Difference between revisions of "The Future of Wireless Broadband in 2010"
Dongsik Chae (talk | contribs) |
Dongsik Chae (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 99: | Line 99: | ||
'''Political Driving Forces''' | '''Political Driving Forces''' | ||
1. Control of the Internet | 1. Control of the Internet | ||
2. Power of the United Nations | 2. Power of the United Nations | ||
3. FTA with U.S.A. | 3. FTA with U.S.A. | ||
'''Economic Driving Forces''' | '''Economic Driving Forces''' | ||
E-commerce in developing countries | |||
Crisis of the capitalism | 1.E-commerce in developing countries | ||
Open Source | |||
Declining Dollar | 2.Crisis of the capitalism | ||
Low growth of korea's economy | |||
3.Open Source | |||
4.Declining Dollar | |||
5.Low growth of korea's economy | |||
'''Societal Driving Forces''' | '''Societal Driving Forces''' | ||
Aging population | |||
Change of a university entrance examination. | 1.Aging population | ||
Community Feeling | |||
Digital Literacy | 2.Change of a university entrance examination. | ||
Increasing influence of Millennials | |||
Increasing Mobility | 3.Community Feeling | ||
Violence in computer games | |||
4.Digital Literacy | |||
5.Increasing influence of Millennials | |||
6.Increasing Mobility | |||
7.Violence in computer games | |||
'''Technological Driving Forces''' | '''Technological Driving Forces''' | ||
Artificial Neural Networks | |||
Gaming Industry | 1.Artificial Neural Networks | ||
Mobility | |||
Peer-to-Peer Technology | 2.Gaming Industry | ||
The Rapid Increase in WiFi Transmission Rates | |||
IPv6 | 3.Mobility | ||
VoIP | |||
4.Peer-to-Peer Technology | |||
5.The Rapid Increase in WiFi Transmission Rates | |||
6.IPv6 | |||
7.VoIP | |||
'''Environmental Driving Forces''' | '''Environmental Driving Forces''' | ||
E-paper solution instead of the paper work | |||
1.E-paper solution instead of the paper work | |||
Revision as of 13:06, 14 July 2006
GROUP COMPOSITION
We are HSE-MBA students in Korea. Our Group comprises of:
- Chan Gun Jeon
- Hong-Kyu Ryu
- Dong-Sik Chae
INTRODUCTION
WHAT IS WIBRO?
Developed in South Korea, WiBro (Wireless Broadband) is the newest variety of mobile wireless broadband access. WiBro is based on the same IEEE 802.16 standard as WiMax, but is designed to maintain connectivity on the go, tracking a receiver at speeds of up to 37 miles per hour (60 km/h). WiMax is the current standard in the United States, offering wireless Internet connectivity to mobile users at fixed ranges of up to 31 miles (50 km) from the transmitting base. However, WiMax is not designed to be used while the receiver is in motion. WiBro can be thought of "mobile WiMax," though the technology and its exact specifications will change as it undergoes refinements throughout its preliminary stages.
Korean-based fixed-line-operators KT, SK Telecom and Hanaro Telecom were awarded licenses by the South Korean government to provide WiBro commercially. According to Asia Media News Daily, the Korean Times reported a glitch in the initial excitement of WiBro, as published 31 August 2005. Hanaro Telecom gave up its license for WiBro after concerns that the considerable investment required would not see a return, while SK Telecom was also said to be hanging back. Only KT remained enthusiastically committed in the push to make WiBro a reality. Meanwhile Samsung has shown great interest in providing devices with WiBro capability.
WiBro is expected to be widely deployed in South Korea by the middle of 2006. As it may become the 4G (4th Generation) wireless standard, the global market will be watching. WiBro will operate in the 2.3 gigahertz band and is interoperable with WiMax.
