Difference between revisions of "Future of Broadband"
| (99 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==GROUP MEMBERS== | |||
We are the MBA students from the Amsterdam Business School UvA. | |||
Our Group comprises of: | |||
# Edurne Ozaeta | |||
# Jacob Oskam | |||
# Murat Ögat | |||
# Magali Bongrand | |||
''' | ==INTRODUCTION== | ||
We have been requested to come up with 3 scenario for our client, '''[http://www.kpn.com KPN]'''. KPN is faced with a challenge: [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wimax WiMax] technology is developing rapidly and they wonder if they should invest in this new technology. WiMax have clear advantages: full freedom and mobility (can work from the park), cheaper than [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/umts UMTS], constant connectivity; but after the flop of 3G / UMTS such investment decisions make the top management nervous and they want to know whether they should invest, and if so when they should start their investment? As a first mover or after letting another player pays the cost of the learning curve? Does this have to be at industry wide effort at the European level? Considering that Wimax addresses the needs of outdoor professional primarily, coverage is crucial else UMTS is a better option. So, where should the investment start, in the main cities or nationally? How fast should it spread to the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rural rural areas]? Who is going to be responsible for paying the costs of such an infrastructure (can they expect the government to subsidize this infrastructure)? Which clients should be the first targets (business or consumers?)? KPN also wonders about the impact of [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Network_externality network externalities] (computers, PDA’s) on the demand for mobile technologies and the effects that exit barriers in some countries will have on the European diffusion on WiMax technologies (France and Finland have barred access to this technology to protect their UMTS investments). | |||
== CATEGORIES == | |||
We consider the following questions crucial in understanding the broadband technology and it's future: | |||
# [[Future_of_Broadband#Basic_Questions_on_Broadband|Basic Questions]] | |||
# [[Future_of_Broadband#Current_Issues_in_Broadband|Current Issues]] | |||
# [[Future_of_Broadband#Trends_in_Broadband|Trends and Future Issues]] | |||
These are elaborated in next section. | |||
== RESEARCH QUESTIONS == | |||
===[[Basic Questions on Broadband]]=== | |||
* What is broadband? | |||
* What are the advantages of broadband? | |||
* What are the techniques available? | |||
===[[Current Issues in Broadband]]=== | |||
* What are the current usages of broadband? | |||
* What is the current broadband penetration? | |||
* Who are the main players? | |||
* what are the main bottlenecks to broadband diffusion? | |||
* How is the internal rivalry among the main players? | |||
===[[Trends in Broadband]]=== | |||
* What broadband techniques will emerge in the future? | |||
* Will the emerging broadband-over-powerline (BPL) technology be successful? | |||
* What are the future opportunities of broadband? | |||
* Will the limited availabilty of broadband in under-developed countries limit their development? | |||
* What will be the issues raised in mass multimedia download and sharing related to broadband growth? | |||
* When will hardware bottlenecks limit the growth of broadband? | |||
* When will the marginal utility of increased bandwidth be negligible? | |||
* What security problems arise by the combination of fast computational speed limits and broadband communications? | |||
* What problems have to be solved before broadband communication can be used as a substitute to other ways of communication? | |||
== DRIVING FORCES == | |||
Three variables are of crucial importance for the future of broadband. Those are | |||
===[[Speed of Broadband]]=== | |||
The infrastructure, standards and device capabilities will affect the future of the speed of broadband. Increased speed is the key enabler for any optimistic Internet scenario. | |||
===[[Applications of Broadband]]=== | |||
The more applications using broadband connection are available, the more business will be moved to the Internet. This variable represents the usefulness | |||
level of the increased technology and faster broadband. | |||
===[[Penetration of Broadband]]=== | |||
This driving force defines the cultural acceptance and usage of broadband Internet in the world. It is the direct driver of all Internet-based markets. | |||
<br> | |||
===Useful Driving Forces Proposed by Group 2: [[Future of the Creation of Software]]=== | |||
To further explain the driving forces of broadband Internet we found those driving forces of Group 2 useful: | |||
[[Increase demand for user friendly software|User Friendly Software]] | |||
[[Increase in demand for secure software|Software Security]] | |||
