Research Questions and Findings
For readability sake – and since these research questions are only for internal use - we will not give in text references. All our references can be found on the bottom of this page.
What is advertising? (by Klaas-Jan)
Generally speaking, advertising is any paid form of nonpersonal promotion of goods, services, companies and ideas, usually by an identified sponsor. Marketers see advertising as part of an overall promotional strategy (i.e. one of the elements of the marketing mix). Other components of the promotional mix include public relations & publicity, personal selling, direct marketing, events and sales promotion. [1]
What are the objectives of advertising? (by Klaas-Jan)
Advertising objectives can be classified according to whether their aim is to inform, persuade, remind or reinforce. [1]
- Informative advertising. Aims to create brand awareness and knowledge of new products or new features of existing products.
- Persuasive advertising. Aims to create liking, preference, conviction and purchase of a good or service.
- Reminder advertising. Aims to stimulate repeat purchase of a good or service.
- Reinforcement advertising. Aims to convince current purchasers that they made the right choice.
How does advertising fit in marketing? (by Klaas-Jan)
Marketing consist of numerous value-enhancing decisions/activities. One traditional depiction of marketing activities is in terms of the "marketing mix", the four Ps [1]:
- Product (e.g. quality, design, packaging, warranties)
- Price (e.g list price, discounts, credit terms)
- Promotion (e.g. advertising, public relations, direct marketing)
- Place (e.g. channels, transport, coverage)
Since people play such an important role in marketing (for instance, they can have a tremendous impact on how customers perceive a company) a fifth P is often added: people.
Why is advertising necessary? (by Klaas-Jan)
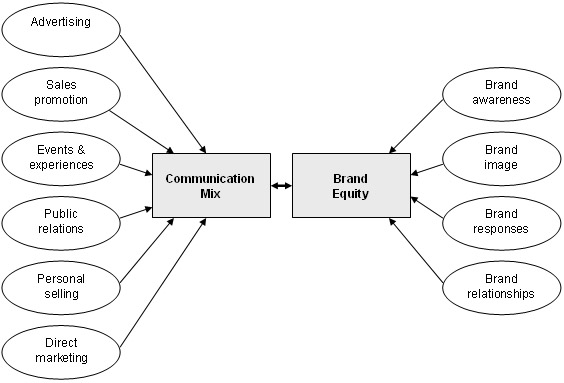
Advertising is, as said before, an essential part of the marketing communication mix. This communication mix affects, on its turn, the brand equity of a company. Brand equity is the customer’s subjective and intangible assesment of the brand, above and beyond its purely perceived value. In a market where many products are rather similar, the brand can have a large effect on whether customers want to buy the product and what price they will pay. Brands therefore add more and more value to the basic product. How the communication mix and brand equity are related, is visualized in the figure below. [1]
What is the general advertising process and which parties are involved? (by Klaas-Jan)
Organizations handle advertising in different ways. In small companies, advertising is handled by someone in the sales or marketing department, who works with an advertising agency. A large company will often set up its own department, whose manager reports to the “big boss” of marketing. The department’s job is to propose a budget, develop strategy, approve ads and so on. [1]
Most companies use an outside agency to help create advertising campaigns and to select and purchase media. Today, advertising agencies are redefining themselves as “communication companies” that assist clients to improve their overall communications effectiveness. They do this by offering strategic and practical advice on many forms of communication.
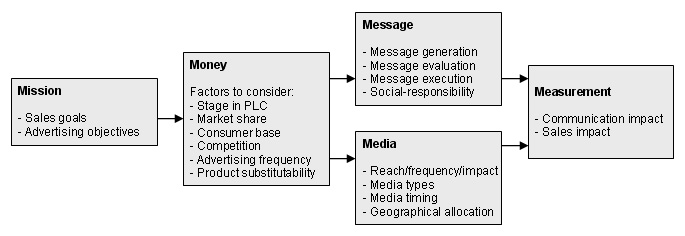
The general process can be described with 5 major decisions, the 5 Ms.
