The future of the global economy in 2015
Introduction
This page will contain the results of the scenario planning process of group 3 of class RSM EMBA05 on the following subject:
The future of the global economy in 2020
The members of Group 3 are:
- Peter Groen
- Wendi Mennen
- Maarten Post
- Harry Schoots
- Eric Verbeek
Research Documentation
http://www.stern.nyu.edu/globalmacro/ which contains a link to an Economist article to get us started: Analysis: The Economist, Sep 06, 2005 The perfect storm.
http://scenariothinking.org/wiki/index.php/The_Future_of_the_Global_Village_in_2020 which contains a scenario of last years students.
http://www.odci.gov/nic/NIC_home.html is the homepage of the National Intelligence Councel. Mapping the Global future is a useful report.
http://www.millenniumassessment.org is the homepage of the Millenium Ecosystem Assessment. Latest research of the MA states that environmental concerns increase opportunities and challenges for business that ultimately might influence the global economy.
http://t21.ca contains a selection of world global trends on different aspects based on many sources. http://t21.ca/economic/index.htm lists the economic key findings.
The Netherlands Bureau for Economic Policy Analysis (CPB) performed a scenario analysis on the economic future of Europe, downloadable from http://www.cpb.nl/eng/econ/lange_termijn/recente_studies.html
Try also this report on Globalisation and the Global Environment: four quantitative scenarios: http://www.cpb.nl/nl/general/org/homepages/aml/gitage_si.pdf
The OECD published a study on the future of the global economy: The Future of Global Economy: Towards a long boom? http://www.oecd.org/dataoecd/42/0/35394025.pdf
The CIA publishes facts of every country and region in the world. http://www.cia.gov/cia/publications/factbook/index.html
International Energy Agency publisehes the World Energy Outlook: http://www.iea.org/Textbase/publications/index.asp
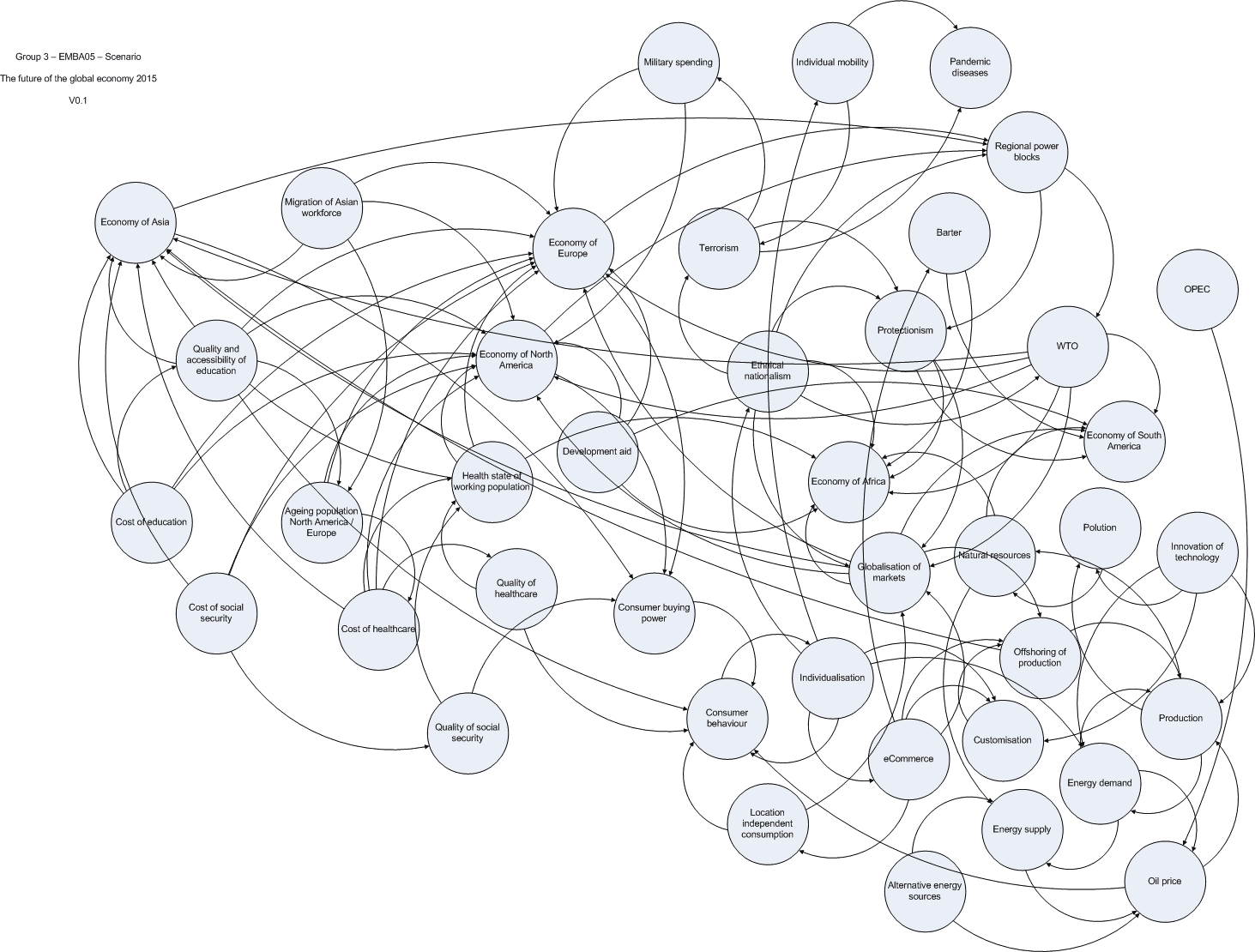
Provisional Systems Diagram (as of Tue Sep 27, 05)[[1]]
Research Questions
Note to group: please add your research questions below.
ECONOMY
Asia
- What is relative GDP to world economy?
- Which countries drive the regional economy?
- What are the trade balances of the major economies in region
- Are the regional economies in terms of GDP increasing, and how rapidly?
Middle East
- What is relative GDP to world economy?
- Which countries drive the regional economy?
- What are the trade balances of the major economies in region