South Korea is one of the most connected nations in the world. Broadband Internet access is widespread via DSL, cable and WiFi. South Korea also led the world market in quickly commercializing 3G (3rd Generation) cellular services like CDMA2000, a faster version of the Code Division Multiple Access network. Like the United States, South Korea is one of the few nations to use the cellular CDMA network more prominently than the more widespread GSM (Global System for Mobile communications). With its great enthusiasm for wireless technology, Korea promises to provide a solid testing ground for WiBro. (From 'http://www.wisegeek.com/what-is-wibro.htm')
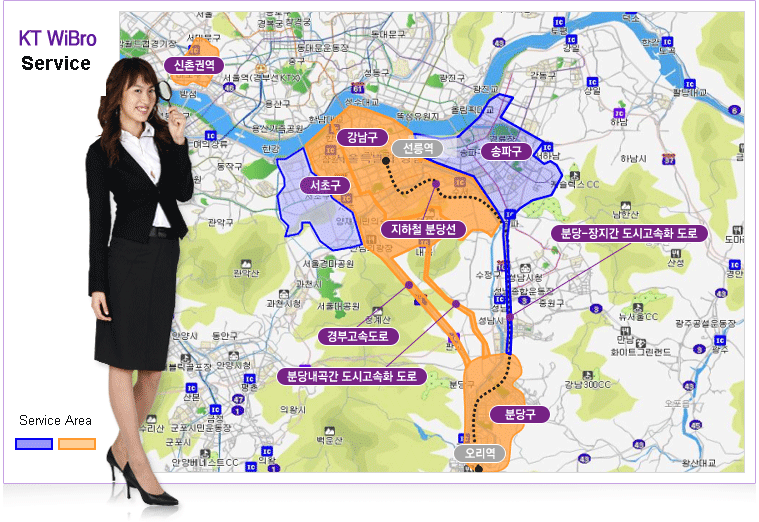
WIBRO SERVICE
WiBro (Wireless Broadband) is a service that provides high-speed broadband communications in the mobile environment, anytime anywhere. WiBro is based on Mobile WiMAX technology, which is based on IEEE 802.16e TDD OFDMA standards. In February 2002, the Korean government allocated 100 MHZ of frequency spectrum in the 2.3GHz bandwidth. WiBro offers an aggregate data throughput of 20 to 30 Mbps from base stations with a cellsite radius of 1 km~5 km. Samsung and Korea Telecom showed the fully expanded coverage of WiBro services at the APEC 2005 Summit in Busan, South Korea (November 15~21, 2005).
And KT and SKTelecom had started their commercial services in serveral areas of Seoul at last 30th June. 2006 with PCMICA type terminal.
Research Questions
- Technology
1. When will IEEE Standardizatoin be finalized for the Global Service Providers?
2. What is the superiorities comparing with other Technologies; WCDMA, WiMAX, WiFi, CDMA Ev-DO?
3. When will the Roaming with other 802.16e profiles available? Especially WiMAX?
4. Will Intel accept Wibro Profile in WiMAX chipset?
5. Is the Mobility(60km/h) enough?
6. Is the Security perfect?
7. Will it be possible the Time-to-Market Development?
8. What is the next from Wibro? (the Evolution of Wibro)
- Industry
9. What kinds of Business Models(Service Package) will be possible?
- What kind of services do the existing Wireless Service provide?
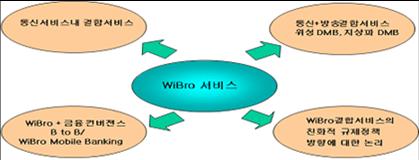
-> Wire Broadband case (like DSL) in Korea, "the Cable TV Service + Broadband Cable + PSTN phone package" is popular. "Wiless Broadband; Wibro" is conceptually new service. So I believe that "Wibro + VoIP + DMB (if DMB supported with terminal)" could be attractive. And Wibro is drived by telecom companies; SKTelecom and KT. So providing services pacakage could be a good approach for KT and SKT because Wibro and their services (Mobiel, PSTN, DSL services) will compete each other.
10. What price will be presented?
11. What kinds of Terminal will be available?
12. What is/will be Telecom Companies's Canibalization Strategies?
13. How much CAPEX will be needed/invested for national-wide coverage?
14. How much OPEX will be needed?
15. What about PDA and NotePC business?
- Society
16. Is the Maturity of IT Environment enough?
17. How fast will Wibro be spreaded?
18. Do the killer application Services exist?
- Government
19. For Wibro service expansion to the new category (ex. VoIP, IPTV), can the current systems be changed willingly? If so, When?
20. Will MIC (Korean Ministry of Information & Telecommunication) drive Wibro?
Driving Forces
Political Driving Forces
1. Control of the Internet
2. Power of the United Nations
3. FTA with U.S.A.
Economic Driving Forces
1.E-commerce in developing countries
2.Crisis of the capitalism
3.Open Source
4.Declining Dollar
5.Low growth of korea's economy
Societal Driving Forces
1.Aging population
2.Change of a university entrance examination.
3.Community Feeling
4.Digital Literacy
5.Increasing influence of Millennials
6.Increasing Mobility
7.Violence in computer games
Technological Driving Forces
1.Artificial Neural Networks
2.Gaming Industry
3.Mobility
4.Peer-to-Peer Technology
5.The Rapid Increase in WiFi Transmission Rates
6.IPv6
7.VoIP
Environmental Driving Forces
1.E-paper solution instead of the paper work