about the safety of said devices. Some users are starting to mistrust the new technologies and have started a new trend in thinking for the next decennia.
2012
Health Doctors have found the first proof of health problems caused by mobile phones. They say up to five per cent of the population could be suffering headaches, mood swings and hearing problems caused by radiation from mobile devices. Experts are advising people - especially children - to limit their use of phones if they experience headaches or other symptoms. The symptoms including nausea, headaches and dizziness which researchers believe are a clear indication of radiation.
Cybercrime & Security Since the introduction of E-wallet technology in 2009 mobile devices are now used to pay in a variety of different situation, from buying a train ticket to paying for online purchases. The mobile devices are also starting to get used for storing personal information off all sorts, medical history and the likes, allowing for easy and accurate sharing of information when needed. This also sound brilliant, but there is a very large problem. As with all relatively young and sensitive technology the above mentioned developments are an easy target for cybercriminals. Since using a mobile device as a payment method is done wireless it has proven to be easy to copy and replicate the signal, resulting in a huge problem for the users of this technology. Losing your mobile device, or being robbed from it, means losing a lot of personal and sensitive information. Several cases are know where this information, sometimes of people in important position, was abused.
Trust in mobile devices Where the problems with mobile devices as a health hazard and a target of cybercrime were minor a few years ago, they now prove to be much more serious. Now that the health hazards are proven and the security of the new technologies for mobile devices severely breached, the trend of thinking started in 2009 is picking up. More and more users are exchanging their mobile device for a simple cell phone and are putting their trust in older but proven technology to replace the lost functionality.
2015
Health The impact that mobile phones have on health is clear. What is clear is that there is a syndrome associated with excessive mobile phone use. Around 40% of users complain that they suffer from headaches, and many people find that after a day's heavy use of the phone that they have a thumping headache. After a while users feel extremely tired, and their reaction times start to fall off.
Cybercrime & Security The security of integrated mobile devices with a host of different functionalities is at its lowest point yet. Cybercrime is organised to easily abuse people that are still using several of those mobile technologies and haven’t got their devices properly secured. Basically any functionality beyond the simple calling an messaging is soon abused by criminals. There is still a niche market for elaborate mobile devices, where the customers are tech-savvy people with enough knowledge to keep their devices well secured.
Trust in mobile devices The sales of headsets and earpieces are declining because the enormous adverse effect, because they conduct radiation directly to the head. People are only buying basic cell phones just to be reachable while traveling. Some people are even reverting back to the now outdated and hardly used landlines. Users don’t want to spend much money on these devices anymore and are expecting them to last for up to five years. In general people are putting their trust in older and proven technology. These developments have had a major impact on the producers of mobile devices, only a few have survived and are now focusing their effort on a small niche market where competition is fierce. Companies that used to produce the older technologies and that managed to survive are growing again and can hardly keep up with the renewed demand for their products.
f2VL1Y <a href="http://ufoopfmnnykj.com/">ufoopfmnnykj</a>, [url=http://brpzblbmjywj.com/]brpzblbmjywj[/url], [link=http://qxspehthcgnh.com/]qxspehthcgnh[/link], http://isdnoegqnmfx.com/
Scenario 3: Mobile Heaven
In this scenario, both market dynamics and adoption of new media is high, fuelled by customer needs and responsiveness, a favorable economy and relentless technological development. The device convergence, a media sector which is a patchwork of numerous niche markets and the unification of service providers under a wireless umbrella, constitute an ideal environment for digital adepts, driven by the consumer who is always “in control”.
2008/9
Device Convergence - Main Players: In 2008 the introduction of the iPhone 3G set a new benchmark for the mobile landscape and swayed consumers, experts and critics alike, marking the obsolescence of device divergence. What used to be a ridiculous variety of single-purpose gadgets (notebooks, GPS, mp3 players, mobile phones, cameras, PSPs and Nintendo DSs etc) has shaped up to become a single device for mobile and home applications. Location based services outgrew the traditional GPS market. New standards such as on demand video and Mobile TV, as well as ubiquitous open-source applications are about to become the norm. Mid 2009 and Google has taken the lead with Android, featuring rich point-of-interest content as well as location-bound social networking. iPhone 3G may have been the first to make mobile Internet real and usable, Android’s open platform however won over the developer community, leaving behind Nokia’s Symbian and delivering the final blow to Blackberry’s limited interface.