- Are the regional economies in terms of GDP increasing, and how rapidly?
Europe (incl E Eu & Russia)
- What is relative GDP to world economy?
- Which countries drive the regional economy?
- What are the trade balances of the major economies in region
- Are the regional economies in terms of GDP increasing, and how rapidly?
Africa
- What is relative GDP to world economy?
- Which countries drive the regional economy?
- What are the trade balances of the major economies in region
- Are the regional economies in terms of GDP increasing, and how rapidly?
North America
- What is relative GDP to world economy?
- Which countries drive the regional economy?
- What are the trade balances of the major economies in region
- Are the regional economies in terms of GDP increasing, and how rapidly?
South America
- What is relative GDP to world economy?
- Which countries drive the regional economy?
- What are the trade balances of the major economies in region
- Are the regional economies in terms of GDP increasing, and how rapidly?
Global
- What are the trade balances between of the important economies? What is the size and trend in global trade?
- What are the resource constraints with respect to economy? (in terms of natural resources)
- What is the strength of the American Dollar compared to the Euro, Yen, Guan,...? Is it declining of increasing in the past 10 years?
- What other forms of exchange (except) money are used or can be used?
- In the article http://www.ode.nl/article.php?aID=4160 the following exchange forms are mentioned: Communities building Temples in Bali, Elderly Care in Japan, Health insurance companies 'pay' for healthy behahiour, frequent flyer programs and other customer programs.
- On the site http://www.ex.ac.uk/~RDavies/arian/barter.html links are given of all sorts of other forms of trade without using money.
Statistics on barter in 2004: http://www.irta.com/Page.asp?Script=56
Politics
PG:* What will be the role of the Central Banks (ECB, FED)to the economy? (in terms of 'mission statements')
Article on the role of the central banks: http://www.bis.org/publ/cpss55.pdf
Mission of ECB: http://www.ecb.int/pub/pdf/other/ecbhistoryrolefunctions2004en.pdf
Speech Greenspan 25/8/2005: http://www.federalreserve.gov/boarddocs/speeches/2005/20050826/default.htm
PG:* What will be the role of the WTO and UN to the economy? (in terms of 'mission statements')
Role of the UN: http://www.un.org/millennium/sg/report/full.htm
Article on the role of the WTO: http://www.ccc.nps.navy.mil/si/oct03/trade.asp
PG: * What will be the role of the NGOs to the economy?
