Difference between revisions of "Technological factors"
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
What LB technology will be accepted by large amounts of potential users? And how fast can this users adapt to this technologies? | What LB technology will be accepted by large amounts of potential users? And how fast can this users adapt to this technologies? | ||
4. What are the required infrastructure for enabling LBS? <br> | 4. What are the required infrastructure for enabling LBS? <br> | ||
5. What devices are currently available? <br> | 5. What devices are currently available? <br> | ||
Revision as of 15:37, 26 March 2006
Research Questions Technological factors
What is Location Based Service?
Location Based Services (LBS) are business and consumer services that givers users a set of services starting from the geographic location of the client. This position can be known by user entry, or a GPS receiver. These services offer the possibility to users or machines to find/locate other persons, machines, vehicles, resources and also location-sensitive services, as well as the possibility for users t track their own location. The request for location can be originated from the client himself and from other entity such as an application provider or the network. Anyway, whenever location is requested the customer has to give the permission for the location request. Most Location Based Services include two major actions:
[1] Obtaining the location of user
[2] Utilising this information to provide a service
Types & Groups
There are three basic types of LBS: pull, push and tracking. In the case of pull service, a customer mskes by himself a request for LBS. The push service differ from the pull services on thr point that the request for service is not technically made by the customer but by the service provider. Tracking services are the third basic type of LBS. The idea for that type of service is that someone asks for a location of the mobile terminal. All the available services until now can be divided in four major groups:
[1] Business Applications (Asset Tracking / Field Services /
Billing / Buying / Advertising)
[2] Entertainment & Leisure (Gaming / Location-based Imaging /
Athletics / Travel)
[3] Navigation / POI Look-up / Traffic
[4] Social Networking (Peer to Peer / Find Me / Personal Security)
Players in LBS
It is likely that many LBSs will require the involvement of many different parties in oreder to provide the complete service.
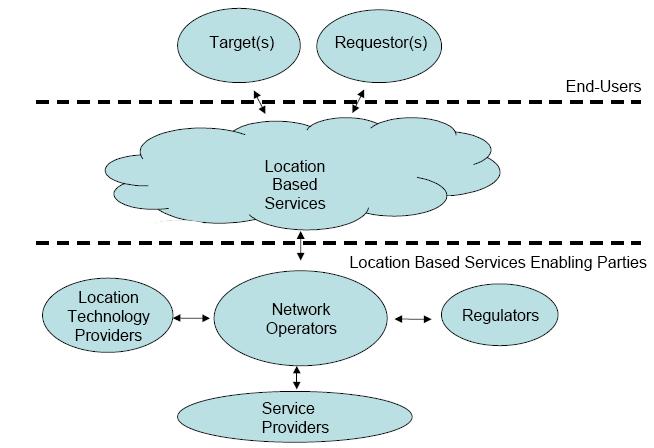
The LBS Enabling parties are described at the bottom of the picture. These players are divided roughly into four categories: Location Technology Providers (LTP), Network Operators (NO), Regulators (REG) and Service Providers (SP).
LTP are manufacturers of different hardware and software which enables positioning of mobile terminals.
NO are companies that have infrastructure for GSM telecommunications.
REG in general enables LBS through investing in sattelite technologies (e.g US government's GPS and EU's Galileo) and also by setting up laws and regulations which give guidelines how LBS can be legally implemented.
SPs are the companies that implement service logic and user interfaces, interfaces between LSB and NO systems.
What LB technology will be accepted by large amounts of potential users? And how fast can this users adapt to this technologies?
4. What are the required infrastructure for enabling LBS?
5. What devices are currently available?
6. What future devices may be available?
7. What are the limitations of LBS?
8. What are the technical implications of LBS?
9. Are there any substitutes for this technology?
Amarantha:
1. What are the planned future developments of the infrastructure?