Difference between revisions of "Future of the Bottom-Up Internet"
Rsparnaaij (talk | contribs) (removed pictures (misplaced here)) |
|||
| Line 179: | Line 179: | ||
== Scenarios == | == Scenarios == | ||
[[Scenario 1: bottom-up Internet| Scenario 1: | [[Scenario 1: bottom-up Internet| Scenario 1: Trouble, trouble, trouble]]<br> | ||
[[Scenario 2: bottom-up Internet| Scenario 2: Life goes on]]<br> | [[Scenario 2: bottom-up Internet| Scenario 2: Life goes on]]<br> | ||
[[Scenario 3: bottom-up Internet| Scenario 3: I can do computers me]]<br> | [[Scenario 3: bottom-up Internet| Scenario 3: I can do computers me]]<br> | ||
[[Scenario 4: bottom-up Internet| Scenario 4: We are the Borg. Resistance is futile!]]<br> | [[Scenario 4: bottom-up Internet| Scenario 4: We are the Borg. Resistance is futile!]]<br> | ||
Revision as of 11:40, 14 May 2006
Welcome
Introduction
In our group, we discussed the future of Bottom-Up Internet. Bottom-up is part of what is called Web 2.0. Bottom-up Internet is all about user contributions to the Internet and the development of it. By using availanble web resources, driving forces, diagrams, matrixes and group discussions we developed 4 scenarios of where these developments might take us.
Group Members
Research Questions
To research the bottom up internet we had to set up some research questions. The questions have been set up together and briefly discussed in the group. The Q&A have been grouped in who formulated the final answer.
Jim
-
What is bottom up internet?
- The “bottom up internet” is a descriptive term meaning a collection of techniques / services / products that make it possible to transform normal internet users into content providers. This can be with the purpose of providing leisure but also with the purpose of sharing and creating knowledge.
- What techniques are used for the bottom up internet?
- A combination of standards that are available to the public but combined to provide a better user experience, for example: AJAX (Javascript, (X)HTML, XML, DOM, XMLHttpRequest), RSS, CGI.
- Additional technologies that can also be used are the Server based scripting languages, JAVA and databases.
- In short everything that can be used to provide internet content.
-
What services are used for the bottom up internet?
- Offerings of: Blogspaces, Webspaces, Forums, Wikispaces, Podcasts, Open source participation and support for all the previously mentioned development techniques.
- Also additional services related to improving the surfing quality of the individual users like identification services and content generation based on the user profile.
-
What products are used for the bottom up internet?
- There are a lot of products relating to the bottom up internet, they are provided by different companies but all are related to the techniques and services offered: BitTorrent, Wikipedia, Napster, CU2, SNARFER, SharpReader, NetNewsWire, Straw, Bloglines, www.blogger.com, www.podcast.com, www.ipodder.org,
-
How many blogs are there?
- More than 80 million blogs created online in 2005 (http://www.blogherald.com)
- Currently http://www.technorati.com/ tracks more than 30.8 million active Latin/American blogs.
-
How many users are blogging?
- Around 30% of internet users read blogs
-
Is there an increase in blogs / users?
- The amount of blogs to track doubles every 5 months
- The amount of bloggers increases a little less fast than the blogs.
-
How big are blogs?
- The total number of messages on tracked blogs is 2.1 billion.
- The number of blogs tracked is 30.8 million.
- 2.1 billion divided by 30.8 million is around 70 messages per blog. However there are blogs which are for personal use only and others that have more than 100 posts a day.
- How big is the bittorrent community?
- 1/3 of the internet traffic now a days is due to bittorrent usage.
- At any time there are more than 2.5 million transfers going around.
- How big is the open source community
- It consists of more than millions of developers ( http://sourceforge.net/docs/about ) and the OSTG of which almost all open source creaters are a member from has more than 18 million unique visitors a month.
- More than 100.000 open sourceprojects are currently registered and underway.
- http://asay.blogspot.com/2005/09/analyst-nature-and-size-of-open-source.html
Robert
- What techniques are being used to attract visitors?
- For websites web 2.0 helps to attract visitors and/or make them return to the website. An important web 2.0 development for this is RSS support
- Websites that use web 2.0 components are highly interactive and more powerful than regular websites. In some cases they can actually replace locally installed applications. We cab see this by the new web based mail clients like from Gmail and Windows Live Mail.
- How are these products/sites/services funded?
- Sites that offer content or tools for free are mainly funded by means of advertising and donations. Funding is dependent on the success of the website/tool.
