Difference between revisions of "Tsoe Loong Li"
Tsoe Loong (talk | contribs) |
Tsoe Loong (talk | contribs) |
||
| (54 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
[[Image:Cereals.JPG]] | [[Image:Cereals.JPG]] | ||
'''What is Bio-diesel?''' | '''What is Bio-diesel?''' <br> | ||
Bio-diesel is a domestic, renewable fuel for diesel engines derived from natural oils like soybean oil, and which meets the specifications of ASTM D 6751 [http://www.biodiesel.org/resources/definitions/default.shtm] | Bio-diesel is a domestic, renewable fuel for diesel engines derived from natural oils like soybean oil, and which meets the specifications of ASTM D 6751 [http://www.biodiesel.org/resources/definitions/default.shtm] | ||
Made from: | Made from:<br> | ||
Vegetable oils, peanuts, corn, soybean etc…. | Vegetable oils, peanuts, corn, soybean etc…. | ||
'''Why Bio-diesel?''' | '''Why Bio-diesel?''' <br> | ||
- Safer, cleaner alternative to petroleum diesel | - Safer, cleaner alternative to petroleum diesel <br> | ||
- Alternative for the continuing increasing oil prices | - Alternative for the continuing increasing oil prices <br> | ||
- Experts predicted that gas will be exhausted in 50 years | - Experts predicted that gas will be exhausted in 50 years <br> | ||
- No engine modifications required, no need to change vehicles, spare parts … | - No engine modifications required, no need to change vehicles, spare parts … <br> | ||
- Bio-diesel cuts down on targeted emissions, air pollution | - Bio-diesel cuts down on targeted emissions, air pollution <br> | ||
'''Prices''' | '''Prices''' <br> | ||
The price of biodiesel in the United States has come down from an average $3.50 per US gallon ($0.92/l) in 1997 to $1.85 per US gallon ($0.49/l) in 2002. | The price of biodiesel in the United States has come down from an average $3.50 per US gallon ($0.92/l) in 1997 to $1.85 per US gallon ($0.49/l) in 2002. | ||
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Biodiesel] | [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Biodiesel] | ||
A gallon gasoline cost about $2.28/gallon and a gallon diesel is about $2.48 /gallon. | A gallon gasoline cost about $2.28/gallon and a gallon diesel is about $2.48 /gallon. | ||
'''Bio-diesel, a renewable fuel for a cleaner tomorrow!''' | '''Bio-diesel, a renewable fuel for a cleaner tomorrow!'''<br> | ||
Up till now, there are already 1700 Bio-diesel tank-stations in Germany. The European Union is even setting a goal by 2010 that 5.75% of the total volume of energy usage to come from Bio-diesel. | Up till now, there are already 1700 Bio-diesel tank-stations in Germany. The European Union is even setting a goal by 2010 that 5.75% of the total volume of energy usage to come from Bio-diesel. | ||
With more research to bring down the cost and product awareness, Bio-diesel is the product for the future!! | With more research to bring down the cost and product awareness, Bio-diesel is the product for the future!! | ||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
[[Image:Biiostation.JPG]] | [[Image:Biiostation.JPG]] | ||
==Internet TV== | ==Internet TV== | ||
* How is the current market of TV and internet TV? <br> | |||
* Are people ready to accept internet TV? <br> | |||
* What are most potential audience’s ages? locations? their expectations? <br> | |||
* what is the rime we expect to make Internet TV form a large enough popularity? <br> | |||
''' | To answer these question, we did some research on the internet. We found the market analysis of two country: Greek and China. Although it is only 2 country, China have one third of the TV users in the world and is here by very representative of the global TV users. Below are the info of the Greek TV market. <br> | ||
'''Country Fundamentals of Greek''' | |||
[[Image:Contry fundatmentals greek.JPG]] | |||
''' | '''Equipment''' | ||
[[Image:Equipment.JPG]] | |||
'''Television Market estimates''' | |||
[[Image:Television market.JPG]] | |||
''' | '''TV market of China ''' | ||
China has the world’s largest number of cable television subscribers – 115 million by the | |||
end of 2004 – and is expected to have 150 million by 2010. According to the latest | |||
statistics from State Administration of Radio, Film and Television (SARFT) China’s | |||
2,569 broadcasting operators broadcast 2,355 radio programs and 1,255 TV programs by | |||
the end of 2004. China’s cable TV network stretches over 4 million kilometers. The value | |||
