Aging population
Description:
The average age of the population in Western Europa will be increasing dramatically in the coming decades. Figure 1 gives the essence of the problem in the Netherlands.
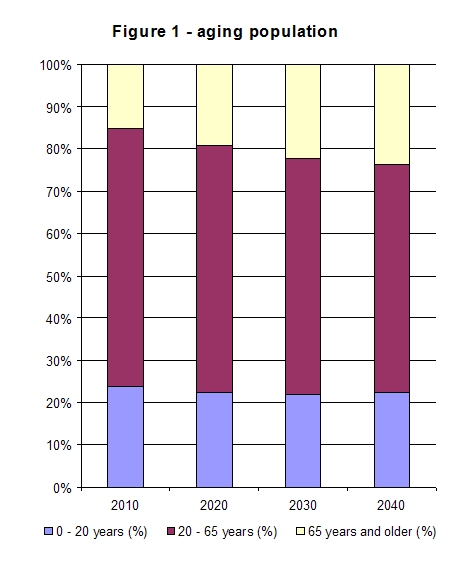
The 65+ population in the Netherlands from 2010 to 2040 is expected to grow from 15% to 24%, whereas the 20-65 population is expected to decrease from 61% to 54%.
The same trend counts for the most of Western Europe.
Aging population is a driving force which for example is driving Europe to accept Turkey into the EU. With the advances in medicine the population of the world is living longer which means that the world needs more resources to support this population. The birth rate however is diminishing around the world and resources are limited. Therefore a new balance will be established.
Enablers:
- Technogical advances in medicine - Better living conditions in the Developing world - More health awareness - Better food quality - More hostital beds (from 1994-2001, the number of hospital beds increased with 78%)
Inhibitors:
- Extending the retirement age another 10 years so people will have to work more & retire later
Paradigms:
There has been enormous concern about the consequences of human population growth for the environment and for social and economic development. But this population growth is likely to come to peak and then decline in the foreseeable future.
Experts:
United Nations US Department of Health and Human Services
Timing:
Improving on earlier methods of probabilistic forecasting, here we show that there is approximately 85 per cent chance that the world's population will stop growing before the end of the century. There is a 60 per cent probability that the world's population will not exceed 10 billion people before 2100, and around a 15 per cent probability that the world's population at the end of the century will be lower than it is today. For different regions, the date and size of the peak population will vary considerably.