[[Increase in demand for web-service based applications|Web-Based Applications]] | |||
[[Rapid advancement in technology drives innovation in software|Innovation in Software Development]] | |||
[[NGO%27s increases awareness of society about software industry|Sociological Awareness]] | |||
===Useful Driving Forces Proposed by Group 3: [[Future of Mash Ups]]=== | |||
To further explain the driving forces of broadband Internet we found those driving forces of Group 3 useful: | |||
[[More than ever%2C the user experience matters|The User Experience]] | |||
[[Emergence of broadband / growing online community / a new culture|A New Culture]] | |||
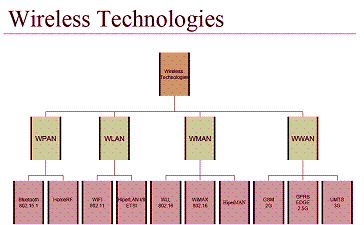
===Different types of WiMax Proposed by Daniel=== | |||
[[Image:Wireless.gif]] | |||
'''WBAN and WPAN''' | |||
A WBAN provides the connectivity among various devices of wearable computers whose components are distributed on the body | |||
E.g. microphones, earphones, etc. | |||
A WPAN connects one-person’s BAN with the environment around it (devices around the person) | |||
Bluetooth is an example of a wireless PAN that allows devices within close proximity to join together in an ad hoc fashion to exchange information | |||
Many cell phones have two radio interfaces: one for the cellular network and one for PAN connections | |||
'''WLAN''' | |||
A WLAN provides a wider range of connectivity with higher data rate than that of WPAN and WBAN | |||
Infrastructure mode: requires an AP and provide access to Internet backbone | |||
Ad hoc mode: peer-to-peer communication | |||
Typical applications: hot spots, buildings | |||
Requirements of a WLAN | |||
High capacity | |||
Full connectivity among the attached nodes | |||
Broadcasting capability | |||
In terms of standardization | |||
In US: IEEE 802.11 and IEEE 802.15 (Bluetooth) | |||
In Europe: HiperLANII | |||
'''WMAN''' | |||
WMAN provides a broadband and fast access (higher data rate) with even wider range than that of WLAN | |||
Standards: | |||
In US: IEEE 802.16 | |||
In Europe: HiperACCESS(>11GHz) and HiperMAN(<11 GHz) | |||
IEEE802.16: | |||
Support multiple services simultaneously with QoS | |||
IPv4, IPv6, ATM, ETHERNET | |||
Support multiple frequency allocation (2-66GHz) | |||
Point-to-multipoint topology with mesh extension | |||
BS is connected to public networks | |||
BS serves subscriber stations (building, residence) | |||
Link adaptation (adaptive coding and modulation) | |||
Support for advanced antenna systems | |||
WiMAXForum (Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access) | |||
Promotes deployment of BWA (Broad Band Wireless Access) by usinga global standard and certifying interoperability of products and technologies | |||
upport IEEE802.16 | |||
===System Diagram -=== | |||
[[Image:diagram.gif]] | |||
== SCENARIOS== | |||
[[Image:Bubble.jpg|thumb|150px|right|The Internet bubble explosion was devastating for many, but do people learn from history?]] | |||
===Scenario 1 - [http://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Système_D Systeme D]=== | |||
At the middle of 2006 the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Economic_recession economic recession] that has been hampering world-economy since the Dot-com crises appears to be over. In the United States growth has been picking up for a little while. And in continental Europe consumers have become optimistic again. | |||
However, because of increasing oil-prices and oil-shortages, the US-deficit and the political situation in the world this optimism will not be long lasting. The US has problems to finance their huge oil-demand, the dollar is getting weaker. Europe, and within it [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_netherlands The Netherlands], will suffer from this due to its strong thighs with the US-economy. | |||
====Mobile Technologies==== | |||
Consumers loose faith in the economy again, and stop spending their money. More money is being put on [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Savings_account savings accounts]. Nobody knows how long the expected recession will last. Further, people want to make sure that they will be able to life a decent live after their retirement. | |||
In these circumstances, no consumers are interested in new mobile technologies. They keep using their mobile phones and their internet connection at home. Less and less people want to spend money on new technologies. The companies will show the same approach. Since, cost-cutting will be the credo again they will cut cost and investments on new gadgets. | |||
Therefore, mobile technology companies such as [http://www.nokia.com Nokia] and [http://www.ericsson.com Ericsson] will have to cut their [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/R%26D R&D] budgets. They don’t want to develop technologies that they won’t be able to sell. With the same reasoning the number of applications available for mobile technology won’t increase. For the industry as a whole this means that there will be a slower shift in communication methods such as voice-over-IP ([http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Voip VOIP]). | |||
