Carbon Trading, Finances and related Economics
Description:
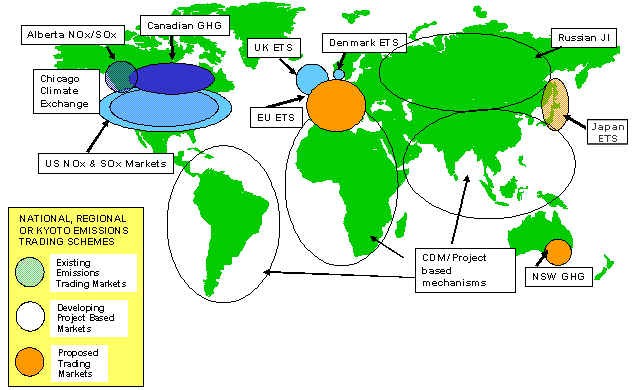
Carbon trading is also known as emissions trading, is a market-based approach used to control pollution by providing economic incentives for achieving reductions in the emissions of pollutants.[1].There are active trading programs in several air pollutants. For greenhouse gases the largest is the European Union Emission Trading Scheme.In the United States there is a national market to reduce acid rain and several regional markets in nitrogen oxides.
The emissions trading system is based on different organizations' regulation or agreements, such as EU and Tyoto Protocol.[2]There are alreay some emissions trading platforms, like The European Climate Exchange (ECX) [3], Chicago Climate Exchange (CCX)[4]
Enablers:
1. Emissions trading lowers the cost to participants and gives business flexibility choose the form of compliance.
2. If Governments, or companies, want to reduce emissions, then providing an economic incentive improves compliance and benefits the environment.
3. The market for the purchase of carbon has grown exponentially since its conception in 1996 according to the data were presented in World Bank.
Inhibitors:
1. The emissions trading schemes operat in different ways, and it might result in speculations between companies, cities, or countries.[5]
Paradigms:
Web Resources:
What is Emissions Trading?
Experience with Market-Based Environmental Policy Instruments
International Emissions Trading Association
Emissions Trading
Chicago Climate Exchange
The European Climate Exchange
UK Emissions Trading Group
ICE
Carbon Finance - World Bank
Global Carbon Market Grows to $144 billion Despite
Financial and Economic Turmoil[7]