The Future of Hospitals in the Netherlands in 2015
A project for the Rottedam School of Management Executive MBA course by
Ton Jonker, Anton Koonstra, Gerben Hagenaars, Jeffrey Sweeney, Coen van Paassen.
SCOPE: non academic ('peripheral') hospitals
RESEARCH QUESTIONS:
1. Financial structure
- Who is financing (externally)? How structured? Solidarity?
- Influence new insurance system? What in basic insurance and what should be additional insured?
- What is finance structure internally?
- What are the consequences of the integrations (mergers) of health insurance companies...buying power?
- Who pays the costs that are a result of life style induced illness? Where begins own responsibily and risk?
- Involvement government H or L?
- Percentage of GDPspend on healthcare?
2. Demand for hospital care
http://www.kiesbeter.nl/Home/Start.aspx
3. Supply side of hospital care
- Labour market for physicians, nurses
- What is development of technology and influence thereof on hospital care; what are costs involved?
- Care remains labour-intensive? Scarcity of labour? Costs involved?
4. Organization of hospital care
- Public owned vs private owned hospitals?
- Differentiated care (per indication, per type of patient)? Differentiated tariffs?
- Limitations to free market? Currently 'B-segment'
- Emergency care responsibility governments as oposite to elective care? How about 'cherry picking' or cross-subsidizing between DFCs?
- Other suppliers (e.g. private enterprises for diagnostics)?
- What are the consequences of the integrations (fusions) of hospitals with other hospitals and homes for the elderly (less and bigger hospitals, less choice where to go etc.)??
- In that matter: what will happen with prices when the free market for hospital care changes because of the integration of market parties
- Involvement government H or L?
5. Ethical debate
- At the the moment there is a (sort of) general opinion that we have to apply every possible technical solution to cure people, even when this is very expensive. This opinion will probably not hold because of rapid technical developments. What will happen? - change in public opinion?
- Role of QUALY (quality adjusted lifeyear)? A life year added in fair quality in the western world is allowed to cost appr. € 18.000
- Technological developments in genomics and biotechnology will imply a shift from cure to prevention - this implies another type of healthcare and a significant decrease in the number of hospital bed days. Uncertainty is what comes out of the ethical debate.
6. Other external factors
- MRSA ?
- Birdflu?
- Othere pandemia?
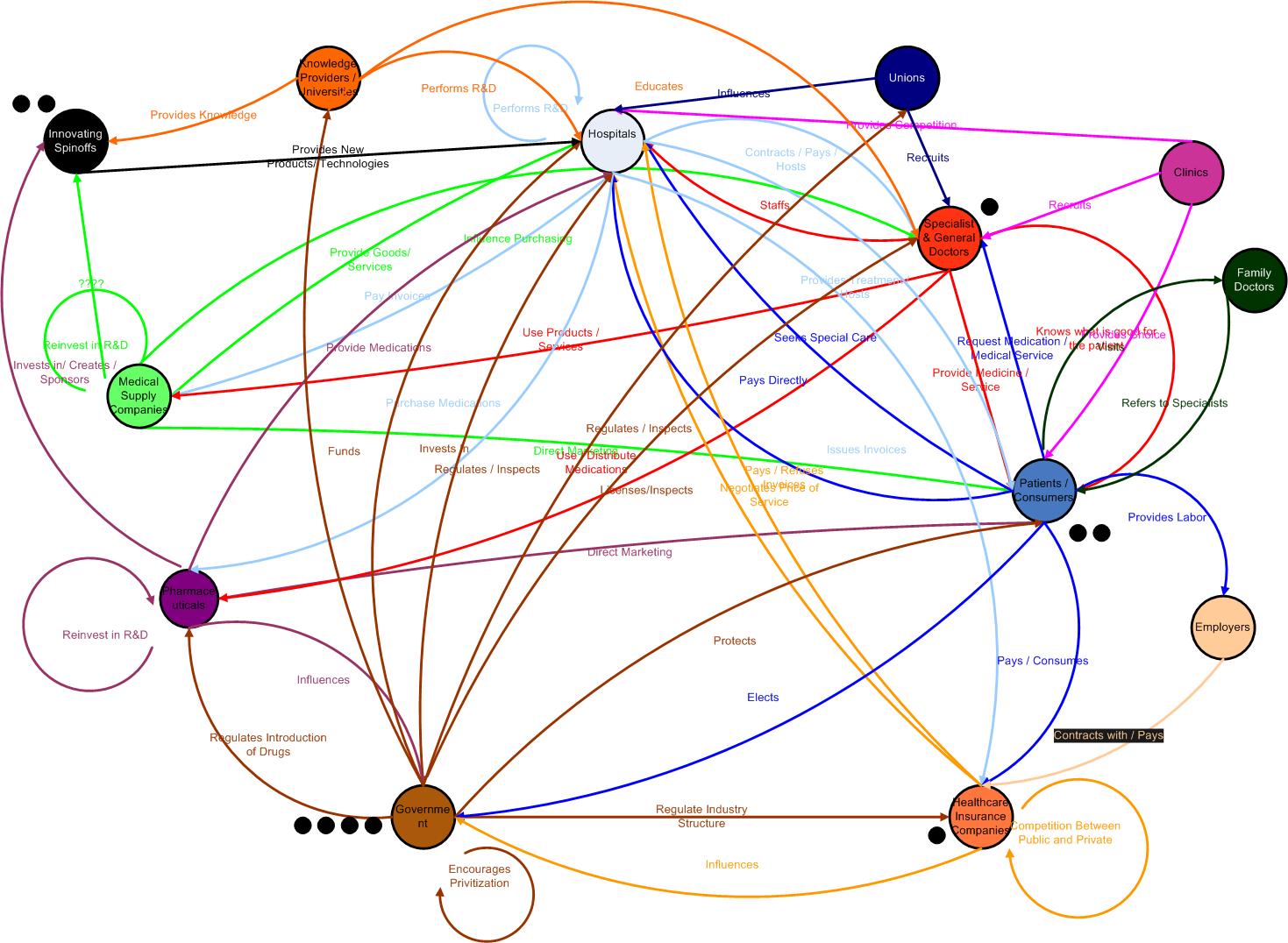
BACKGROUND:
Medical cost and demand in healthcare are swelling. An intensifying dissatisfaction among patients, government officials, insurers, employers, clinicians and healthcare executives is noticeable. The soaring prices paid to treat the growing volumes of demanding, aging patients are prompting payers to search for more efficient ways of treatment and care. Next to that the government in Holland has introduced the new healthcare payment system with a new insurance system and