All this will result in the stagnation of mobile broadband penetration. | |||
====E-Commerce==== | |||
As consumers are becoming less willing to spend their money, the demand for [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/E_commerce e-commerce] decreases. Consumers are only willing to buy at e-businesses that really add value. Because of this, the “[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Survival_of_the_fittest survival of the fittest]” will eliminate weak e-commerce companies. This will result in a little 2nd Dot-com crash, or what could merely be seen as the last convulsion from the bigger dot.com crash of 2001.The effect will be that the industry as a whole becomes healthier. The good companies will survive and the bad ones will past away. | |||
This will also lead to increased competition among software companies by requesting them to develop better applications for more demanding e-commerce companies. Better applications will improve the security and the user-friendliness of doing business through the internet. The cultural embedding of internet usage will be enhanced, and also the elderly become more willing to participate as a consumer in the e-commerce business. Altogether, this will alter shopping habits. | |||
However, we don’t expect this to result in a high increase in broadband connections. People will do the e-commerce business through their existing broadband connections and use more of their overcapacity. This counts especially in the Netherlands, where the penetration of broadband is already very high. Additionally, due to the economic down-time the cost of marginal efficiency will be too high for most broadband users. Therefore, they won’t be motivated to pay for increased speed of their broadband connection. | |||
====The Government==== | |||
The | With the economic depression the government will decrease [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Subsidies subsidies] towards [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Disruptive_technology disruptive technologies]. This will affect mainly [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Developing_countries developing countries]. But, the government wants to stimulate the home-economy and to show the electorate that it takes actions to enhance such stimulation. Therefore, they are willing to invest in infrastructure that will serve as a motor for the economy. The information technology subsidies of the government will flood towards new technologies such as [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wimax WiMax] to provide broadband access to the rural areas. The availability of the WiMax network will reduce the switching cost from dial-up to broadband (only a small card will be needed to connect any PC to the network, no more personal DSL, WiFi or cable modem needed, switching costs also include the perceived cost of the initial investment and the practical cost of getting the information and the connection itself). Further, the government will help schools to give computer education to pupil from younger and younger ages. This will increase the cultural embedding of broadband technology in the long term. By the end 2010, the shopping habits will be forever altered and the economy will experience an upturn. Consumers will start to regain interest in mobile technologies and gadgets. The mobile technology developer will respond by heavily increasing the investment in R&D to develop new attractive devices. The full fleshed digital age is reached by end 2011. | ||
---- | |||
===Scenario 2 - Warriors at rest=== | |||
For the last few years a number of telecom companies had invested huge amounts of money in [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Umts UMTS] technology. As a result any change in the current system will interfere with their opportunity to recover its initial investments. The spread of WiMax in the market is a threat for these companies therefore they are going to react negatively to this change. We expect that following the example of France and Finland, a number of telecom companies in Europe will block their Wimax frequencies in order to protect their previous [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Umts UMTS] investments. | |||
[[Image:Umts.jpg|thumb|300px|left|Vodafone's advertisement of [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Umts UMTS] services and compatible devices. A standart that is aging too fast to cover the investments.]] | |||
====Effects of Mobile Broadband Penetration==== | |||