Article on the future of NGO's: http://www.globalpolicy.org/ngos/role/intro/gen/2000/111400.htm
- What will the effect be of global terrorism on the economy?
The following articles give insight in this topic:
- http://ksghome.harvard.edu/~aabadie/twe.pdf. The main theme of this article is that mobility ofproductive capital in an open economy may account for much of the difference between the direct and the equilibrium impact of terrorism.
- http://www.cia.gov/nic/speeches_terror_and_econ_sec.html Gives an account of the current situation, but also the uncertainties. The speech introduces the NIC 2020 project.
- http://www.odci.gov/nic/NIC_globaltrend2020.html report of the NIC 2020 project with information on terrorism.
- How will the (in)stability of the Middle-Eastern states influence the global economy and the relation of nations?
The following articles give insigth in this subject:
- http://www.cia.gov/nic/confreports_mideast_future.html (Again) from the NIC side. This is an overview of a one-day conference about the middle east for the scenarios of the NIC 2020 project.
- http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/globalconnections/mideast/themes/economics/ gives an overview of economy in the middle east and some usefull links to other sites.
PG:* What will be the effect of the European Union on the global economy (if any)?
Speech Managing Director of the IMF: Towards a stronger Europe in the global economy: http://www.imf.org/external/np/speeches/2003/110303.htm
See the NIC report (top of this page)
PG:* What are the blocks of power and what was the past development?
PG:* What is the global military spending in relation to the global development aid?
- Military expenditures - dollar figure: aggregate real expenditure on arms worldwide in 1999 remained at approximately the 1998 level, about $750 billion (1999) Military expenditures - percent of GDP: roughly 2% of gross world product (1999)(source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/World_economy#Gift_economy)
- Global development aid: Yearly economic aid - recipient: official development assistance (ODA) $50 billion )(source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/World_economy#Gift_economy)
Society
- What are the effects of the ageing population in Europe and North America to the economy?
- How sustainable is the current social security level and health care per region?
Answer to these 2 questions:
- The IMF has published excellent material on how demographic change affect the global economy http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2004/02/pdf/chapter3.pdf
- What is the effect of increasing education levels on the economy of developing regions?
Environmental
- What are alternative energy sources and what is the speed of development?
From http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Renewable_resource (Sep 30,05):Wind power is one of the most cost competitive renewables today. Its long-term technical potential is believed 5 times current global energy consumption or 40 times current electricity demand. This requires 12.7% of all land area, or that land area with Class 3 or greater potential at a height of 80 meters. It assumes that the land is covered with 6 large wind turbines per square kilometer. Offshore resources experience mean wind speeds ~90% greater than that of land, so offshore resources could contribute substantially more energy.[45][46]. This number could also increase with higher altitude ground based or airborne wind turbines
- What are the scarce resources?
From http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Future_energy_development (Sep 30, 05) World energy production by source: Oil 40%, natural gas 22.5%, coal 23.3%, hydroelectric 7.0%, nuclear 6.5%, biomass and other 0.7% [5]. In the U.S., transportation accounted for 28% of all energy use and 70% of petroleum use in 2001; 97% of transportation fuel was petroleum
- What is the effect of climate change on the global economy?
- What are the effects of mobility on the environment?
Based on http://www.iea.org/Textbase/publications/index.asp: World Economic Outlook 2000
Technology and business
PG: * How will the development of ICT increase the access possibilities to markets?
See the global Digital Opportunity Initiative:http://www.opt-init.org/framework/pages/contents.html
- What are the effects of off shoring production work by rich countries to low wage countries, and what is the trend?
PG: * What is the growth rate of E-commerce in the world?
- How long does it take the OPEC countries to double their refinery capacity?
The OPEC site http://www.opec.org gives information about OPEC and current prices, supply and demand and considerations. The Annual statistical report.
http://www.nation.com.pk/daily/sep-2005/22/bnews8.php gives a brief overview of current considerations about refining.
http://deseretnews.com/dn/view/0,1249,610152116,00.html gives the plans for expanding refinery capacity.
I still have to call HP for more detailed info!