Economy turnaround:
The success of 2008 Beijing Olympics, the fall of Burma’s junta and North Korea’s modernization gave the Asia-Pacific market a remarkable lead. Inflation rates in western markets have gone down, while innovation is now guided by “living lab” communities throughout Europe and Asia. Europe is still number one market, followed by Asia and US in the third place. In the meantime, ecological awareness and political shifts reflected onto mobile activism, which in turn translates into more intense and ubiquitous mobile device usage.
2012
Device Convergence - Main Players: In 2012, after taking over TomTom and acquiring Canon’s lens licenses, Nokia responds with the bendable OLED, fully customizable and WiMax capable Aeon model, rivaled only by LG’s Prada 3. Sony, yet to recover from PS3’s and Bravia’s commercial misgivings, doesn’t make a move on the mobile market until 2012, alongside with Samsung, delivering the 4G PSP3.
Economy turnaround:
The thawing of the Arctic polar icecaps in 2011 unleashed a wealth of natural resources, mineral and oil, reanimating a global economy struck by 2008’s oil shortage. New resources and increased consumer buying power and needs are the main reasons that made the electronics boom possible.
Privacy web quality mark:
Crucial to the mass acceptance of new appliances and services is that consumers trust the integrity of the providers, with privacy and security being the hotly debated subject in the years 2008 to 2012. Providers listened to calls for regulation and set up an international watchdog in conjunction with an activist privacy-protection organization.
Device Convergence:
The most important aspect is that services are perceived as being relevant and convenient. On the one hand the dependability of well-known services has increased (eg. anytime, anywhere mobile video), on the other hand new ones are conjured and developed such as GPS-based location bound services. Both WiFi hotspots and Wimax have taken off, aided by Fem-to-cell hubs and wide user acceptance. As a result the consumer has permanent broadband access which enables rich media content, HD mobile TV and mobile MMORPG gaming. And of course the implications for service providers are huge, with the existence of a single service providing end-to-end IP-based network.
Device convergence – Media consequences:
DVB-H, the broadcast technology for handhelds was unsuccessful. People, being accustomed to have complete control over what they watch and when, are unwilling to settle with a linear broadcast. Only parties that embraced a cross-media strategy have survived, which left out a majority of laggards.
2015
By 2015 personal electronics have become an integral part of the lives of most people, young and old. Technology sophistication is closely bound with user friendliness so that everybody can handle it. Nor is the price an obstacle, since most of the services are offered for free, thanks to adverts and sponsoring models. Thus the age and status demographic margins are blurred, with devices and protocols usable by consumers of virtually any age and financial state.
Device Convergence:
By 2015 there is no distinction between home and mobile phones, with the device simply searching for the most appropriate network to carry its traffic. With self-service now being the majority of service requirements, the call centers’ purpose of existence are to deal with the exceptions and manage more complex interactions.
By 2015, the first nanite-enhanced concept handsets are appearing in technological exhibitions in Tokyo and Korea. The outdated Li-ion batteries have been fully replaced by hydrogen cells, the increased capability and easy recharge of which have made the long sustainability of converged devices possible. Since 2012, mobile wallet, m-banking, and RFID product encoding, recognizable by mobile devices, have shifted the way payments are conducted.
Device Convergence - Main Players:
By 2015 Motorola and Blackberry have completely retracted from the mobile landscape. The company formerly known as Microsoft has been severed and spread threefold into Linux, and the now merged Google and Apple, being one of the three global players: the other two are Nokia-Ericsson in Europe and LG-Sony-Samsung in Asia. And last but not least, the ubiquitous mobile phone is more than ever a fashion-driven piece of gadgetry, with either minimalist or extravagant designs, such as the swiveling 2011 Nokia N99 which automatically revolved into a standing picture/video frame.
Privacy web quality mark:
Based on government funding, Wimax license providers and private groups, this project has proved itself efficient by 2015, and is able to conduct effective supervision over the protection of user privacy. Each site and software provider who subscribes to the strict protocol and undergoes an annual privacy audit is entitled to carry the privacy-proof web quality mark.
Device convergence – Media consequences:
The advent of personal electronics has revolutionalized the media landscape. While some large parties are still active as oligopolists, such as CNN and BBC, most media segments have lots of small providers and some have lost ground completely. Competition is fierce and margins wafer-thin. Newspapers are barely read, since mobile blogging and live mobile RSS have made them redundant. TV stations compete fiercely, but despite the immense number of offerings it’s almost impossible to surpass the nearly-perfect navigation system Google has created for all possible kinds of content; the latter includes the fully mobile operative gTunes which has overthrown iTunes since late 2009.