In Europe, UMTS will be the only option available for customers interested in mobile broadband access. Because UMTS is rather expensive, there will be not move towards commoditization of the mobile broadband technologies. Customers will not be exposed to the advantages of full mobility and full connectivity; hence, the cultural embedding mobile broadband and its applications will be very slow, almost stagnating. | |||
As a result of that, the market will not give sufficient incentives for the mobile devices producers to invest in R&D. The supply of more mobile devices integrating broadband technologies will be low. | |||
====Effects on Customer’s Habits==== | |||
The growth of static (home/ office) broadband will not be disrupted and will continue to growth slowly at the same rate as it does now. As a result, the growth of e-commerce will not suffer any high growth or decline. In view of this slow growth economy, software and technology based companies are just going to “digest” their previous investments. There will be only little improvement in the user friendliness or the security of the applications, and in QoS in general. The effect will be a slow cultural embedding of Internet usage. | |||
At the same time, economic development and broadband penetration in developing countries will go on at the same high pace rate. The early adoption of disprutive technologies that is common to those countries enable them to "leap-frog" to the next standard such as WiMax quicker than Europe and the USA. This might cause a short time discripancy such as that known to mobile phone lag in the USA in the 90's. | |||
====Role of the Government==== | |||
Because there is not recession, the government will not be motivated in interfere. There will be not program to increase broadband access to everyone or to help cultural embedding at schools in excess of what is being done at the moment. | |||
---- | |||
===Scenario 3 - Easy come, Easy go=== | |||
[[Image:Tvphone.jpg|thumb|200px|right|A japanese phone with satellite TV receiver proves that high speed and high quality combined can open a new dimension of possible devices and applications.]] | |||
====Effect on Utilization Patterns==== | |||
One of the most critical problems faced by technological companies and e-businesses to increase the demand for e-commerce and the switch in communication methods has been the stand still of QoS. Technology companies are now for years striving to find critical applications that will improve it to a substantial level. The debate today is whether or not the improvement of QoS is even possible. The hadware bottleneck stands at the ethernet hubs. In this scenario, we expect that the efforts of technological companies towards compression and encryption techniques reached a momentum and drastically improved the level of QoS and the security of transactions over the Internet and for a solution to the ehternet bottleneck to be divised in order to increase the speed. As a result of the improved service, the cultural embedding of the Internet usage is accelerated. Likewise, QoS increases the shift in communication methods, in the first place, especially for businesses, such as video conferencing Over IP and VOIP. | |||
====Effects of Broadband Penetration==== | |||
- | With the shift in communication methods, the higher QoS level will reduce the cost of marginal efficiency of getting larger broadband accounts for the private users. It will also increase the transfer rate from dial-up to broadband and trigger a trend towards commoditization of broadband access (with BOPL technologies for instance). These 3 factors will in turn lead to a massive growth in the broadband penetration rate. In this case, if Wimax is available it will be proposed to clients as a competing option to DSL, Wifi, UMTS, BOPL or cable. | ||
====Effect on E-Commerce==== | |||
The increase in security systems and the cultural embedding of Internet usage will improve the demand for e-commerce: now, everyone is online at all times and going shopping gradually means typing a URL. Unfortunately, this increase of e-commerce demand without economical pressures will lead to more “crap-for-sale" online: the long tail in its all grandeur. The number of credible business model will be lower as a ratio to the total business model generated. The percentage of reliable e-business suppliers is lower and feeling of security decreases. The increase in broadband penetration will also increase the level of Internet vandalism. Internet commerce will be perceived as a "fad" and consumers will be thrown rapidly back in their old/safe shopping habbits. Added to that, the learning curve limitation will hamper the cultural imbedding of the Internet usage and will affect the client’s choice for Wimax. Indeed, consumer are bombarded with options and compared to the rest, Wimax is the newest will be interesting to early adopters only at first. | |||
====Government Influence==== | |||