NB: Although this is not a complete picture it gives a very good picture of how it works in general.
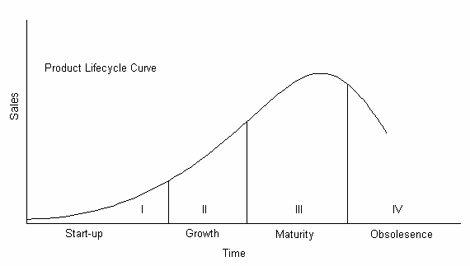
How can the Product Life Cycle be related to advertising? (by Klaas-Jan)
The figure below shows the Product Life Cycle. Each stage of a product’s life requires a different approach of advertising. [1]
- Start-up stage. Build product awareness among early adopters and dealers.
- Growth stage. Build awareness and interest in the mass market.
- Maturity stage. Stress brand differences and benefits.
- Obsolesence stage. Reduce to level needed to retain hard-core loyals.
What is the impact of Internet on advertising?
With the dawn of the Internet have come many new advertising opportunities. Popup, Flash, banner, and email advertisements (the last often being a form of spam) are nowadays widely known.
The Internet has emerged as a medium for marketing and advertising since 1994. The Internet is different from conventional advertising media in several respects. First, it can serve as not only a communications channel but also a transaction and distribution channel. Consumers can get information and make purchases and payments all through the Internet. No other medium can accomplish these marketing functions instantly, without resorting to other means. Second, the Internet is by nature interactive. Users can initiate a shopping process by visiting a Web site and then clicking on hyper-linked text for more information. It is a two-way communication, with the Internet serving as a provider of customized content that meets an individual's needs. Third, it has the capacity for multimedia content. It can carry not only text and graphics but also audio and video content. The multimedia nature of the Internet is suitable for high-impact advertising. The Internet has become an integral part of the media mix for many advertisers, and new forms of advertising have filled the World Wide Web landscape, including animated banner ads, sponsor logos, interstitials, “advertorials,” “advertainment,” and 3-D visualization.
What are the media costs?
Advertising rates are more stable for print media than broadcast media largely because print media can adjust the number of advertising pages on an issue-to-issue basis while broadcast media have a fixed amount of daily programming hours. Thus, demand by advertisers has a stronger impact on the rates for broadcast time. Newspaper space is usually sold according to rate cards; buyers of large volumes get discounted rates. Magazine space is sold similarly. Advertising rates for radio and television are normally determined through negotiation and often vary by the time of day. A 30-second spot on network television costs the most in prime time (8:00 p.m. to 11:00 p.m.) and the least during daytime (10:00 a.m. to 4:00 p.m.). According to Optimum Media, in the third quarter of 1999, a 30-second commercial on U.S. network television cost $190,000 in prime time but $21,960 in daytime. Advertisers use CPM (cost per thousand impressions) and CPP (cost per rating point) to compare media costs. CPM is used for both print and electronic media while CPP is more popular for electronic media. CPM is calculated by multiplying the unit cost of a media vehicle by 1,000 and dividing the result by the audience size of the vehicle. The unit cost of a media vehicle is the cost for a single ad placement in that vehicle. Fro example, if a 30-second commercial in a TV program costs $5,000 and the program has an audience of 250,000, then CMP for the commercial will be $20. CPP is calculated by dividing the unit cost of the media vehicle by the rating of the vehicle. If a 30-second commercial in a TV program costs $5,000 and the program has a rating of 10 in the market, CPP for the commercial will be $500. CPP can also be used to compare newspaper or magazine costs if the audience is described as a percentage.
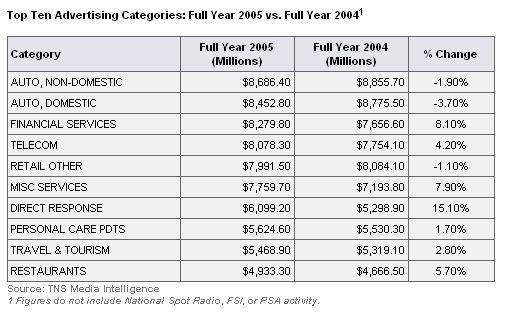
Which industries advertise most? And which less?