- What is the effect of the oil prices on the economy?<br>
http://www.globalization101.org/news.asp?NEWS_ID=84 provides a good overview of this subject with useful links.
http://economist.com/printedition/displayStory.cfm?Story_ID=4321834 to show some factors which help to see what the effect is.
http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2005/01/pdf/chapter1.pdf describes how the oil prices can effect global economy.
I still have to call HP for more detailed info!
- What are the effects of the reducing energy supply on the global economy?
good links on the amount of oil that is there:
From the BBC: http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/business/4681935.stm
From Exxon Mobil where Colin Campbel is refering to in his interview: http://www.feasta.org/documents/wells/contents.html?one/longwell.html
Systems Diagram
Driving Forces
The increasing gap between developed, emerging and poor economies
The increasing effect of the development of technology on the global economy
The effect of Brazil's economy on the global economy
The increasing role of barter in the global economy
The impact of limited availability of natural food resources on the growth of the global economy
Scenario's
Armageddon
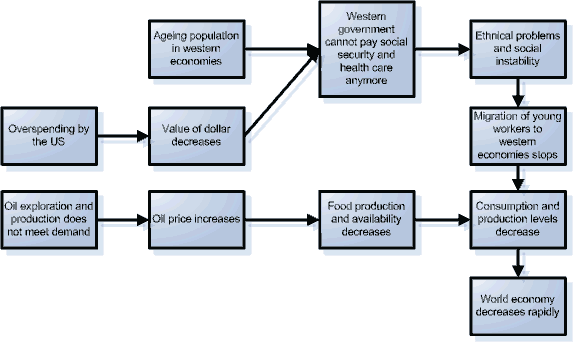
Amsterdam 2020 - In the past 20 years the US public deficit has grown with staggering numbers. The US balance of payments has risen with it to an all time high. The crash of the dollar five years ago has aggravated this effect. Asian governments and investment hedge funds started selling dollars at large amounts, since they lost confidence in the strength of the US economy. Western Europe has followed the Asians, in an attempt to minimize their losses.
The world is sending 5 billion dollar to the US every day in order to finance the deficits. The Fed had to raise the interest rates (now 7%) every quarter for the past years to keep inflation within proportion. This led to a drop in house prices. In the meanwhile, the average debt of US households has increased. The effect of these trends is that the numbers of bankrupt US citizens has risen.
At the moment several smaller banks have problems with their financial obligations and file for bankruptcy. The central banks of the USA, Europe, China and Japan try to minimize the damage by supporting the smaller banks, but with hardly any result. Stock markets decline as an effect of the decreasing stock prices of these Financials. Following the Financials other companies with big stakes in the US are also getting into trouble. Especially after the announcement of the OPEC a year ago that the decreasing dollar rate has caused them to sell oil barrels from now on in Euros. The insecurity of the financial markets has let to more barter agreements than ever, the increasing access to Internet-2 hosted non-financial markets has provided the ability to do this.
Four years ago, ExxonMobil, Shell, BP and Texaco opened their books on the search for new oil wells. None of them has been able to meet their targets in the search and exploration of new wells, while the existing wells are depleting. Oil consumption has increased in the past decades, while oil production has stayed at the same level for the past years. A few years ago an American Nobel Price winner predicted that sustainable alternative energy sources will not be cost effective in 2040 at the earliest. These announcements resulted in a steep increase of the oil price. Nowadays, a barrel of crude oil costs €100. This high oil price has affected the supply of food in the world tremendously. The production and transportation has never been so expensive, people are hungry and are starving because they cannot pay for food anymore, even in Western Europe and the US.
The decline in use of oil in the past two years, and the technology of using and producing energy cleaner, does have a positive effect on the quality of the air and environment. The Amazon rain forest is starting to grow again to the surface area level of 2000 via the UN Oil for Forest program. For every barrel of oil that is produced, 10 trees are planted. Global warming has almost come to a halt.
The oil companies now put their cards on the exploration of liquefied natural gas. This type of energy has two advantages: it is abundantly available in Russia and the Middle East. Next to that, it causes less CO2 and NO2 emissions.
