Difference between revisions of "Alternative Energy"
| Line 86: | Line 86: | ||
1970s: Coal gasification became the alternative to expensive petroleum. | 1970s: Coal gasification became the alternative to expensive petroleum. | ||
2000s: Renewable Energy (such as sunlight, wind, rain, tides and geothermal heat) had been advocated to be alternative to non-renewable energy. The Group of Seven (G7) economies had been calling for the development of alternative energy sources in the face of record high crude oil prices and depletion of nature resources. | 2000s: Renewable Energy (such as sunlight, wind, rain, tides and geothermal heat) had been advocated to be alternative to non-renewable energy. The Group of Seven (G7) economies had been calling for the development of alternative energy sources in the face of record high crude oil prices and depletion of nature resources. | ||
==Web Resources:== | ==Web Resources:== | ||
Revision as of 16:40, 1 October 2009
Description:
“Right now more energy passes through the windows of buildings in the U.S. than flows through the Alaska pipeline.” ~K. Bidwell and P. A. Quinby
Alternative energy is an umbrella term that refers to any source of usable energy intended to replace fuel sources without the undesired consequences of the replaced fuels e.g biofuels, solar power, wind power, wave power, geothermal power and tidal power.
Conventional sources of energy are diminishing and many experts have already pointed out a time horizon for their depletion. This implies that current oil and carbon reserves that remain for future generations will not suffice for their needs. It is possible that the future generation might find better uses for these energy sources as raw materials, rather than using them as energy and pollute the environment. The technology already exists for the use of renewable and alternative energy and this will slow the rate of consumption of fossil fuels and reduce the pollution.
Since energy sources are diminishing, common sense says that humankind should contemplate two different but complementary options:
Reduce fossil fuel consumption in order to extend the life of existing reserves, not only by lessening the dependency in fossil fuels, but also by using them more efficiently.
Switch to alternative sources
The first option has been in force for decades, and now there are ‘fuel efficient’ aircrafts and car engines, power plants and manufacturing processes. Even so, it appears that these advantages are offset by population growth, with its demand on services, and the consequent creation of more consumption.
Therefore, it is reasonable to think that society’s options point to the second alternative, to alleviate the load and demand on fossil fuels.
Enablers:
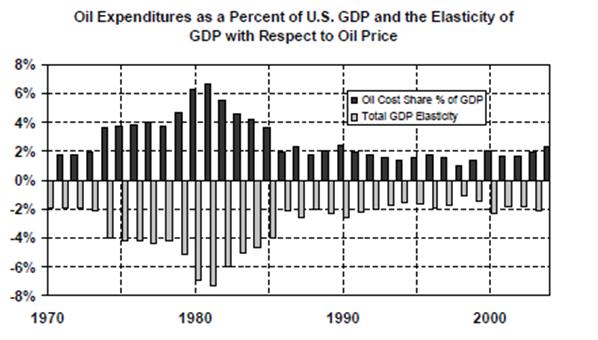
• Rising energy prices. Rising energy prices, which will increase in the oil bill, has been severe for some countries, especially those which combine high energy intensities with a heavy reliance on imported oil as the main source of energy. This will encourage these countries to reduce reliance on oil by developing alternative energy sources. For example, the cost of imported oil had been around 2% of US’s GPA, as shown in the graph below. In the 1980s, with the prices of oil reaching new heights, 6-7% of US’s GPA was spent on oil. This was when US started to investmore money into the development of alternative energy to reduce its reliance of oil.
• Education: Environmental education programs can create children who are enthusiastic about nature. School’s curriculum could include learning expeditions that require students to be actively engaged in nature. Wilderness trips and in-class environmental lessons could be tailored for each grade. The thinking and logical behind these activities is that the more the children know about and appreciate the environment, the more likely they are to protect it.
• Worsening condition of the environment: Abnormal weather conditions with unusual torrential rains and flooding, global warming, increased greenhouse gases, heavy pollution, unnaturally heavy rains and increased frequencies of hurricanes worsen the environment that human lives in. It would encourage human to treasure the environment more by protecting it. The use of fossil fuel energy would cause more harm to the environment and cause these abnormal weather conditions. Thus, people would be more willingly to turn to alternative energy.