The following table shows the U.S. advertising expenditures per industry. Unfortunately, we don't have figures for Europe, Asia etc.
What are the differences between B2C and B2B advertisement?
Although the target of the advertisement is not the same as B2C, there is no difference in the way the advertisement is set up. The way the advertisement is brought to the other business is the same. Focus on B2B advertisement besides product is also service and long term relations.
'Is advertisement mostly done by the company themselves or is it outsourced? ’
At this moment most of the MNC’s have their own advertising departure or they have an entire advertisement company fully available. Nike is a nice example how their advertisement company grew together with Nike and how both existence now rely on each other. Like the outsourcing trend of IT, also advertisement follows the trend to be outsources. While the first major outsourced location was India, now the trend moves slowly to China, Philippines, Malaysia, Singapore, South Africa and Australia. Studies show that this will increase in the future when the western knowledge of these countries improves.
What are general qualities/benefits of advertisements? And what are the qualities/benefits of other methods?
Advertising General Qualities:
- Public presentation
- Pervasiveness
- Amplified expressiveness
- Impersonality
Sales Promotion Benefits:
- Communication
- Incentive
- Invitation
Public Relations and Publicity Distinctive qualities:
- High credibility
- Ability to catch buyers off guard
- Dramatization
Personal Selling Distinctive qualities:
- Personal confrontation
- Cultivation
- Response
Direct Marketing Distinctive qualities:
- Nonpublic
- Customized
- Up-to-date
- Interactive
Is the role of advertisement changed in the last decades? And how?
Over the years, the public perception of advertising has become very negative. It is seen as a medium that inherently promotes a lie, based on the purpose of the advertisement - to encourage the target audience to submit to a cause or a belief, and act on it to the advertising party's benefit and consequently the target's disadvantage. They are either perceived as directly lying (stating opinions or untruths directly as facts), lying by omission (usually of terms unfavorable to the customer), portraying a product or service in a light that does not reflect reality or even making up realities where their product has a new role.
What are the available advertisement media types? (e.g. newspaper, TV, internet, radio)
The most common forms of advertising media types are:
- Television: Broadcast, Syndicated and Cable
- Radio
- Internet
- Newspapers
- Magazines
- Direct Mail
- Yellow Pages
- Outdoor: Billboards, Posters, etc.
- Word of mouth (“the buzz”)
What are the advantages and limitations of these media types?
Within the Internet media type, several advertising approaches exist. While banners and pop-up ads are the most common forms of Internet advertising, other methods similar to direct mailing are often employed over email. Furthermore, the Internet offers the best ways to customize advertising for each unique person. Based on the content of the website and the available information on the user, appropriate and relevant advertisements can be displayed to the user. This benefit is the easiest to achieve with the Internet compared with other media types.
Physically printed ads such as in newspapers or magazine have the limitation that a single message is broadcasted to the audience, and no form of customization exists. In order to reach a specific target market, advertisements have to be printed in more focused/dedicated printed media. Televised advertising has the advantage of containing video. However, Internet advertising is already at the stage where advertising videos are often embedded in websites. Thus television no longer is the only media type with that feature.
What advertising media types will diminish due to the growth of new advertising methods?
Especially televised advertising will become less effective due to the users’ ability to avoid advertisements with technologies like video-on-demand. Furthermore, the common consensus is that many advertisements are a nuisance and intrusive, and therefore users prefer advertisements that they can switch off or avoid. Here also lies the advantage of newer media types like Internet because advertisements can be customized to be more relevant to the user, and hence is less likely to be considered a nuisance. Other possible growth media types including mobile phone or PDA advertising. However it will be difficult to advertise over these channels without giving off a spam-like notion.
What's the people's perception related to advertising?