- Since web 2.0 websites are highly configurable lots of sites offer a login. Some services are only available when you take a paid subscription.
- Who are the big players in the bottom-up market?
- Microsoft (Windows Live)
- Yahoo
- Whereto are big players in the market moving?
- Offering web based versions of applications that are normally installed locally. Currently these are mainly tools like RSS readers, web mail and portal pages. Microsoft is moving towards bigger applications with offering Microsoft Office Live.
- How will content be checked/authorized?
- There are three main methods to check and authorize content. These are by consensus, voting and finally the site owner.
Andrew
-
What is blogs ? And why using blogs?
- A blog (short for "Web log") is a cross between a personal diary and a list of links to articles on the Web. Internet users can create them, and anyone surfing the Web can read them.
- Everyone can express his meaning/thought or sharing information on a easy way.
- In Web 1.0, a small number of writers created Web pages for a large number of readers. Over time, however, more and more people started writing content in addition to reading it.
-
What will the bottom-up internet effect?
- New search engines, an online marketplace, solutions for spam, communication.
- People have stuff they want to share (or axes to grind or stuff they want to say), so giving them a place to express themselves and a community of users to share it with will result in a system that grows exponentially through the network effect to become more than the sum of its parts
-
What is bottom-up internet important for?
- According to some expert bottom-up internet infrastructure is the key to achieve a knowledge-based society. It can change peoples lifestyle, knowledge, view, politics … etc.
-
how many podcast users?
- The study estimates that 4.8 million persons have at some time during 2005 downloaded a podcast from either a radio station or other source. While in 2004 only 820,000 podcast users.
- More interestingly, on average less than 20% listen to their podcast downloads on an MP3 player or other digital device.
- By 2010 podcast audience growth is expected to reach a conservative 45 million users who will have ever listened to a podcast. Aggressive estimates place this number closer to 75 million by this date.
Driving Forces
We have identified the following driving forces:
Jim
- Customer expectency: People are becoming accustomed to the fact that products are specialised for their needs. In areas in which the customization doesn't fit their needs they try to find solutions of their own. The internet is a very good place to share those customizations.
- Improved user friendliness of web based publishing services: Because it has become easier to publish content online most of the borders preventing publishing have fanished and thus more users publish.
- ICT accustomed society Improved integration of IT into the current society: More and more people are growing up with computers or know how they work because of having to work with them at a company. This makes the group of internet and thus also bottom up internet users bigger and better.
Robert
The founders and executive management of the first batch of companies have moved on - either joined one of the big players, left to join VCs, or start or join a completely new thing. This means a lot of experience of what did and didn't work is in the mix.
More people go online; bottom-up is all about delivering content to people and also make them (individual) the source for new content. The more people go on-line the more gets contributed
Increase in broadband; P2P and POD casts are just some of the bottom-up techniques that require a lot of bandwidth to perform optimally. Increase in broadband will also aid in bringing more powerful web applications and services to the client.
Andrew
-
More possibility by faster internet connection.
As internet connection speed keeps increasing, people want to share/download music, movie or information with/from others. Therefore WebLogs, P2P networks, bittorrents and different file sharing system arise. -
Freedom of speaking.
As new technology develops, more and more people have access to the internet at low cost. And so more and more people wants/needs to express his meaning/thought. And some people wants Freedom on expression, especially in China where use internet is restricted. But in a community using blog they can talk about anything, including politics and sex. Since China have the second highest number of internet users on the world, the influence will be great. -
New service opportunity.
Companies try differentiate from his competitors by prividing better services. Websites provides extra services for example RSS . Or the web-service like amazone, ebay, MyYahoo, Gmail ... are provided.
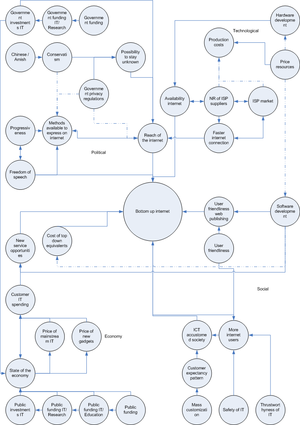
Map
This map shows the relation and effects of outside forces on the development of the bottom-up Internet. These forces have been categorized in;
- Political
- Technical
- Economy
- Social
Solid lines indicate a positive relation or effect and a dotted line a negative relation or effect.
Scenarios
Scenario 1: Trouble, trouble, trouble
Scenario 2: Life goes on
Scenario 3: I can do computers me
Scenario 4: We are the Borg. Resistance is futile!