Difference between revisions of "Waste minimization"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
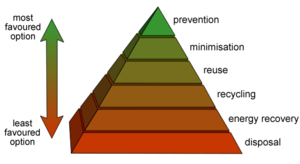
Waste minimisation is the process and the policy of reducing the amount of waste produced by a person or a society. It is part of the wider aim of waste reduction which is often described as a component of the waste hierarchy. In the hierarchy, the most effective policies and processes are at the top. Waste minimisation is also strongly related to efforts to minimise resource and energy use. For the same commercial output, usually the fewer materials are used, the less waste is produced. Waste minimisation usually requires knowledge of the production process, cradle-to-grave analysis (the tracking of materials from their extraction to their return to earth) and detailed knowledge of the composition of the waste. | Waste minimisation is the process and the policy of reducing the amount of waste produced by a person or a society. It is part of the wider aim of waste reduction which is often described as a component of the waste hierarchy. In the hierarchy, the most effective policies and processes are at the top. Waste minimisation is also strongly related to efforts to minimise resource and energy use. For the same commercial output, usually the fewer materials are used, the less waste is produced. Waste minimisation usually requires knowledge of the production process, cradle-to-grave analysis (the tracking of materials from their extraction to their return to earth) and detailed knowledge of the composition of the waste. | ||
[[Image:WasteHierarchy.png|thumb|right]] | |||
Latest revision as of 00:36, 6 March 2007
Waste minimisation is the process and the policy of reducing the amount of waste produced by a person or a society. It is part of the wider aim of waste reduction which is often described as a component of the waste hierarchy. In the hierarchy, the most effective policies and processes are at the top. Waste minimisation is also strongly related to efforts to minimise resource and energy use. For the same commercial output, usually the fewer materials are used, the less waste is produced. Waste minimisation usually requires knowledge of the production process, cradle-to-grave analysis (the tracking of materials from their extraction to their return to earth) and detailed knowledge of the composition of the waste.