Statistics show that an average person is exposed to thousands of advertisements through the course of a day from printed ads, to logos on clothes and buildings, to banners on websites. The general consensus is that advertisements are a nuisance and often intrusive. With the rise of new media types such as the Internet, there is a chance that more relevant advertising will diminish this negative perception of advertising somewhat. Having said that, some people may perceive targeted advertising over new media types to be an even greater breach of their privacy. Thus overall the image of advertising is likely to remain something that while ubiquitous is rather intrusive and annoying.
What can be said about advertising timing? (see page 582, Kotler)
<Can’t find my Kotler. Will fill in tomorrow>
Chen Li:
What are important non-technological trends which affect advertising?
Non-technological trends are direction or sequence of events that has some momentum and durability (from Kotler).
Globalization:
Globalization will bring changes in all levels from culture to communicating methods. Globalization is a very general descrpition, a 'megatrend' which influence almost every 'subtrends'.
One excisting model of scenarios analysis of globalization developed by last year's IIB students is illustrated below:
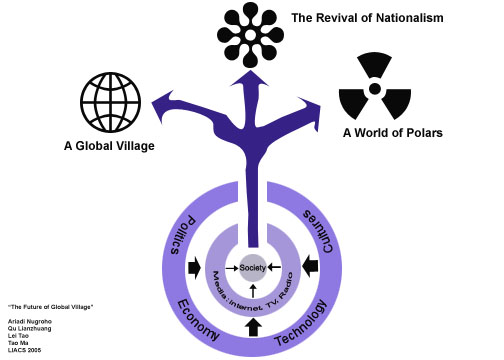
According to this model, the three different results means many different possible situations in culture trends, global ecnomic trends, social trends, etc. Forthcoming research questions will give detail analysis in these trends.
Product customization:
There is no doubt that the market differentiation is becoming more explicit. Certain groups of customers’ needs are unique. Their favor, and the way to reach them is diversified. The consistency of the advertisement's content, media type, targetd market, and the product's sustainable competitive advantage is the criteria for a eligible advertisment.
Economic trends
Ecnonmic trend can deeply influence people’s living style, purchase behavior, which has direct or indirect impact on advertising.
One forthcoming research question will give detailed explaination.
Culture trends
Because advertising is very culture sensitive, culture trends will certainly influence advertising.
One forthcoming research question will give detailed explaination.
Other trends
Social trends, political trends can also impact on advertising.
What are the social factors which will influence on advertising?
Protection towards Children There have been increasing efforts to protect the public interest by regulating the content and the reach of advertising. Some examples are the ban on television tobacco advertising imposed in many countries, and the total ban on advertising to children under twelve imposed by the Swedish government in 1991. Though that regulation continues in effect for broadcasts originating within the country, it has been weakened by the European Court of Justice, which has found that Sweden was obliged to accept whatever programming was targeted at it from neighbouring countries or via satellite.
In Europe and elsewhere there is a vigorous debate on whether and how much advertising to children should be regulated. This debate was exacerbated by a report released by the Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation in February 2004 which suggested that food advertising targeting children was an important factor in the epidemic of childhood obesity raging across the United States.
In many countries - namely New Zealand, South Africa, Canada, and many European contries- the advertising industry operates a system of self-regulation. Advertisers, advertising agencies and the media agree on a code of advertising standards that they attempt to uphold. The general aim of such codes is to ensure that any advertising is 'legal, decent, honest and truthful'. Some self-regulatory organisations are funded by the industry, but remain independent, with the intent of upholding the standards or codes (like the ASA in the UK).
Critiques of the medium
As advertising and marketing efforts become increasingly ubiquitous in modern Western societies, the industry has come under criticism of groups such as AdBusters via culture jamming which criticizes the media and consumerism using advertising's own techniques. The industry is accused of being one of the engines powering a convoluted economic mass production system which promotes consumption. Some advertising campaigns have also been criticized as inadvertently or even intentionally promoting sexism, racism, and ageism. Such criticisms have raised questions about whether this medium is creating or reflecting cultural trends. At very least, advertising often reinforces stereotypes by drawing on recognizable "types" in order to tell stories in a single image or 30 second time frame. Recognizing the social impact of advertising, MediaWatch, a non-profit women's organization, works to educate consumers about how they can register their concerns with advertisers and regulators. It has developed educational materials for use in schools. The award-winning book, Made You Look - How Advertising Works and Why You Should Know , by former MediaWatch president Shari Graydon, provides context for these issues for young readers.