The government will not take any action in the homeland since the economy is going well. On the other hand, it will help the developing countries be subsidizing disruptive technologies such as satellite broadband connections infrastructure for remote area in developing countries. The penetration in developing countries will increase. | |||
== STRATEGIC INPUT FOR KPN == | |||
Based on the 3 scenario presented, the insights found are: | |||
* The current cultural embedding of mobile technologies is not optimal amongst private users. This means that they will not rush to but a WiMax adaptable laptop or PDA is KPN invested tomorrow in a WiMax network because they do not have the use for it | |||
* Most important clients will be businesses. Nevertheless, businesses currently are equipped for WiFi and UMTS technologies, which means that the only motivation for them to invest in new equipment and subscription would be full connectivity and full mobility. That implies that going WiMax needs to be done on an “all or nothing” approach. | |||
* Other interested parties would be clients for which the switching costs from dial up to current Broadband technologies are too high (because of original investment in modem, etc. and private customers interested in mobile broadband and which find UMTS too expensive. This market will not be sufficient to justify such infrastructure investment, even if only in the big cities. | |||
* Besides, exit barriers from previous technologies such as UMTS safeguards that other telecom companies in Europe and nationally will eagerly invest in setting up a WiMax infrastructure. | |||
As a result, we would recommend to KPN not to invest in WiMax at this time. We recognize the importance of the mobile broadband technologies and their effect on the society and its contribution to economic growth. With that in mind, KPN should look at the long term and ensure that WiMax will be a part of the broadband infrastructure. That goal could be reached by focusing on lobbying government and other telecom companies in motivate them to invest in such infrastructure for the positive effect this would have on society and the positive economical boost it will bring. | |||
'''''Useful links:''''' | '''''Useful links:''''' | ||
http://www.cis.state.mi.us/mpsc/comm/broadband/broadband/broadband.htm | |||
http://www.oecd.org/document/39/0,2340,en_2649_34223_36459431_1_1_1_1,00.html | http://www.oecd.org/document/39/0,2340,en_2649_34223_36459431_1_1_1_1,00.html | ||
Latest revision as of 14:53, 12 June 2006
GROUP MEMBERS
We are the MBA students from the Amsterdam Business School UvA. Our Group comprises of:
- Edurne Ozaeta
- Jacob Oskam
- Murat Ögat
- Magali Bongrand
INTRODUCTION
We have been requested to come up with 3 scenario for our client, KPN. KPN is faced with a challenge: WiMax technology is developing rapidly and they wonder if they should invest in this new technology. WiMax have clear advantages: full freedom and mobility (can work from the park), cheaper than UMTS, constant connectivity; but after the flop of 3G / UMTS such investment decisions make the top management nervous and they want to know whether they should invest, and if so when they should start their investment? As a first mover or after letting another player pays the cost of the learning curve? Does this have to be at industry wide effort at the European level? Considering that Wimax addresses the needs of outdoor professional primarily, coverage is crucial else UMTS is a better option. So, where should the investment start, in the main cities or nationally? How fast should it spread to the rural areas? Who is going to be responsible for paying the costs of such an infrastructure (can they expect the government to subsidize this infrastructure)? Which clients should be the first targets (business or consumers?)? KPN also wonders about the impact of network externalities (computers, PDA’s) on the demand for mobile technologies and the effects that exit barriers in some countries will have on the European diffusion on WiMax technologies (France and Finland have barred access to this technology to protect their UMTS investments).
CATEGORIES
We consider the following questions crucial in understanding the broadband technology and it's future:
These are elaborated in next section.
RESEARCH QUESTIONS
Basic Questions on Broadband
- What is broadband?
- What are the advantages of broadband?
- What are the techniques available?
Current Issues in Broadband
- What are the current usages of broadband?
- What is the current broadband penetration?
- Who are the main players?
- what are the main bottlenecks to broadband diffusion?
- How is the internal rivalry among the main players?
Trends in Broadband
- What broadband techniques will emerge in the future?
- Will the emerging broadband-over-powerline (BPL) technology be successful?
- What are the future opportunities of broadband?
- Will the limited availabilty of broadband in under-developed countries limit their development?
- What will be the issues raised in mass multimedia download and sharing related to broadband growth?