of China’s cable TV equipment market reached $1.6 billion in 2000. Growing at a 45 | |||
percent clip, the market is expected to be $12 billion by 2005. The broadcasting and TV | |||
equipment sector will continue to be promising over the coming years because the market | |||
is still relatively under-developed in China. SARFT has announced that it intends to | |||
provide TV services to 90 percent of the population, a feat that will require much more | |||
satellite, microwave and optical fiber equipment as well as program production and TV | |||
reception equipment. | |||
China has the world’s largest number of cable television subscribers – 115 million by the | |||
end of 2004 – and is expected to have 150 million by 2010. | |||
Chinese households now own more than 400 million TV sets and they enjoy a standard 50-channel cable selection for an average fee of $2 per month. China TV subscribers occupy one third of the international TV users. | |||
It is analyzed that China TV viewers’ demand for TV programming is 9 million hours each year, while the current supply is only 2 to 3 million hours. China’s TV stations such as CCTV and provincial level TV stations plan to launch 50-80 pay TV channels by the end of 2005. | |||
A recently survey reflected seven main behaviors of consumers [2]:<br> | |||
• First, consumers look for high-quality programs and regard this as a decisive factor in whether or not to choose digital TV. <br> | |||
• Second, consumers’ complaints focus on too many commercials inserted into | |||
programs. This indirectly pushes them to explore new paths to acquire information and entertainment and thus issues a challenge to the current TV model of earning profits. <br> | |||
• Third, most consumers know little about digital TV, which results in insufficient dynamic to foster digital TV markets.<br> | |||
• Fourth, consumers prefer to choose programs by themselves and to avoid | |||
commercials rather than enjoying high definition digital TV, which conveys that | |||
consumers regard the content as their first preference.<br> | |||
• Fifth, consumers are willing to pay extra charges for news and TV plays in the first place.<br> | |||
• Sixth, it is whether consumers recognize the content and how they evaluate its value that obstructs the popularization of digital TV. Therefore, the satisfaction of experimental users is of vital importance. <br> | |||
• Seventh, many consumers hesitate to accept digital TV for they are waiting to see its perspective in the days ahead. <br> | |||
References:<br> | |||
[1] http://europa.eu.int/ISPO/infosoc/telecompolicy/en/Eurorep99gr.pdf <br> | |||
[2] http://www.buyusainfo.net/docs/x_2737062.pdf <br> | |||
==Driving Forces== | ==Driving Forces== | ||
===Driving Forces 1=== | ===Driving Forces 1=== | ||
| Line 93: | Line 98: | ||
broadening age span of internet user | broadening age span of internet user | ||
====Description:==== | ====Description:==== | ||
While internet where mainly used by teenagers and business man in the past 10 years. More and more individual knows how to use the internet now. Internet TV therfefore can reach much more people. The number of users has grown from an estimated 38 million in 1994 to 580 million in may 2002. | While internet where mainly used by teenagers and business man in the past 10 years. More and more individual knows how to use the internet now. Internet TV therfefore can reach much more people. The number of users has grown from an estimated 38 million in 1994 to 580 million in may 2002. While in 1994, the graph show a peak, it soon flatten and broaden because teenagers begin to use internet at a earlier age, while more and more elderly people learn how to use internet. | ||
[[Image:Age span2.JPG]] | |||
====Enablers:==== | ====Enablers:==== | ||
• '''increasing awareness of the importance of internet''' <br> | |||
More and more people see the importance of the use of internet. Not just businessman or scientist, but also students, kids and elderly people. Without doubt, internet is a necessary tool for students when doing their assignment. Kids use the internet for all kind of purposes, gaming, chatting, homework. While elderly people now see internet more than just a medium to look for information, but as entertainment as well. <br> | |||
• '''internet become cheaper and faster''' <br> | |||