Public interest groups and free thinkers are increasingly suggesting that access to the mental space targeted by advertisers should be taxed, in that at the present moment that space is being freely taken advantage of by advertisers with no compensation paid to the members of the public who are thus being intruded upon. This kind of tax would be a Pigovian tax in that it would act to reduce what is now increasingly seen as a public nuisance. Efforts to that end are gathering momentum, with Arkansas and Maine considering bills to implement such taxation. Florida enacted such a tax in 1987 but was forced to repeal it after six months, as a result of a concerted effort by national commercial interests, which withdrew planned conventions, causing major losses to the tourism industry, and cancelled advertising, causing a loss of 12 million dollars to the broadcast industry alone.
Public perception of the medium
Over the years, the public perception of advertising has become very negative. It is seen as a medium that inherently promotes a lie, based on the purpose of the advertisement - to encourage the target audience to submit to a cause or a belief, and act on it to the advertising party's benefit and consequently the target's disadvantage. They are either perceived as directly lying (stating opinions or untruths directly as facts), lying by omission (usually of terms unfavorable to the customer), portraying a product or service in a light that does not reflect reality or even making up realities where their product has a new role.
Future
With the dawn of the Internet have come many new advertising opportunities. Popup, Flash, banner, and email advertisements (the last often being a form of spam) abound. Recently, the advertising community has attempted to make the adverts themselves desirable to the public. In one example, Cadillac chose to advertise in the movie 'The Matrix Reloaded', which as a result contained many scenes in which Cadillac cars were used. Similarly, product placement for Rolex watches and BMW cars featured in recent James Bond films.
Each year, greater sums are paid to obtain a commercial spot during the Super Bowl. Companies attempt to make these commercials sufficiently entertaining that members of the public will actually want to watch them.
Particularly since the rise of "entertaining" advertising, some people may like an advert enough that they wish to watch it later or show a friend. In general, the advertising community has not yet made this easy, although some have used the Internet to widely distribute their adverts to anyone wishing to see or hear them. Source: Wikipeida
What are the economic trends and how can it impact advertising?
First, we find the trends in Economy from Faith Popcorn's Popcorn report 1996, and listed it below. Second we will explain how can these trends impact advertising directly or indirectly.
Anchoring - The tendency to use ancient practices as anchors or support for modern lifestyles: aromatherapy, meditation, yoga, & Eastern religions.
- New lifestyles means new behaviors, also means new channels, new ideas for advertiseing.
Being Alive - The desire to lead longer and more enjoyable lives: vegetarianism, low-tech medicine, mediation.
ashing out - The desire for a simpler, less hectic lifestyle. A nostalgic return to small-town values.
- Above two trends are related people's attitude to life. According to that, advertisement with a 'fallow' style may be more popular.
Clanning - The need to join groups in order to confront a more chaotic world: Harley-Davidson's Harley Owners Group (Hog).
- People are willing to join groups, which means there can be ways to reach similar people more efficiently. TV advertisements broadcasted in Salons are good examples.
Cocooning - The impulse to stay inside when outside gets too tough and scary: redecorating, watching TV & rental movies, ordering from catalogs.
- No matter traditional TV will change to internet based or not, people will still spend much time watch TV programms and movies with their family theater. There are tools to block advertisements in TV, but it will still remain be the best way to reach your customers.
Down-Aging - The tendency for older people to act and feel younger than their ages: youthful clothes and hair coloring, adult toys, adventure vacations.
Egonomics - The wish to individualize oneself through passions & experience: customized goods, services, experiences.