The combination of the declining dollar and the increasing oil price is tipping the world economy. Large US debt holders turn away from the US when it becomes evident that the US will not be able to pay back their debt. The Chinese and Japanese economies suffer a severe blow, since they are owing a large percentage of the US public debt. Furthermore, their export market is disappearing with the decline of US spending. Still, their economies are growing, but slowly. They suffer from high unemployment rates, because of the high numbers of population in their working ages.
Western Europe shows a slightly shrinking economy. This is fostered by the ageing population. The decline in the major stock markets and the inability of the governments to change retirement programs led to serious liability problems of pension. In more and more cities retired people are looking for jobs to earn a living. Consumer spending is declining, and most of it goes to basic needs, like food, shelter and healthcare.
The economic downturn in Europe and the USA is an extra burden for the public sector and the social security system. The huge amount of elderly have a great impact on social security spending. Government cannot raise enough taxes to cover public spending. This causes several social problems in Europe and the US: nationalistic and fascistic sentiments rise.
These sentiments have a negative effect on the growing flow of skilled workers from Eastern Europe, Asia and the Middle East that run away from unemployment in their own regions. Problems grow bigger because of this, because the young and skilled workers can pay taxes and can help to stabilize social security. The desperately needed workforce is neglecting the USA and Western Europe and are looking for their fortune in Australia and South America.
The focus of most EU administrations turn inwards and some anti-EU sentiments gain power. The negotiations with Russian states on their potential EU membership are aborted. France, the Netherlands and Germany abort their membership of the EU, while maintaining the Euro as the their currency. The power block of Europe is gone now, and bargaining power to receive the new energy sources is declining. Asia will be the next power block in the world.
As a consequence of the economic dismay in the world, production and consumption decreases. Less commercial trading and less tourism takes place between Asia, Europe and the USA. The trust between these 3 power blocks after the collective victory over the waves of terrorism in the 2010’s has instantly vanished. Governments are blaming each other for the economic trouble and are focusing on their own needs.
The world economy has basically come to a stand-still the past years. Globalisation as a trend has come to a grinding halt. The world has to find a way to let the economy start growing again.
The Good Samaritan
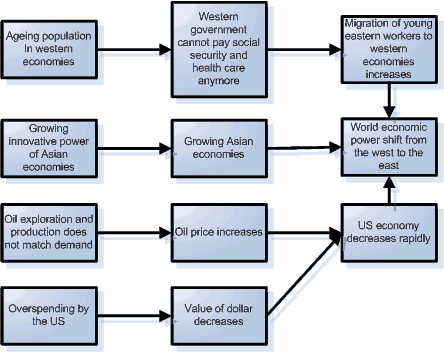
Amsterdam, 2020 – Last years the trend of the increasing US outstanding public debt and trade deficit, which started during the Bush administration in the early 2000’s, emerged further. More and more economic and political heavyweights have been warning the US administration that this path is not sustainable in the long term. To make this even clearer a senior economist of Morgan Stanley used the following metaphor: “it’s like jumping of the 100th floor of a building without a parachute and saying at the 50th ‘So far so good’”. However, the administration replied time after time that “these so called experts said the same 15 years ago and still nothing really happened”.
This time however, things seems to be different than before; the US economy really threatens to collapse which started with a 7 per cent fall of the $. China and the other Asian power block India realises that their investments in the US debt are bound to be rendered valueless, they cannot afford standing idle and they decide to support the US economy as the Good Samaritan (once again). The World economy has known unprecedented growth figures for a period of three years, but the United States and Europe have underperformed consistently. Because of the help of China and India for the US, the US and the EU economy are saved from a potential crash but have limited growth. However, weaker economies like the developing and poor countries have a serious setback of this and become poorer. In order to keep up these countries increase their debt as well.
In addition, the dollar-euro exchange rate has fallen dramatically and has caused tensions within the western world to rise. In this crisis, America has refused to come to the assistance of Europe, claiming that they needed to take care of “America First”. This increased tensions in the world not only within the Western world, but also between the different power blocks. This is the result of the fact that the United States have continued to rule the world: after their forced withdrawal from Iraq in 2009, they relived their Vietnam War syndrome, and resurrected with renewed vigour to prove they were still the world’s superpower. Although the US attempted to invade North Korea, they were stopped by the rest of the world, not by diplomatic or military means, but by the financial power.