- When will hardware bottlenecks limit the growth of broadband?
- When will the marginal utility of increased bandwidth be negligible?
- What security problems arise by the combination of fast computational speed limits and broadband communications?
- What problems have to be solved before broadband communication can be used as a substitute to other ways of communication?
DRIVING FORCES
Three variables are of crucial importance for the future of broadband. Those are
Speed of Broadband
The infrastructure, standards and device capabilities will affect the future of the speed of broadband. Increased speed is the key enabler for any optimistic Internet scenario.
Applications of Broadband
The more applications using broadband connection are available, the more business will be moved to the Internet. This variable represents the usefulness level of the increased technology and faster broadband.
Penetration of Broadband
This driving force defines the cultural acceptance and usage of broadband Internet in the world. It is the direct driver of all Internet-based markets.
Useful Driving Forces Proposed by Group 2: Future of the Creation of Software
To further explain the driving forces of broadband Internet we found those driving forces of Group 2 useful:
Innovation in Software Development
Useful Driving Forces Proposed by Group 3: Future of Mash Ups
To further explain the driving forces of broadband Internet we found those driving forces of Group 3 useful:
Different types of WiMax Proposed by Daniel
WBAN and WPAN
A WBAN provides the connectivity among various devices of wearable computers whose components are distributed on the body E.g. microphones, earphones, etc. A WPAN connects one-person’s BAN with the environment around it (devices around the person) Bluetooth is an example of a wireless PAN that allows devices within close proximity to join together in an ad hoc fashion to exchange information Many cell phones have two radio interfaces: one for the cellular network and one for PAN connections
WLAN
A WLAN provides a wider range of connectivity with higher data rate than that of WPAN and WBAN Infrastructure mode: requires an AP and provide access to Internet backbone Ad hoc mode: peer-to-peer communication Typical applications: hot spots, buildings Requirements of a WLAN High capacity Full connectivity among the attached nodes Broadcasting capability In terms of standardization In US: IEEE 802.11 and IEEE 802.15 (Bluetooth) In Europe: HiperLANII
WMAN
WMAN provides a broadband and fast access (higher data rate) with even wider range than that of WLAN Standards: In US: IEEE 802.16 In Europe: HiperACCESS(>11GHz) and HiperMAN(<11 GHz) IEEE802.16: Support multiple services simultaneously with QoS IPv4, IPv6, ATM, ETHERNET Support multiple frequency allocation (2-66GHz) Point-to-multipoint topology with mesh extension BS is connected to public networks BS serves subscriber stations (building, residence) Link adaptation (adaptive coding and modulation) Support for advanced antenna systems WiMAXForum (Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access) Promotes deployment of BWA (Broad Band Wireless Access) by usinga global standard and certifying interoperability of products and technologies upport IEEE802.16
System Diagram -
SCENARIOS
Scenario 1 - Systeme D
At the middle of 2006 the economic recession that has been hampering world-economy since the Dot-com crises appears to be over. In the United States growth has been picking up for a little while. And in continental Europe consumers have become optimistic again. However, because of increasing oil-prices and oil-shortages, the US-deficit and the political situation in the world this optimism will not be long lasting. The US has problems to finance their huge oil-demand, the dollar is getting weaker. Europe, and within it The Netherlands, will suffer from this due to its strong thighs with the US-economy.
Mobile Technologies
Consumers loose faith in the economy again, and stop spending their money. More money is being put on savings accounts. Nobody knows how long the expected recession will last. Further, people want to make sure that they will be able to life a decent live after their retirement. In these circumstances, no consumers are interested in new mobile technologies. They keep using their mobile phones and their internet connection at home. Less and less people want to spend money on new technologies. The companies will show the same approach. Since, cost-cutting will be the credo again they will cut cost and investments on new gadgets. Therefore, mobile technology companies such as Nokia and Ericsson will have to cut their R&D budgets. They don’t want to develop technologies that they won’t be able to sell. With the same reasoning the number of applications available for mobile technology won’t increase. For the industry as a whole this means that there will be a slower shift in communication methods such as voice-over-IP (VOIP). All this will result in the stagnation of mobile broadband penetration.