- Advertisements will also be customized. Internet can achieve that easily, many search engines give you relevant commercials while searching.
Fantasy Adventure - The need to find emotional escapes: safari vacations, exotic foods.
99 Lives - Doing many things at once, "multitasking": cluster marketing enterprises-all-in one service stops.
S.O.S. (Save our Society) - The desire to make society more socially responsible: education, ethics, the environment.
Female Think - The recognition that men and women act and think differently.
Mancipation - The emancipation of men from stereotypical male roles of being macho and strong, and instead showing them as nurturing dads and concerned husbands.
- These are all trends that distinguish one group of people from others.
Small Indulgences - The desire to indulge in small-scale splurges to obtain an occasional emotional lift.
Pleasure Revenge - The proud and public pursuit of pleasure as a rebellion against self-control and self-deprivation.
Icon Toppling - The return to interest in smaller and more local organization and products.
- How can an advertisement give consumers this feeling.
The Vigilant Consumer - Intolerance for shoddy products and poor service.
- Quality of advertisement is important, too.
From the analysis above we can see that the economic trends have significant impact on people's lifestyle and consuming behaviors.
What affects the advertising budget?
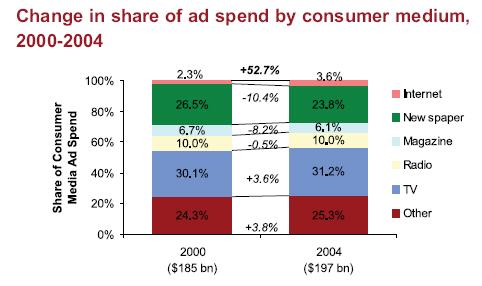
www.doubleclick.com made an research on the current situation. According to their number, online advertisement spending grew 63% from 2000 to 2004 in absolute terms ($4.3 billion in 2000 to $7.1 billion in 2004). The Internet’s growth, meanwhile, was 52.7% as a share of total consumer media ad spending (excluding direct mail and yellow pages) in that same period. By comparison, overall ad spending in the same period on TV grew 10.6% in absolute terms (from $51 billion to $62 billion) and 3.6% as a share of total consumer media ad spending. The newspaper sector was the biggest loser in the media mix in terms of share of all ad dollars. Its readership is aging and declining, and its important base of classified ad revenue faces stiff competition online from the likes of eBay, Craig’s List, Monster.com and Match.com. Newspaper ad revenues were down 4.3% in absolute terms over the last five years ($49 billion to $47 billion), and they fell 10.4% in terms of share of media spend.
But those numbers do not tell the whole story. While at a high level, the growth of the industry remains steady and the budget allocation among media outlets is shifting only gradually.
Source: The decade in online advertising. www.doubleclick.com 2006
How much time does a person spend on Internet and watching TV? how will it influence advertising?
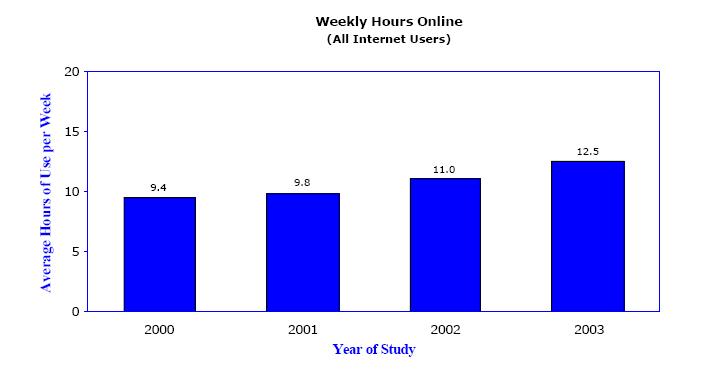
Number of hours people spend on Internet
Data source: Digital Future report 2004, by Jeffrey I. Cole, Ph.D., University of California.