Due to the technological development in the recent years, internet become much cheaper than before. While the cost are going down, speed become faster and faster. Where internet users have to wait and wait for a web site to open, now it is just a matter of a mouse click. <br> | |||
• '''user familiartiy with computers and lower computer prices''' <br> | |||
While three decades ago, only computers nerds and geeks use a personal computers. PC is now considered a commodity, most peoples have one at home and know how to use it. <br> | |||
====Inhibitors:==== | ====Inhibitors:==== | ||
Increasing internet control by government for political reason | • '''Increasing internet control''' <br> | ||
In creasing internet control by government for political reason. Some contries are blocking what in their opinion sensitive websites that may influece the government. <br> | |||
• '''spams, spywares & viruses''' <br> | |||
Although spams & spywares doesn't do damage like viruses, it is quite disturbing when u see your mailbox full of spams. Or when your personal information might be "leak" due to spywares. All these factors may inhibit people from using internet.<br> | |||
====Paradigms:==== | ====Paradigms:==== | ||
Internet is no longer seen as information retrieval alone. People use internet for all kind of stuff, like entertainment such as games, music and downloading.Due to the increasingly in use of the internet and the broadening of the age span, more and more new service will emerge. | Internet is no longer seen as information retrieval alone. People use internet for all kind of stuff, like entertainment such as games, music and downloading.Due to the increasingly in use of the internet and the broadening of the age span, more and more new service will emerge. Internet is become a commodity, that is used by user with different age groups.<br> | ||
====Timing:==== | ====Timing:==== | ||
o In 1989, internet was mainly used by governmental agencies, with an estimate of 3900 | o In 1989, internet was mainly used by governmental agencies, with an estimate of 3900 <br> | ||
o In 1999, extension like .com, .org, .net. .edu extension are becoming increasingly populiar. With an estimated totoal of more than 4 million. Country names has also becoming increasingly populair | o In 1999, extension like .com, .org, .net. .edu extension are becoming increasingly populiar. With an estimated totoal of more than 4 million. Country names has also becoming increasingly populair <br> | ||
====Web Resources:==== | ====Web Resources:==== | ||
o basic net data, Richard T. Griffiths (Leiden University) <br> | |||
o http://www.let.leidenuniv.nl/history/ivh/chap5.htm <br> | |||
o http://ist-socrates.berkeley.edu/~zook/domain_names/Domains/international.html <br> | |||
o http://www.gvu.gatech.edu/user_surveys/survey-1998-10/graphs/general/q54.htm <br> | |||
===Driving Forces 2=== | ===Driving Forces 2=== | ||
====Name:==== | |||
increase internet accessibility | |||
====Description:==== | ====Description:==== | ||
Internet was once considered as luxurious, only available for the wealthy. It was expensive for the oridinary people. A technology usually only use by govermental agencies and multinationals. Due to the continuosly improvement of internet technology, internet become much faster and cheaper than before. The cost of internet have been brought down tremendously. Most of the household in Europe now have internet. The accessibility of internet have increase alot. People now can access the internet almost everywhere, offices, schools, hotels etc. The accessibility become even greater when WiFi was introduced. Now internet have become a commodity, something that belongs to the everyday life. | |||
====Enablers:==== | ====Enablers:==== | ||
• '''increasing number of internet users'''<br> | |||
A factors that strengthen this driving force is the increasing number of users of internet, because of the increasing awareness of the use of the importance of internet.<br> | |||
• '''internet become cheaper and faster'''<br> | |||
Due to the technological development in the recent years, internet become much cheaper than before. While the cost are going down, speed become faster and faster. Where internet users have to wait and wait for a web site to open, now it is just a matter of a mouse click. | |||
• '''user familiartiy with computers and lower computer prices'''<br> | |||