E-Commerce
As consumers are becoming less willing to spend their money, the demand for e-commerce decreases. Consumers are only willing to buy at e-businesses that really add value. Because of this, the “survival of the fittest” will eliminate weak e-commerce companies. This will result in a little 2nd Dot-com crash, or what could merely be seen as the last convulsion from the bigger dot.com crash of 2001.The effect will be that the industry as a whole becomes healthier. The good companies will survive and the bad ones will past away. This will also lead to increased competition among software companies by requesting them to develop better applications for more demanding e-commerce companies. Better applications will improve the security and the user-friendliness of doing business through the internet. The cultural embedding of internet usage will be enhanced, and also the elderly become more willing to participate as a consumer in the e-commerce business. Altogether, this will alter shopping habits. However, we don’t expect this to result in a high increase in broadband connections. People will do the e-commerce business through their existing broadband connections and use more of their overcapacity. This counts especially in the Netherlands, where the penetration of broadband is already very high. Additionally, due to the economic down-time the cost of marginal efficiency will be too high for most broadband users. Therefore, they won’t be motivated to pay for increased speed of their broadband connection.
The Government
With the economic depression the government will decrease subsidies towards disruptive technologies. This will affect mainly developing countries. But, the government wants to stimulate the home-economy and to show the electorate that it takes actions to enhance such stimulation. Therefore, they are willing to invest in infrastructure that will serve as a motor for the economy. The information technology subsidies of the government will flood towards new technologies such as WiMax to provide broadband access to the rural areas. The availability of the WiMax network will reduce the switching cost from dial-up to broadband (only a small card will be needed to connect any PC to the network, no more personal DSL, WiFi or cable modem needed, switching costs also include the perceived cost of the initial investment and the practical cost of getting the information and the connection itself). Further, the government will help schools to give computer education to pupil from younger and younger ages. This will increase the cultural embedding of broadband technology in the long term. By the end 2010, the shopping habits will be forever altered and the economy will experience an upturn. Consumers will start to regain interest in mobile technologies and gadgets. The mobile technology developer will respond by heavily increasing the investment in R&D to develop new attractive devices. The full fleshed digital age is reached by end 2011.
Scenario 2 - Warriors at rest
For the last few years a number of telecom companies had invested huge amounts of money in UMTS technology. As a result any change in the current system will interfere with their opportunity to recover its initial investments. The spread of WiMax in the market is a threat for these companies therefore they are going to react negatively to this change. We expect that following the example of France and Finland, a number of telecom companies in Europe will block their Wimax frequencies in order to protect their previous UMTS investments.

Effects of Mobile Broadband Penetration
In Europe, UMTS will be the only option available for customers interested in mobile broadband access. Because UMTS is rather expensive, there will be not move towards commoditization of the mobile broadband technologies. Customers will not be exposed to the advantages of full mobility and full connectivity; hence, the cultural embedding mobile broadband and its applications will be very slow, almost stagnating.
As a result of that, the market will not give sufficient incentives for the mobile devices producers to invest in R&D. The supply of more mobile devices integrating broadband technologies will be low.
Effects on Customer’s Habits
The growth of static (home/ office) broadband will not be disrupted and will continue to growth slowly at the same rate as it does now. As a result, the growth of e-commerce will not suffer any high growth or decline. In view of this slow growth economy, software and technology based companies are just going to “digest” their previous investments. There will be only little improvement in the user friendliness or the security of the applications, and in QoS in general. The effect will be a slow cultural embedding of Internet usage.
At the same time, economic development and broadband penetration in developing countries will go on at the same high pace rate. The early adoption of disprutive technologies that is common to those countries enable them to "leap-frog" to the next standard such as WiMax quicker than Europe and the USA. This might cause a short time discripancy such as that known to mobile phone lag in the USA in the 90's.
Role of the Government
Because there is not recession, the government will not be motivated in interfere. There will be not program to increase broadband access to everyone or to help cultural embedding at schools in excess of what is being done at the moment.