diagnosis treatment combinations. The main aim of this transition is the development from a budget oriented system to a more market oriented health care system. The belief is that a market oriented system will create more incentives for efficiency, quality and innovation. Many hospitals in the Netherlands have to withstand those forces and the severe capital crunch they create. As many of our group have a certain affinity with the healthcare sector (from different angles: Insurer, pharmaceutical, hospital and client perspective) we formulated the following scenario definition.
Scenario definition: ‘The future of hospitals in the Netherlands in 2020’ Main driving forces: There are a few driving forces (PWC, 1999) which create the severe capital crunch the hospitals in The Netherlands are getting in to.
- The impact of E-health on the healthcare business;
- E-health will be used for transactions between suppliers, other providers, payers, regulators and patients
- E-health will be used for information for patients and healthcare workers and will be used as a marketing and branding tool for the hospitals;
- E-health will be used for interaction between with providers and intermediaries
The shift from cure to prevention due to new technologies like genomics and biotech advances
- Genomics will open markets for diagnostic testing, preventive medicine, follow up treatments and even support services such as lifestyle counselling
- Life sciences and information technology will fuse into biotechnical discoveries in the decade ahead, restrained only by the financial purse strings of government agencies (like NWO), private foundations, pharmaceutical companies and informal investors
- The impact of the new healthcare financing system in the Netherlands
- The new (privatized) healthcare system will have it’s impact on the amount of services, the patients, the healthcare insurers, the intermediaries, the suppliers like pharmaceutical companies and the hospitals
- The impact of the new market oriented financing system with the diagnosis treatment combinations
- Finally a driver we want to include in our scenario’s is the future scarcity of labor in the Netherlands
- The aging population will have it’s impact on the health care sector. It will be growing. At this moment about 300.000 people are working in the health care sector. But will there be the estimated necessary 600.000 workers in the future? Methodology: So far, we have identified four plausible drivers. In the further development of our project we will have to ‘dig into the facts’. We will do this by a thourough literature study. Gather the facts and figures and substantiate on our findings this far. Secondly, our intention is to have some in-depth interviews with some opinion leaders in the field of hospital care, farmaceutics and insurance. We wil speak with them about their expectations, and will try to verify our findings. These two angles (literature study and interviews) will be our solid academical ground in defining our scenario’s and the strategic possibilities as a result of the scenario’s we will try to define for this project.