While three decades ago, only computers nerds and geeks use a personal computers. PC is now considered a commodity, most peoples have one at home and know how to use it. | |||
====Inhibitors:==== | |||
• '''Increasing internet control'''<br> | |||
In creasing internet control by government for political reason. Some contries are blocking what in their opinion sensitive websites that may influece the government. | |||
• '''spams, spywares & viruses'''<br> | |||
Although spams & spywares doesn't do damage like viruses, it is quite disturbing when u see your mailbox full of spams. Or when your personal information might be "leak" due to spywares. All these factors may inhibit people from using internet. | |||
====Paradigms:==== | ====Paradigms:==== | ||
People to | Internet is no longer seen as information retrieval alone. People use internet for all kind of purposes, like entertainment such as games, music and downloading.Due to the increasingly in use of the internet and the broadening of the age span, more and more new service will emerge. While a decade ago, people need to goto the library to find information. With the increasing internet accessibility, people can get information at their finger tips. <br> | ||
====Timing:==== | ====Timing:==== | ||
o In 1962, first proposed global network of computers<br> | |||
o In 1969, the Internet, then known as ARPA net was brought online<br> | |||
o In 1972, first e-mail program created by Ray Tomlinson of BBN <br> | |||
o In januari 1993, leased line was used with a speed of 56 kilobits per second <br> | |||
o In fall 1995, the technology of single T-1 was used. Internet can reach a speed of 1544 kilobits per second <br> | |||
o In fall 1998, multiple T-1 was introduced, speed is twice of the single T-1 <br> | |||
o In fall 2002, Fractional DS-3, which can reach the speed of 15000 kilobits per second <br> | |||
====Web Resources:==== | ====Web Resources:==== | ||
o http://ist-socrates.berkeley.edu/~zook/domain_names/Users/index.html <br> | |||
o http://www.nua.ie/surveys/how_many_online/index.html <br> | |||
o http://ist-socrates.berkeley.edu/~zook/domain_names/ <br> | |||
o http://www.let.leidenuniv.nl/history/ivh/chap5.htm <br> | |||
o http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/History_of_the_Internet <br> | |||
o http://www.cedarville.edu/departments/compserv/historyinternet.htm <br> | |||
o http://www.davesite.com/webstation/net-history.shtml | |||
==Learning Log== | |||
[[Media:Learning Log5.doc]] | |||
Latest revision as of 21:21, 15 May 2006
Profiel
Tsoe Loong Li University of Leiden M.Sc. ICT in Business
Object of the future
My Object of the future is: Bio-diesel
Bio-diesel, a clean burning alternative fuel
What is Bio-diesel?
Bio-diesel is a domestic, renewable fuel for diesel engines derived from natural oils like soybean oil, and which meets the specifications of ASTM D 6751 [1]
Made from:
Vegetable oils, peanuts, corn, soybean etc….
Why Bio-diesel?
- Safer, cleaner alternative to petroleum diesel
- Alternative for the continuing increasing oil prices
- Experts predicted that gas will be exhausted in 50 years
- No engine modifications required, no need to change vehicles, spare parts …
- Bio-diesel cuts down on targeted emissions, air pollution
Prices
The price of biodiesel in the United States has come down from an average $3.50 per US gallon ($0.92/l) in 1997 to $1.85 per US gallon ($0.49/l) in 2002.
[2]
A gallon gasoline cost about $2.28/gallon and a gallon diesel is about $2.48 /gallon.
Bio-diesel, a renewable fuel for a cleaner tomorrow!
Up till now, there are already 1700 Bio-diesel tank-stations in Germany. The European Union is even setting a goal by 2010 that 5.75% of the total volume of energy usage to come from Bio-diesel.
With more research to bring down the cost and product awareness, Bio-diesel is the product for the future!!
Renewable Fuel for a Cleaner Tomorrow!
Internet TV
- How is the current market of TV and internet TV?
- Are people ready to accept internet TV?
- What are most potential audience’s ages? locations? their expectations?
- what is the rime we expect to make Internet TV form a large enough popularity?
To answer these question, we did some research on the internet. We found the market analysis of two country: Greek and China. Although it is only 2 country, China have one third of the TV users in the world and is here by very representative of the global TV users. Below are the info of the Greek TV market.