Although relative shortage of oil is increasing, the western economies are too rigid to switch to alternative energy sources and therefore still focus on oil as a primary source of energy. The developing and growing eastern economies are still flexible enough to make the transition to gas as a primary source of energy. They benefit from the lower gas price and this gives their economies an extra boost compared to the western economies that rely on expensive oil. The oil prices will keep increasing and the US economy will decrease rapidly. This will also result in a Shift in the balance of power from oil producing countries to gas producing countries.
As a result of these developments, it becomes more and more clear that the real global political and economic power has already shifted from the west to the east. The US administration does still not want to see this, but large US companies like Coca Cola, GE and Ford have moved their headquarters a view years ago already to the eastern part of the world. Asia has really become the locus of international logistics and trade.
The fact that Asia became the centre of the world was also caused by a trend that emerged in the latter part of the 20th century: the difference in education between the western world (but especially the US) and China and India. In 2005 the National Research Council calculated that China had five times as many graduates majoring in engineering as the US (300,000 vs. 60,000). Because of the steady turnout of Chinese PhD’s over the last 20 years, China became the most innovative country of the world. The 2005 projection of the US Bureau of Labour Statistics that scientific and engineering occupations would grow at three times the rate of the overall workforce came true as well. The last years this effect gave a huge boost on the innovative power of eastern economies. Innovation is now more and more governed by Asian companies and their inventions boost the technical development of efficient and effective production techniques.
Western Europe sees the signs of an ageing population. A decreasing number of workers have to sustain an increasing number of the retired people. The inability of western governments to change retirement programs led to a serious liquidity problem in sustaining existing health and social security plans. In more and more cities retired people are looking for jobs to earn a living. Consumer spending is declining, and most of it goes to basic needs, like food, shelter and healthcare. This means a significant decline in the standards of living in western societies. The combination of the increased oil prices and reduced consumer budgets means that mobility is reduced and the focus on the immediate environment increases. The growing need for young workers makes large numbers of young Asian people migrate to Western Europe. Compared to the global economy of the early 2000’s this is an era where the western world is becoming more and more internally focused. Combined with the fact that the local population is now looking at the same jobs as the immigrant workers this increases social tension between the native workers and the large communities of Asian workers and causes a renewed surge of ethnical nationalism. The EU countries see a natural urge to protect their own (natural) assets. This leads to a threatening collapse of the EU, exacerbated by the fact that Europe no longer has the financial power to sustain the European Union (EU).
The norms and ethical values turn also into more eastern (Asian) focussed norms and ethical values. The economy changes its focus from eternal growth to a more holistic approach to living in the world. Humanity takes on a new responsibility as world research and development into global diseases and development aid spending is becoming more and more dependent on endowments of wealthy people and companies because governments have less money to spend. This is because the decreasing tax incomes in the western world and the demands for social welfare and education.
Overseeing the ‘Easternization’ of the EU countries Mr. Balkenende (chairman of the EU and former Dutch prime minister), states that it is very important to ‘safeguard our Western norms and values’. His statement is as futile as his politics; it isn’t nothing, but it isn’t much either.
The Tower of Babel
Amsterdam 2020 – The world has suffered increasing shortages of oil in the last decade. After dramatic fluctuations between 2008 and 2012, oil prices have stabilised at a high price levels in the last decade. This has caused many of the oil dependant economies to suffer.
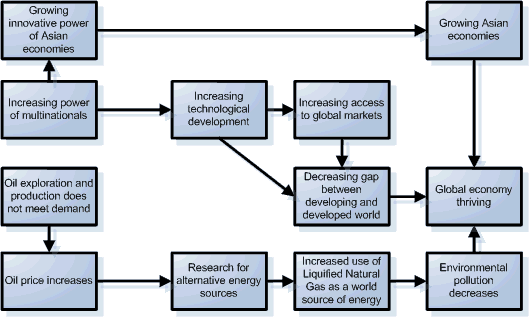
Western governments have been unable to sustain their start of millennium levels of spending, giving space to a free market economy, in which big multinationals take up their corporate social responsibility.