References:
- PricewaterhouseCoopers Healthcast 2010 – smaller world, bigger expectations, 1999
- PricewaterhouseCoopers HealtCast Tactics: A blueprint for the future, 2002
DRIVING FORCES
- Driving forces (from a hospital point of view):
Internal driving forces:
• Shortage of nurses (especially OK and IC);
• Shortage of (male) doctors (more part-time workers on all layers of the organization);
• Doctors on the payroll instead of independent partnerships (fight for hospital leadership, who is the boss, the CEO or the head of surgery?);
• Professionalization of hospital management;
• Enormous drive to be effective and efficient (cost cutting vs. high investments in people and technology);
• More and higher investments in ICT and other technology because of new treatment concepts demands (care and cure on a distance)
• More attention for hospital quality because of; better monitoring, peer pressure and external attention;
• More competition among hospitals (also with private clinics) for the best nurses and doctors;
• Increasing dependence on ‘third money stream’ (research);
• Integration of general practitioner (house doctor) in the hospital;
• Specialization and concentration trends will have impact on hospital building, infrastructure and organization;
• ..
• ..
External driving forces:
National level:
• Greying population will affect hospital occupancy rate and patient mix;
• Population with overweight will affect hospital occupancy rate and patient mix;
• Demographic factors (changing population / diversity) which cause changing needs;
• Empowered, more informed patients, More information available because of all kinds of new information systems (TV, internet / e-mail)
• Empowered pressure groups and patient associations;
• Environment (society) with different ethical standards (less ‘respect’ for doctors and hospital organization, belief in the manipulability of life etc.);
• More violence in hospitals against hospital staff (especially in the after hours but also in ‘normal’ situations);
• New threats (diseases like chicken flu, terrorist attacks with large scale casualties, MRSA etc.)
• New healthcare (market oriented) insurance system which should be able to finance the healthcare in the Netherlands (DBC’s etc.);
• Liberalization of the Dutch healthcare market;
• Bigger influence of healthcare insurance companies on hospitals;
• Market/Government problems (competition and market regulation rules will cause administrative and legal problems for hospitals);
• Hospital for the future demands other building- specs and infrastructure (the hospital building and infrastructure does not fit anymore);
• Hospital building and infrastructure will probably change in one main - specialized - hospital with a few outpatients’ clinics in the vicinity (‘buitenpoli’s);
• Other transportation models for all involved (ambulances, patients, family, hospital staff etc.);
• More specialization among hospitals based on medical intervention and/or ethical background of the patients (concentration and specialization e.g. hospitals with cardio vascular specialization vs. Muslim hospitals);
• More specialization in the ‘chain’ (diagnostics, care and cure)
• Keen joint ventures between hospitals, private clinics and other partners in the chain to enforce efficiency;
• New hospital organizations (hospitals with care hotels, houses for the elderly etc.) with new organization models;
• ..
International level:
• EU regulation will have an indirect impact on Dutch hospitals;
• International competition between hospitals in EU (and even worldwide) will have an impact on Dutch hospitals;
• New technologies (ICT, Genomics and Biotechnology) which makes hospital healthcare (prevention, care and cure) better but much more expensive;
• Changing ethical morale in society (e.g. self centred egoistic patients, manipulability of life, who pays decides etc.);
• Increasing threats of pandemics, new diseases, terrorist attacks and natural disasters will have a large impact on hospital(s) in afflicted areas;
• ..
• ..
Clustered driving forces (from a hospital point of view):
Main driving forces that work on the model:
1. Free market mechanism;
2. Empowered patients;
3. Technology push and pull (ICT genomics, biotechnology);
4. Ethical debate (manipulability of life).
5. ..?
