OPEC
Background
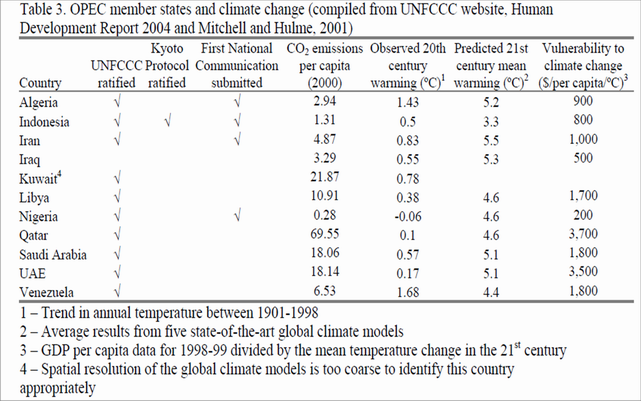
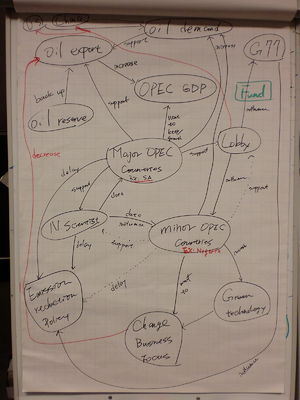
1. OPEC's role in G77 has been simultaneously positive and negative: positive in so far as it brings to G77 a large team of experienced lawyers and negotiators; negative in so far as OPEC is largely concerned with the impact of climate policies on their oil export and revenues rather than in reducing greenhouse gas emissions or in developing policies and measures to facilitate adaptation.OPEC and in particular Saudi Arabia have close associations with the oil industry, in particular US companies. This has led them to oppose greenhouse gas reductions, disrupt the whole negotiation process[1]
2.In 1976, OPEC member countries established the OPEC Fund for International Development, a multilateral development finance institution aimed at promoting cooperation between OPEC and other developing countries, in particular the least developed countries (LDCs). It does this mainly by providing financial resources to assist the latter group of countries in their economic and social advancement.
3.In 2009, OPEC countries accounted for 80% of proved oil reserves in the world.
4.Overall OPEC has become more dependent with an average of 27% of GDP coming from oil exports.OPEC annual statistic report 2009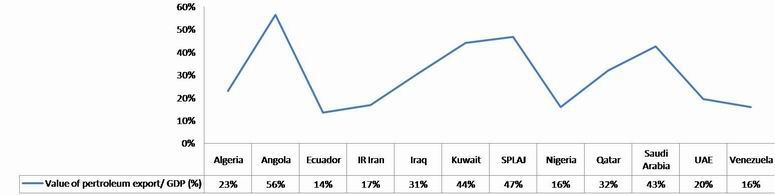
6. OPEC in the UNFCCC:
Representatives of these countries consequently emphasized the scientific uncertainty about climate change and the flaws in existing economic analysis. They went to great lengths to minimise any specific commitments to emissions reductions, avoid any reference to energy and generally to delay the conclusion of an agreement.
8.In general,the influence of OPEC will still grow since other countries' oil production capacities will decrease in the future. However, the oil comsuption is increasing in the recent years, and this the increaseing comsuption trend will affect the oil export amount of OPEC.[2]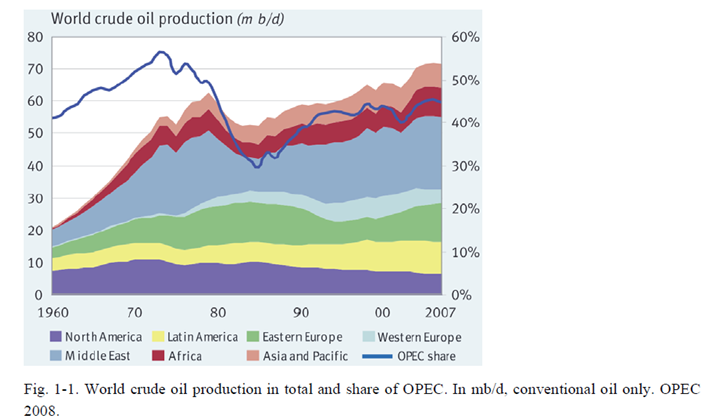
9. OPEC offically announces the oil reserves sufficient until 2020.[3]