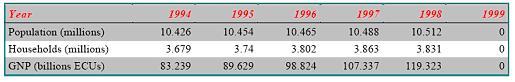
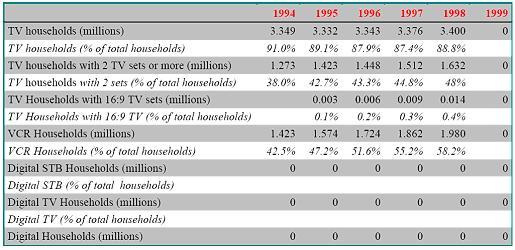
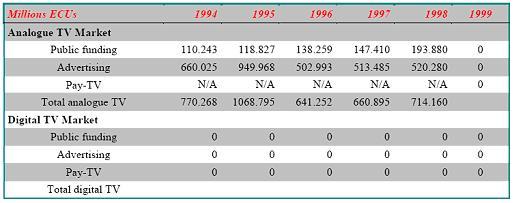
Country Fundamentals of Greek
Equipment
Television Market estimates
TV market of China China has the world’s largest number of cable television subscribers – 115 million by the end of 2004 – and is expected to have 150 million by 2010. According to the latest statistics from State Administration of Radio, Film and Television (SARFT) China’s 2,569 broadcasting operators broadcast 2,355 radio programs and 1,255 TV programs by the end of 2004. China’s cable TV network stretches over 4 million kilometers. The value of China’s cable TV equipment market reached $1.6 billion in 2000. Growing at a 45 percent clip, the market is expected to be $12 billion by 2005. The broadcasting and TV equipment sector will continue to be promising over the coming years because the market is still relatively under-developed in China. SARFT has announced that it intends to provide TV services to 90 percent of the population, a feat that will require much more satellite, microwave and optical fiber equipment as well as program production and TV reception equipment.
China has the world’s largest number of cable television subscribers – 115 million by the end of 2004 – and is expected to have 150 million by 2010. Chinese households now own more than 400 million TV sets and they enjoy a standard 50-channel cable selection for an average fee of $2 per month. China TV subscribers occupy one third of the international TV users. It is analyzed that China TV viewers’ demand for TV programming is 9 million hours each year, while the current supply is only 2 to 3 million hours. China’s TV stations such as CCTV and provincial level TV stations plan to launch 50-80 pay TV channels by the end of 2005.
A recently survey reflected seven main behaviors of consumers [2]:
• First, consumers look for high-quality programs and regard this as a decisive factor in whether or not to choose digital TV.
• Second, consumers’ complaints focus on too many commercials inserted into
programs. This indirectly pushes them to explore new paths to acquire information and entertainment and thus issues a challenge to the current TV model of earning profits.
• Third, most consumers know little about digital TV, which results in insufficient dynamic to foster digital TV markets.
• Fourth, consumers prefer to choose programs by themselves and to avoid
commercials rather than enjoying high definition digital TV, which conveys that
consumers regard the content as their first preference.
• Fifth, consumers are willing to pay extra charges for news and TV plays in the first place.
• Sixth, it is whether consumers recognize the content and how they evaluate its value that obstructs the popularization of digital TV. Therefore, the satisfaction of experimental users is of vital importance.
• Seventh, many consumers hesitate to accept digital TV for they are waiting to see its perspective in the days ahead.
References:
[1] http://europa.eu.int/ISPO/infosoc/telecompolicy/en/Eurorep99gr.pdf
[2] http://www.buyusainfo.net/docs/x_2737062.pdf
Driving Forces
Driving Forces 1
Name:
broadening age span of internet user
Description:
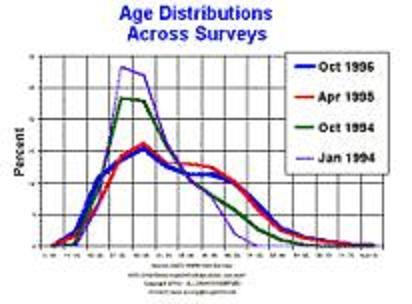
While internet where mainly used by teenagers and business man in the past 10 years. More and more individual knows how to use the internet now. Internet TV therfefore can reach much more people. The number of users has grown from an estimated 38 million in 1994 to 580 million in may 2002. While in 1994, the graph show a peak, it soon flatten and broaden because teenagers begin to use internet at a earlier age, while more and more elderly people learn how to use internet.
Enablers:
• increasing awareness of the importance of internet
More and more people see the importance of the use of internet. Not just businessman or scientist, but also students, kids and elderly people. Without doubt, internet is a necessary tool for students when doing their assignment. Kids use the internet for all kind of purposes, gaming, chatting, homework. While elderly people now see internet more than just a medium to look for information, but as entertainment as well.
• internet become cheaper and faster
Due to the technological development in the recent years, internet become much cheaper than before. While the cost are going down, speed become faster and faster. Where internet users have to wait and wait for a web site to open, now it is just a matter of a mouse click.