CLUSTERED DRIVING FORCES
- Technology (genomics, biotechnology, E-health, medical technology)
- Free-market mechanisms
- Changing patient profiles (aging population, empowered patients, more morbidity and lifestyle)
- Ethical debate (to what extent does this inhibit innovation)
DRAFT SCENARIO GRID
File:Tweebijtweetje def.jpg
SCENARIO'S/SHORT STORIES (still WIP)
1.A drastic cure is needed
Since the insurers by 2006 are no longer obliged to contract hospitals, medical care can be offered at other physical venues than hospitals. Under the influence of for profit insurers hospital care becomes desintegrated production lines. This fragmentation is financially driven by all stakeholders: insurers, hospitals and patients. People choose their insurance only based on price, insurers compete on insurance premium and are forced to purchase hospital care with the lowest price. Hospital budgetting and organization are not organized around patients, but efficiently per DBC and /or per product line. Local efficiency rules.
In 2007 the salary cap for hospital and insurance management is introduced. Specialists / doctors discover liberalization and make scandalous amounts of money with helping only the people who pay extra, result: with bad hospital- an insurer management there is no countervailing power for doctors. As a result of power in the production lines and bad negotiating power of insurance companies, the “B-DBC’s” (free prices) lead to an increased price exceeding inflation. Ethical arguments are found irrelevant in discussing the use of new technology. In the hospital care market every new medicine and technology should be possible for all patients. This translates into even more increased insurance premium for patients in 2008 and 2009. In 2009 several hospitals will go bankrupt because of bad hospital management. The cost of bankrupcy is included in the insurance premiums. Patients have no choice but to pay health insurance premiums, result: poverty and bad publicity. Cost of health care (and hospital care) in the Netherlands explodes to more than 17% of GDP in 2011. At the end (2013), the system crashes. Dutch parliament initiates a parliamentary inquiry on the (un-)equal access to hospital care and bad negotiation of insurance companies, conclusion: government has to intervene in the free market. Government in 2015 re-introduces budgeting and private stakes in hospitals are prohibited. State hospitals are (re-)introduced.
2.Remarkable Recovery
After the crash of the Dutch insurance system in 2007 (only 1.5.year after introduction) a visionary not for profit HMO took the initiative to regionally organize insureres, first line health care, home care, hospital care. This system is driven by societal responsibility and solidarity. Financing happens through contributions of all stakeholders, including private investments. There is cross-subsidising between DBCs; care as well as budgetting is organized around patients. Prevention of (life style induced) risks are a priority and individuals assume greater responsibility for their healh. Patient/consumer movement and government are happy with these developments and are fully supportive. As the system is self-steering, central government only plays a limited (participative in stead of regulatory) role.
Integrated care is one of the cornerstones of the new health care system. With Kaiser Social, consumers don't just buy insurance. For a fixed monthly fee, they gain easy access to an organized system that provides integrated preventive, routine, emergency, and hospital care. Not only the organization will be integrated; also the physical place. GPs and pharmacies will have accomodation in the same building as the hospital.
There is an integrated health delivery system, which means that the entire scope of care for the community is provided and coordinated, including:
- preventive care
- well-baby and prenatal care
- immunizations
- emergency care
- screening diagnostics
- hospital and medical services
- pharmacy services
New medical and supportive technologies (broadband, long distance observation and advice, telemonitoring, day-treatment) enable people to stay home longer and leave hospital earlier. Patients also can use software agents that arrange appointments and administration. All these developments result in less demand for inpatient care in hospitals (only 20% of current demand for peripheral hospitals in 2012). The same technological platform ensures efficiencies in (all) the relationships between hospitals, health professionals, providers, suppliers. Care is thereby less labour intensive but there are sufficient qualified health professionals willing to work in hospitals. The system flourishes by depending much on social interaction and costs are driven down. In decisions about investments, ethical arguments play an important role; community serves as a 'basis of common sense'.
Futher keyword(s): vertical integration
TBD: % GDP
3.European Cure
The Dutch healthcare is tsunamied away by the increasing demand through the aging population, EU ruling (Decker-Kohl, Smits-Peereboom), NMA limits on national M&As among hospitals and by scarcity of (qualified) labor. Financial structures (towards the specialists as well as towards the hospitals themselves)are complex and do not keep pace with the current practice. Hospitals are unable to manage both increasing demand and the suffocating, sometimes conflicting, rules.
