Scenario 3, Ubiquitous Browsing:
Overview
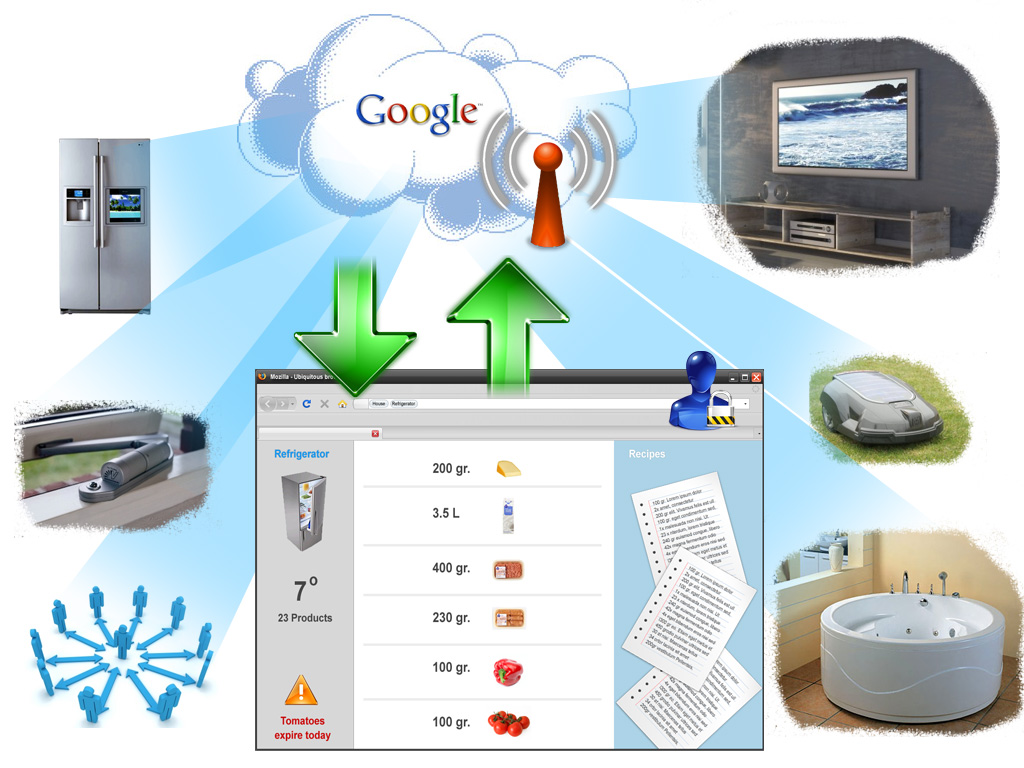
Via the PC that we all know for so long, we still browse. But websites are not the only thing we can browse. People can also browse their own house and electrical appliances within their house. Most of the important electrical appliances are connected to the web via wireless access points. Let say that “Average Joe” goes to his work, arrives at work and sees that there is a big thunderstorm coming. He suddenly realized that his bedroom window is still open. He quickly opens the browser, logs on to his house, and closes the window. At the end of the day, Joe is wondering what to make for dinner. He realized that he doesn’t remember what kind of products were present in his refrigerator. So he browses his refrigerator and sees what products are available. He can also see the expiration data and some suggested recipes. One of the suggestions is to cook chicken in the oven. To be sure that the oven is already heated up when he arrives, he sets the timer for the oven.
Time line
2009-2011
The appearance of the desktop is still a very dominant design and therefore did not change much. Screen are bigger, processors faster and computers have 4 times more memory and storage space. But people still browse websites as they did before.
Social networking became part of people daily occupations. But with the rise of so many social networks and web 2.0 applications, people became confused of what to use. And people become very annoyed by the fact that they had to remember hundreds of different user/password combinations from all the different web 2.0 services they used. By the end of 2011, the web 2.0 was at his peak, and ready to evolve into the new web 3.0.
By the end 2010 the economy was clearly recovering from the deep economic crisis. Banks were more transparent and could be trusted again by other banks en consumers, and vice versa. The economic rise had an impact on the buying behavior of people, buying via the web. But, web browsers still lacked to give the buyer a real world experience of “feeling” the product.
2012-2015
Web 2.0 became the past and web 3.0 is born. The problems web 2.0 faced were the organization of data, and finding the right data as fast as possible. Web 3.0 is becoming the semantic web. Meta data and micro formats are becoming very important in order to make the semantic web work. Browsing for information becomes a lot easier and faster since the browser actually understands what you are looking for. The browser is now artificial intelligent and extracts meaning from the way people interact with the web. The browser will recognize who is surfing the web.
Mobile devices are not just devices to call one another, but are mobile devices to browse the semantic web, play social games, and interact with others on your social network.
The biggest browser companies came together and sat around the table with W3C. They concluded that their browsers were too big, slow and complex to build upon. Therefore, they build one platform that forms the core of the browser. Each company then build upon that platform to differentiate themselves.
Different social network features and different web 2.0 applications where blended into modules. These modules are build by different software giants, and could be placed on the single core browser that everyone uses. The single identity replaces all the different username/password combinations people had to remember for all the different applications and social networks.
Google introduces their cloud computer service whereby users can store their data into the big cloud. Data stored on your personal computer is very inconvenient since people want to access them everywhere at any time. It is also not very save to have a single file stored on your personal computer. Therefore Google gives users the opportunity to store their data into the cloud. The data is well protected by advanced encryption methods. The data is scatter around within the cloud, and can only be retrieved by the original owner.
Not only the software but also the hardware took a big leap. RFID chips are not only used by large shipping companies, but also by smaller companies. But RFID chips are still too expensive for consumer goods. Multi-touch screens are common sense and most of the personal computers will be equipped with multi-touch screens.
2016-2019
Almost every household in Europe and the US is connected to the web, and accesses the web via their own Wireless access points. Public spaces are also equipped with wireless access points in order to provide a fast connection for mobile devices.
As RFID chips were used more by smaller companies, they became cheap enough to be used by the consumer. A lot of supermarkets now put RFID chips into their products. RFID readers within household appliances are becoming more available. Also some appliances are connected to the web via the wireless access points within houses.
The speed of the internet also increased over the years. Every household, or user of a mobile device is able to access the web very high speeds. Waiting for information to be downloaded is history.
2020
Almost all electrical appliances are equipped with RFID readers and can be connected to the web. Data generated by the electrical appliances is stored into the big Google cloud and could made be public to share with your peers within your social network.
Browser companies saw the opportunities to build modules that could communicate with those electrical appliances. People are able to buy a module that could communicate with your refrigerator. And since the supermarkets are putting RFID chips into their products, your refrigerator can actually see what’s stored in your fridge. Via the browser module, people are able to let the module suggest what kind of recipes they could make with the products available.
Multimedia that is stored into the cloud, or on the hard drive can also be accessed via the browser.
Now, the browser is a multifunctional piece of software that can be personalized with varies modules. With those modules, people are able to get information from their electrical appliances, operate the appliances, conduct social activities and access their files via the Google cloud.