Scenario 3 - Easy come, Easy go
Effect on Utilization Patterns
One of the most critical problems faced by technological companies and e-businesses to increase the demand for e-commerce and the switch in communication methods has been the stand still of QoS. Technology companies are now for years striving to find critical applications that will improve it to a substantial level. The debate today is whether or not the improvement of QoS is even possible. The hadware bottleneck stands at the ethernet hubs. In this scenario, we expect that the efforts of technological companies towards compression and encryption techniques reached a momentum and drastically improved the level of QoS and the security of transactions over the Internet and for a solution to the ehternet bottleneck to be divised in order to increase the speed. As a result of the improved service, the cultural embedding of the Internet usage is accelerated. Likewise, QoS increases the shift in communication methods, in the first place, especially for businesses, such as video conferencing Over IP and VOIP.
Effects of Broadband Penetration
With the shift in communication methods, the higher QoS level will reduce the cost of marginal efficiency of getting larger broadband accounts for the private users. It will also increase the transfer rate from dial-up to broadband and trigger a trend towards commoditization of broadband access (with BOPL technologies for instance). These 3 factors will in turn lead to a massive growth in the broadband penetration rate. In this case, if Wimax is available it will be proposed to clients as a competing option to DSL, Wifi, UMTS, BOPL or cable.
Effect on E-Commerce
The increase in security systems and the cultural embedding of Internet usage will improve the demand for e-commerce: now, everyone is online at all times and going shopping gradually means typing a URL. Unfortunately, this increase of e-commerce demand without economical pressures will lead to more “crap-for-sale" online: the long tail in its all grandeur. The number of credible business model will be lower as a ratio to the total business model generated. The percentage of reliable e-business suppliers is lower and feeling of security decreases. The increase in broadband penetration will also increase the level of Internet vandalism. Internet commerce will be perceived as a "fad" and consumers will be thrown rapidly back in their old/safe shopping habbits. Added to that, the learning curve limitation will hamper the cultural imbedding of the Internet usage and will affect the client’s choice for Wimax. Indeed, consumer are bombarded with options and compared to the rest, Wimax is the newest will be interesting to early adopters only at first.
Government Influence
The government will not take any action in the homeland since the economy is going well. On the other hand, it will help the developing countries be subsidizing disruptive technologies such as satellite broadband connections infrastructure for remote area in developing countries. The penetration in developing countries will increase.
STRATEGIC INPUT FOR KPN
Based on the 3 scenario presented, the insights found are:
- The current cultural embedding of mobile technologies is not optimal amongst private users. This means that they will not rush to but a WiMax adaptable laptop or PDA is KPN invested tomorrow in a WiMax network because they do not have the use for it
- Most important clients will be businesses. Nevertheless, businesses currently are equipped for WiFi and UMTS technologies, which means that the only motivation for them to invest in new equipment and subscription would be full connectivity and full mobility. That implies that going WiMax needs to be done on an “all or nothing” approach.
- Other interested parties would be clients for which the switching costs from dial up to current Broadband technologies are too high (because of original investment in modem, etc. and private customers interested in mobile broadband and which find UMTS too expensive. This market will not be sufficient to justify such infrastructure investment, even if only in the big cities.
- Besides, exit barriers from previous technologies such as UMTS safeguards that other telecom companies in Europe and nationally will eagerly invest in setting up a WiMax infrastructure.
As a result, we would recommend to KPN not to invest in WiMax at this time. We recognize the importance of the mobile broadband technologies and their effect on the society and its contribution to economic growth. With that in mind, KPN should look at the long term and ensure that WiMax will be a part of the broadband infrastructure. That goal could be reached by focusing on lobbying government and other telecom companies in motivate them to invest in such infrastructure for the positive effect this would have on society and the positive economical boost it will bring.
Useful links:
http://www.cis.state.mi.us/mpsc/comm/broadband/broadband/broadband.htm http://www.oecd.org/document/39/0,2340,en_2649_34223_36459431_1_1_1_1,00.html