• user familiartiy with computers and lower computer prices
While three decades ago, only computers nerds and geeks use a personal computers. PC is now considered a commodity, most peoples have one at home and know how to use it.
Inhibitors:
• Increasing internet control
In creasing internet control by government for political reason. Some contries are blocking what in their opinion sensitive websites that may influece the government.
• spams, spywares & viruses
Although spams & spywares doesn't do damage like viruses, it is quite disturbing when u see your mailbox full of spams. Or when your personal information might be "leak" due to spywares. All these factors may inhibit people from using internet.
Paradigms:
Internet is no longer seen as information retrieval alone. People use internet for all kind of stuff, like entertainment such as games, music and downloading.Due to the increasingly in use of the internet and the broadening of the age span, more and more new service will emerge. Internet is become a commodity, that is used by user with different age groups.
Timing:
o In 1989, internet was mainly used by governmental agencies, with an estimate of 3900
o In 1999, extension like .com, .org, .net. .edu extension are becoming increasingly populiar. With an estimated totoal of more than 4 million. Country names has also becoming increasingly populair
Web Resources:
o basic net data, Richard T. Griffiths (Leiden University)
o http://www.let.leidenuniv.nl/history/ivh/chap5.htm
o http://ist-socrates.berkeley.edu/~zook/domain_names/Domains/international.html
o http://www.gvu.gatech.edu/user_surveys/survey-1998-10/graphs/general/q54.htm
Driving Forces 2
Name:
increase internet accessibility
Description:
Internet was once considered as luxurious, only available for the wealthy. It was expensive for the oridinary people. A technology usually only use by govermental agencies and multinationals. Due to the continuosly improvement of internet technology, internet become much faster and cheaper than before. The cost of internet have been brought down tremendously. Most of the household in Europe now have internet. The accessibility of internet have increase alot. People now can access the internet almost everywhere, offices, schools, hotels etc. The accessibility become even greater when WiFi was introduced. Now internet have become a commodity, something that belongs to the everyday life.
Enablers:
• increasing number of internet users
A factors that strengthen this driving force is the increasing number of users of internet, because of the increasing awareness of the use of the importance of internet.
• internet become cheaper and faster
Due to the technological development in the recent years, internet become much cheaper than before. While the cost are going down, speed become faster and faster. Where internet users have to wait and wait for a web site to open, now it is just a matter of a mouse click.
• user familiartiy with computers and lower computer prices
While three decades ago, only computers nerds and geeks use a personal computers. PC is now considered a commodity, most peoples have one at home and know how to use it.
Inhibitors:
• Increasing internet control
In creasing internet control by government for political reason. Some contries are blocking what in their opinion sensitive websites that may influece the government.
• spams, spywares & viruses
Although spams & spywares doesn't do damage like viruses, it is quite disturbing when u see your mailbox full of spams. Or when your personal information might be "leak" due to spywares. All these factors may inhibit people from using internet.
Paradigms:
Internet is no longer seen as information retrieval alone. People use internet for all kind of purposes, like entertainment such as games, music and downloading.Due to the increasingly in use of the internet and the broadening of the age span, more and more new service will emerge. While a decade ago, people need to goto the library to find information. With the increasing internet accessibility, people can get information at their finger tips.
Timing:
o In 1962, first proposed global network of computers
o In 1969, the Internet, then known as ARPA net was brought online
o In 1972, first e-mail program created by Ray Tomlinson of BBN
o In januari 1993, leased line was used with a speed of 56 kilobits per second
o In fall 1995, the technology of single T-1 was used. Internet can reach a speed of 1544 kilobits per second
o In fall 1998, multiple T-1 was introduced, speed is twice of the single T-1
o In fall 2002, Fractional DS-3, which can reach the speed of 15000 kilobits per second
Web Resources:
o http://ist-socrates.berkeley.edu/~zook/domain_names/Users/index.html
o http://www.nua.ie/surveys/how_many_online/index.html
o http://ist-socrates.berkeley.edu/~zook/domain_names/
o http://www.let.leidenuniv.nl/history/ivh/chap5.htm
o http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/History_of_the_Internet
o http://www.cedarville.edu/departments/compserv/historyinternet.htm
o http://www.davesite.com/webstation/net-history.shtml