Number of hours people watch TV
HOURS/PERSON/YEAR 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 Total Mdia Usage 3,347 3,469 3,519 3,570 3,623 3,661 Television 1,551 1,588 1,640 1,661 1,661 1,656 Broadcast TV 884 867 865 815 810 798 -Network stations 710 706 805 753 749 736 -Independent stations 174 162 61 62 61 61 Cable & satellite TV 667 720 774 846 851 858 -Basic 565 617 638 692 698 706 -Premium 101 103 137 154 153 152
Data Resource: FCC Annual Report 2003.
From the first figure we can see that the time people spend on Internet grew from 9.4 hours/week to 12.5 hours/week, a rise of 30%. And the time people spend on watich TV grew from 3519 hours/year to 3661 hours/year, that is 67.5 hours/week to 70.2 hours/week, a rise of 4%.
A reaserch made by the PRWEB company in 2006 shows that 55% of the online population uses the internet to search for local products and information in US. Source:http://www.wsicorporate.com/images/upload/211_StateoftheClickpr.pdf
We can see that till the year 2003, althrough internet usage is still grow at a high rate, but people still spend 57.7 hours more on TV, and there is no trend that this people will spend less time on TV now. In the newest release on March 07, 2006 of FCC's 12th annual report on TV competition, FCC declear that the death of TV hasn't quite happened yet as the average american household watched 8 hours and 11 minutes of TV per day last year. This was an all time record. The average american person in the average amercan household watched 4 hours and 32 minutes, another all time record.
A personal statics number shows that advertisement consist around 30% of total broadcasting time. http://www.waynesthisandthat.com/commerciallength.htm
Another news is that more and more people now get used to record TV programs, by which mean they can very easily skip all the advertisements. New products like Harddisk recorder, DVD recorder is becoming more and more popular.
From the consumer side, we can conclude that people are spending more time on Internet, people use Internet to search product information. The opportunity for online advertising is still growing. There is no trend that TV advertising will die, but there are certain threats like DVD recorders.
What are the legal issues?
The general rules of advertising are:
* advertising must be truthful and non-deceptive; * advertisers must have evidence to back up their claims; and * advertisements cannot be unfair.
Besides the generals, some addtional rules about Alcohol advertising, there are addtional rules and limits about protect children away from alcohol advertisements, the goverments also established self-regulatory program to let company regular themselves.
The Children's Online Privacy Protection Act, is a federal law that requires websites to obtain verifiable parental consent before collecting, using, or disclosing personal information from children, including their names, home addresses, email addresses, or hobbies.
Internet Advertising Advertising on the Internet subject to the same laws as other advertising. Ad claims on the Internet must be truthful and substantiated. The Rules of the Road for more information. Dot Com Disclosures offers special guidance for online advertisers regarding how to make sure that any disclaimers and disclosures in online ads are clear and conspicuous. It addresses 'Net specific issues such as banner ads, pop-up windows, scrolling, hyperlinks, etc. Internet marketers also should be aware that the FTC's Mail or Telephone Order Merchandise Rule ("Mail Order Rule") applies to online transactions.
Because the World Wide Web is, as its name implies, worldwide, even small online businesses can reach customers around the globe. Electronic Commerce: Selling Internationally - A Guide for Business discusses some online commerce guidelines endorsed by the United States government and 28 other countries.
Consumer privacy online Advertisers should be aware of the privacy issues raised by Internet marketing. The government strongly encourages companies to implement four fair information practices: giving consumers notice of a website's information practices; offering consumers choice as to how their personally identifying information is used; providing consumers with access to the information collected about them; and ensuring the security of the information collected. In addition, companies need to know about the Children's Online Privacy Protection Act and the rule that implements it. The law requires websites to obtain verifiable parental consent before collecting, using, or disclosing personal information from children, including their names, home addresses, email addresses, or hobbies. For more information, ask the FTC for How to Comply with the Children's Online Privacy Protection Rule.
Source: Federal Trade commission of US
References
[1] Kotler, P., & Keller, K.L. (2006). Marketing Management (12th ed.). Upper Saddle River, New Jersey: Pearson Prentice Hall.