The threath of a new outbrake of either birdflu or MRSA can not be adequately managed by the existing health care structure. There is hardly any personnel and there are lots of vacancies in caring profession. Hospitals are actively looking in- and outside the country for qualified medical personel and for doctors that like to affiliate with the hospital. This scarcity increases costs (higher wagers needed and slection-costs)for the hospitals yet still does not solve the problem of a shortage in work-force.
As patient interest is not served, new initiatives fill the vacuum.
The new libaralized model uses economies of scale and competition does not take place on a local but on EU scope. National government does not play a role. Other countries provide well arranged healthcare; international investors (even non EU e.g. US, Arab and Russian)take over hospitals and organize specialized hospitals spread over the EU. EU conglomerates can insure Dutch patients at attractive rates. As the care is internationally organized, it is highly individually driven: no solidarity. The system is only financed by the (sum of) the individual consumers. There is interest in prevention from a strictly financial point of view. For hospitals this implicates that ownership is not longer a national issue: hospitals increasingly get obtained by foreign investors. This implicates that more than ever, the management has to apply to financial targets as monitored by international bookkeeping standards. More and more, investors place trustees on the helm of the management.
Care is diferentiated per indication: for a total hip a patient travels to Turkey, for a coronairy bypass Romania is the place to be. There highly qualified staff is available or is recruited in other countries like India. Less interference of some governments in the ethical debate enable further growth of biotechnology and genomics in these countries, enabling a further preferred position in the healthcare market. Technological developments are thereby not spread evenly hroughout EU: there are 'technological hotspots' providing top clinical care. Technology like genomics and biotechnology also drive preventive healthcare and will open markets for diagnostic testing, preventive medicine, follow up treatments and even support services such as lifestyle counselling. For the Dutch hospitals this specialization implicates that funds in research are not invested in Holland but in other countries. Top talent will follow the financial stream or will be employed by Academic hospitals and by that leave relatively routine care left for Dutch hospitals. In order to survive in that market, cost leadership is important. Further rationalization of the core processes in the hospital are a result of that.
TBD: % GDP
SOURCES OF INFORMATION
- Healthcast 2010: Smaller world, Bigger Expectations. PWC. November 1999. [1]
- Healthcast Tactics: A Blueprint for the future. PWC. May 2002. [2]
- Stress, satisfaction and burnout among Dutch medical specialists. Mechteld R.M. Visser, Ellen M.A. Smets, Frans J. Oort, Hanneke C.J.M. de Haes
- Market in Need of Products That Address Key Concerns of Growing Patient Population and Rising Healthcare Costs; Developing New and Innovative Technologies is the Way Forward. September 6, 2005. PR Newswire Association LLC.
- Specialty Cardiac Hospitals Treat Less Severely Ill Patients Than Non-Specialty Hospitals . July 12, 2005 Tuesday 12:00 PM GMT. Business Wire, Inc
- SER (1999) Gezondheidszorg in het licht van de toekomstige vergrijzing, The Hague: SER
- Rol en positie van medisch specialisten 2005; OCM/ Dr. A.C.J.M. Olsthoorn, September 2005
- www.minvwsnl
- www.zorgaanzet.nl
- www.cbz.nl
- www.ctg-zaio.nl
INTERVIEWS
- Partners PWC
- Director Achmea Healthcare
- Professor of Neurology: routine (peripheral) care vs. highly specialized (university) care will have significant impact on financing hospital care: new structure is needed
- Departmental head Dutch Association of hospitals: hospitals will end up in a hybrid model (partly liberalized market, partly regulated) that will jeopardize continuity; a drastic change in finance structure is needed
- Director regional Patient Organization South West of the Netherlands
- Secretary of the board of Erasmus MC
- Health care entrepreneur/ consultant: technical development (e.g. intelligent multi agent systems) enable patients to make appointments themselves and administration will be automized. This will lead to a 20% occupancy rate of current capacity of periferal hospitals. Top clinical care will be provided by academic hospitals.