Difference between revisions of "Future of Sustainability 2030"
| (129 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
Yojiro Fukaya<br> | Yojiro Fukaya<br> | ||
Eric Lam<br> | Eric Lam<br> | ||
Yunzhu (Carrie) Ma<br> | |||
[[User:Hugh.malkin|Hugh Malkin]]<br> | [[User:Hugh.malkin|Hugh Malkin]]<br> | ||
Kay Mei Tan<br> | Kay Mei Tan<br> | ||
=Introduction= | =Introduction= | ||
"Sustainable Development is a process of change in which the exploitation of resources, the direction of investments, the orientation of technological development; and institutional change are all in harmony and enhance both current and future potential to meet human needs and aspirations." from the United Nations Report of the World Commission on Environment and Development: Our Common Future (Brundtland Commission) http://www.un-documents.net/ocf-02.htm#I<br> | |||
Or in other words: | |||
Sustainable Development meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs<br> | |||
Sustainable development deals with Social Equity, the Economy, and the Environment<br> | |||
=Research Questions= | |||
;Definition | |||
#[[What is the definition of Sustainability?]]<br> | |||
#[[What is "The Tragedy of the Commons"?]]<br> | |||
;General | |||
#[[What is the history of sustainability?]]<br> | |||
;Envirnoment | |||
#[[What is the rate of Ice melt?]] | |||
# [[What is the urgent issue relating to sustainability?]]<br> | |||
# [[What can we do as a individual?]]<br> | |||
# [[What is measurable?]]<br> | |||
#[[What are current international regulations regarding sustainability?]] | |||
;Energy | |||
#[[What are the current major ways of power generation]] | |||
#[[What is the most efficient power generation method in terms of cost and CO2 emission?]] | |||
#[[What to extent cost of renewable energy will be cheeper?]] | |||
;Technology | |||
#[[What are the key technologies?]] | |||
#[[Can technological development solve environmental issues dramatically?]] | |||
;Resource | |||
#[[What is the outlook of world energy in the next 20 years?]] | |||
#[[How much oil is left in the world? When will oil run out?]]<br> | |||
#[[Is water the Key Limiting Factor?]]<br> | |||
#[[Will other natural resource, other than energy, play serious roles in the future sustainability?]] | |||
#[[What are the other threats to sustainability?]]<br> | |||
#[[How do human beings interact with/affect natural resource?]] | |||
#[[What are the energy trends in India and China?]] | |||
#[[What are the impacts of climate change to the future sustainability?]] | |||
;Value | |||
#[[What is the most important value for sustainability?]] | |||
#[[What is the method evaluating values?]] | |||
#[[What are the values of the worlds leading polluters?]] | |||
;Pollution | |||
#[[What is the most important pollutant?]] | |||
#[[Which Fossil Fuels give off most Carbon Dioxide? What are the worst Fossil Fuels?]]<br> | |||
;Population | |||
#[[Is our population growing?]] | |||
#[[Is there a limit to growth?]] | |||
;Education | |||
#[[What is Education for Sustainable Development (ESD)?]] | |||
=Driving Forces= | |||
#[[Sustainable Resources]] | |||
#[[Alternative Energy]] | |||
#[[Technological Development]] | |||
#[[Education]] | |||
#[[Business]] | |||
#[[Economy]] | |||
#[[Regulations for Sustainability]] | |||
#[[Values]] | |||
#[[Population]] | |||
#[[Pollution]] | |||
== | =Systems Diagram= | ||
[[image:Diagram_sustainability1.jpg|200px|1st draft]] | |||
1st draft | |||
[[image:systemmap.jpg|200px|Final version]] | |||
Final version | |||
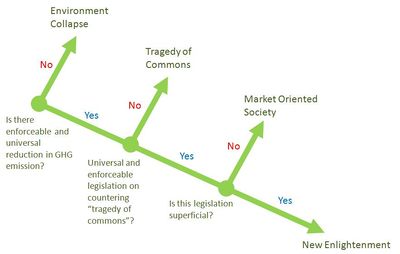
= | =Scenario Tree= | ||
[[image:ScenarioTree_s2.jpg|400px]] | |||
=Scenarios= | =Scenarios= | ||
# [[Collapse of the Environment]] | |||
# [[Tragedy of Commons]] | |||
# [[New Enlightenment]] | |||
# [[Market Regulation]] | |||
=References= | =References= | ||
#[[Websites]] | |||
#[[Books]] | |||
#[[News Articles]] | |||
#[[Notes]] | |||
Latest revision as of 12:31, 17 October 2009
Welcome to the Future of Sustainability in 2030
Group Members
Yojiro Fukaya
Eric Lam
Yunzhu (Carrie) Ma
Hugh Malkin
Kay Mei Tan
Introduction
"Sustainable Development is a process of change in which the exploitation of resources, the direction of investments, the orientation of technological development; and institutional change are all in harmony and enhance both current and future potential to meet human needs and aspirations." from the United Nations Report of the World Commission on Environment and Development: Our Common Future (Brundtland Commission) http://www.un-documents.net/ocf-02.htm#I
Or in other words:
Sustainable Development meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs
Sustainable development deals with Social Equity, the Economy, and the Environment
Research Questions
- Definition
- General
- Envirnoment
- What is the rate of Ice melt?
- What is the urgent issue relating to sustainability?
- What can we do as a individual?
- What is measurable?
- What are current international regulations regarding sustainability?
- Energy
- What are the current major ways of power generation
- What is the most efficient power generation method in terms of cost and CO2 emission?
- What to extent cost of renewable energy will be cheeper?
- Technology
- What are the key technologies?
- Can technological development solve environmental issues dramatically?
- Resource
- What is the outlook of world energy in the next 20 years?
- How much oil is left in the world? When will oil run out?
- Is water the Key Limiting Factor?
- Will other natural resource, other than energy, play serious roles in the future sustainability?
- What are the other threats to sustainability?
- How do human beings interact with/affect natural resource?
- What are the energy trends in India and China?
- What are the impacts of climate change to the future sustainability?
- Value
- What is the most important value for sustainability?
- What is the method evaluating values?
- What are the values of the worlds leading polluters?
- Pollution
- What is the most important pollutant?
- Which Fossil Fuels give off most Carbon Dioxide? What are the worst Fossil Fuels?
- Population
- Education
Driving Forces
- Sustainable Resources
- Alternative Energy
- Technological Development
- Education
- Business
- Economy
- Regulations for Sustainability
- Values
- Population
- Pollution
Systems Diagram
1st draft
Final version