• Government policy: Governments can encourage the development and use of alternative energy by giving tax breaks or subsidies. Serious attempts have been made by governments to switch partially to non-conventional sources of energy: countries such as the UK, Germany, Denmark, Spain, Austria, Canada, the Netherlands, Belgium and the US have taken great strides toward using non-conventional sources of energy. This will increase the use of alternative energy.
• Economics Benefits: If the economic benefits of using or developing alternative energy outweigh the costs of using or developing alternative energy, more corporations and individuasl would be turning to alternative energy.
Inhibitors:
• High Cost: The prohibitive costs associated with developing alternative energy could easily deter companies from investment in such technology. Also, the costs associated with using alternative energy e.g setup costs also deter individuals and corporations from using alterative energy. For example, the initial investment in solar-energy equipment can be expensive as the cost is high because semiconductor materials used in the manufacture of PV panels are expensive. In 2009, the price of solar panels that completely meets the energy needs of conventional homes cost $20,000 to install. The average cost of residential electricity was 12¢/kWh in the U.S. in April 200 and an average household used 12000 kWh per year. Thus, an average household would pay about $1440 for it based on the April 2009 average rate. It will take at least 13 years for an average household to breakeven by installing the solar panels (taking into account an average 5% inflation in energy prices per year).
• Low energy/oil prices: The lower the energy prices, the less motivated individuals and corporations to turn to alternative energy.
Paradigms:
Two main reasons urge replacing fossil fuels energy sources with alternative ones. One is that the world will eventually run out of coal, oil and gas, since of course reserves are limited. But even if new and richer oil and gas fields and carbon deposits were found, or if new techniques can improve extraction and combustion, the main problem is atmospheric pollution, especially with the production of CO2 as a flue gas release, since it makes for climate change by increasing the greenhouse effect. To simply give a broad idea of the order of magnitude involved, bear in mind that calculations show that, to produce one GWh of electricity, renewable/alternative energy plants generate an average of 6 metric tons of CO2. Meantime, coal, gas and oil power stations produce 120 times more than this much CO2 per GWh.
Consequences over the next 50 years due to the greenhouse gases effect could include: significant temperature rises (particularly at high latitudes), rising sea temperatures and levels (causing flooding, coastal erosion, damage to coral reefs), more frequent extreme weather events (such as floods, storms and drought), the need to move agricultural activities and infrastructure to different locations ,substantial reduction in biodiversity, more severe bushfire seasons and an expanded range for tropical diseases.
This is why the utilization of alternative sources is so important.
Experts:
1) John Berton, owner of Green Lizard Solar LLC (Number: 773-362-5332) Www. greenlizardsolar.com
2) Paul Gipe - Internationally Known Wind Energy Expert
3) Jayson Antonoff – President of grnNRG Consulting
info@grnNRG.com
Timing:
Late medieval period: Coal was the new alternative fuel to save the society from overuse of wood, which is the dominant fuel.
Mid 19th century: Petroleum became the alternative to whale oil. Whale oil was the main form of fuel for lamps during this period but by mid 19th century the price of whale oil was skyrocketing due to the depletion of whale and could not compete with the newly discovered cheap source of petroleum from Pennsylvania.
1917: Alcohol became an alternative to fossil fuels. Alexander Graham Bell, an eminent scientist, inventor, engineer and innovator who is credited with inventing the first practical telephone, strongly recommended using ethanol as an alternative to oil, stating that the world was in measurable distance of depleting these fuels.
1970s: Coal gasification became the alternative to expensive petroleum.
2000s: Renewable Energy (such as sunlight, wind, rain, tides and geothermal heat) had been advocated to be alternative to non-renewable energy. The Group of Seven (G7) economies had been calling for the development of alternative energy sources in the face of record high crude oil prices and depletion of nature resources.