The truly free market economy has given multinationals the opportunity to introduce technology in developing and poor economies, resulting in considerable growth of these economies. They successfully marketed their low wage labour and natural sources, which has given them a competitive advantage. In addition, many of the economies designated as “developing” in the last quarter of the 20th century, have been provided with the with powerful alternatives to oil derivatives and other technological innovations.
This innovation is the long term result of the strong trend in education of the latter part of the 20th century: the difference in education between the western world (but especially the US) and China and India. In 2005 the National Research Council calculated that China had five times as many graduates majoring in engineering as the US (300,000 vs. 60,000). Because of the steady turnout of Chinese PhD’s over the last 20 years, China became the most innovative country of the world. The 2005 projection of the US Bureau of Labour Statistics that scientific and engineering occupations would grow at three times the rate of the overall workforce came true as well. The last years this effect gave a huge boost on the innovative power of eastern economies. Innovation is now more and more governed by Asian companies and their inventions boost the technical development of efficient and effective production techniques.
Despite a temporary set back between 2007 and 2010, caused by overheating of the economy and temporarily large stocks, Asian economies keep growing at healthy rates between 4 and 6 % year on year. In addition, Asia’s internal market is on the rise due to the increased prosperity, which balances against the decreased possibilities of exports to the western economies. The increased prosperity gives many Asians the possibilities of visiting countries in the entire world. They become familiar with alternative cultures and they have the spending power to allow them to access to the global economy.
This happens as the result of the more equal spreading of global wealth: the traditional rich countries have suffered consistently in comparison to the rapidly growing emerging economies, which are able to move the political decisions making machines considerably quicker than the traditional economies. This decreases the tensions between the haves and have-nots.
The prosperity becomes better distributed across the world, while the influence of the western governments is decreasing. The Asian economies are flourishing and they succeed where Western governments failed in the second half of the twentieth century: they are treating the developing countries as economical partners and not as beggars holding up their hands.
The increasing relative shortage of oil on the other hand, has now become fully transparent after the major oil companies declared, in a unified statement, that their total resources are now definitely decreasing.
This caused a surge in the search for the application of alternative energy sources. This means that the former developing economies still hold their competitive advantages, since they have built their new economies on new energy technology. In addition, the global political arena became tired of the ‘war on terrorism’ stories of many of the Western countries, headed by the United States. The search for alternative sources of energy unites the world in a similar but more positive manner than the war on terrorism did in the beginning of the millennium.
Sufficient sources of (cheap) alternative energy sources become available as a result, and the price of these energy sources dives below the price of oil. Consumers switch to gas and alternative energy sources and the growth of the global economy has not been levelled as a result of the lack of energy. Moreover the effects of oil usage have now decreased and pollution trend is countered: the world becomes a cleaner place. With the promise of energy production using cold nuclear fusion becoming profitable in the near future, oil and gas lose importance as an energy source but keep their importance as a raw material (e.g. for plastics). Through selling oil and gas as a raw material, the oil and gas producing countries have to change their economies to healthy, raw material producing economies.
The oil producing countries manage this transition due to their political systems of centralised control, but the price of this rapid switch is the stronger calling for democracy in these countries too.
The western societies, although coping, struggle to keep up witjh the new economical powerhouses: their population is not used to going through difficult times of change and are not willing to endure hardship. The ageing population of western economies is compensated by migration of (younger) workforce from the east and south – borders disappear and enhance the development of the new global economy.
On balance, the world is a happy and balanced global village. In 2019, the number of flights across the world is fourfold of that in 2000, yet pollution levels are significantly lower now than they were as a result of new aircraft engine technology.
In a suburb of Shanghai, a number of school girls become seriously ill. Since this particular suburb is home to many international headquarters of the big multinationals, the contagious disease is spread across the main business centres of the world within 48 hours. It turns out that the virus that caused the 2006 bird flu pandemic is resistant to current vaccinations. Within three days, intercontinental flying connections have grinded to a halt and within a week international flying has stopped completely. 60 Million people across the world have caught the bird flu, which has a death rate of 30%.
The global village falls apart as a house of cards. Local economies are forced to with draw from the global forum and have to become self sustainable. There is a growing awareness that the seemingly infinite growth of the world economy is indeed finite and that the material growth has seen its peak. The world is ready for a new balance.