Difference between revisions of "Tsoe Loong Li"
Tsoe Loong (talk | contribs) |
Tsoe Loong (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 94: | Line 94: | ||
====Description:==== | ====Description:==== | ||
While internet where mainly used by teenagers and business man in the past 10 years. More and more individual knows how to use the internet now. Internet TV therfefore can reach much more people. The number of users has grown from an estimated 38 million in 1994 to 580 million in may 2002. | While internet where mainly used by teenagers and business man in the past 10 years. More and more individual knows how to use the internet now. Internet TV therfefore can reach much more people. The number of users has grown from an estimated 38 million in 1994 to 580 million in may 2002. | ||
[[Image:Age span2.JPG]] | [[Image:Age span2.JPG]] | ||
Revision as of 23:23, 27 March 2006
Profiel
Tsoe Loong Li University of Leiden M.Sc. ICT in Business
Object of the future
My Object of the future is: Bio-diesel
Bio-diesel, a clean burning alternative fuel
What is Bio-diesel? Bio-diesel is a domestic, renewable fuel for diesel engines derived from natural oils like soybean oil, and which meets the specifications of ASTM D 6751 [1]
Made from: Vegetable oils, peanuts, corn, soybean etc….
Why Bio-diesel? - Safer, cleaner alternative to petroleum diesel - Alternative for the continuing increasing oil prices - Experts predicted that gas will be exhausted in 50 years - No engine modifications required, no need to change vehicles, spare parts … - Bio-diesel cuts down on targeted emissions, air pollution
Prices The price of biodiesel in the United States has come down from an average $3.50 per US gallon ($0.92/l) in 1997 to $1.85 per US gallon ($0.49/l) in 2002. [2] A gallon gasoline cost about $2.28/gallon and a gallon diesel is about $2.48 /gallon.
Bio-diesel, a renewable fuel for a cleaner tomorrow! Up till now, there are already 1700 Bio-diesel tank-stations in Germany. The European Union is even setting a goal by 2010 that 5.75% of the total volume of energy usage to come from Bio-diesel. With more research to bring down the cost and product awareness, Bio-diesel is the product for the future!!
Renewable Fuel for a Cleaner Tomorrow!
Internet TV
Why do we need Internet TV?
One reason of having internet TV is the flexibility of choosing your own program in your timetable. Your are not depend on the schedule of the normal TV. According to the article of Johna Till Johnson [2]. Another reason of IPTV is that there is a new opportunity for new players to create a creative packing and deliver it to the consumers. New players lead to better service towards to customer because of the competition.
What’s the difference between normal TV and Internet TV / How does internet TV work?
Don’t now how the current tv works but internet tv works as follow: Say that’s Consumer Jane there on the couch. She gets digital video from her local telephone company, which sends it to her over a DSL connection (DSL is rooted in IP, Thus, IPTIV is synonymous with sending TV over DSL). Remote in hand, Jane thumb-surfs via the channel-up arrow. The set-top (or media center) that came with the service issues what’s known as a join request. It wants to dip into a precached set of video frames. The request zings up the phone wire, to that buffer. Maybe it’s in an edge aggregator or maybe it’s in the D-slam, or digital subscribe line access multiplexer. Either way, the tuners aren’t inside anything at Jane’s house. The bits that make up the video frame in the buffer zing back into the box. The boxes used by cable and satellite operators use work differently. On-board tuners work by literally jumping frequencies each time somebody invokes a zap with the remote control. Then they need to demodulate the incoming signal, stabilize it and deal with any error-correction activities. If the processing chip isn’t beffy enough, that to do list can bog down. Symptom: slower zapper action
So conclusion you need a lot of bandwidth. [3]
What kind of new innovation had been made in the era of internet TV?I’m not sure of all the new innovations. But I found a couple innovations that can used on Internet TV. On called Mixtv see paper [1]
• Atomic RSS
• BitTorrent
• Dirac
• HTTP
• NSV - Nullsoft Streaming Video, a technology used by AOL to deliver
Internet based video content.
• RSS
• RSS enclosure
• RTSP
• SMIL
• Theora
• TVU networks - Torrent-like live broadcasting TV technology
Who are the key players of internet TV?http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IPTV --> vendors
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Internet_tv
Conflict with the government? Still researching
What is the impact of globalization? Pros and cons
Still researching
"
(NEW) What is the difference between IPTV, the Internet Protocol-based TV
http://www.masternewmedia.org/2005/06/04/iptv_vs_internet_television_key.htm
[1] Samuel Miller, ACM computer in Entertainment, Vol. 3, No.2, April 2005, Article 6A, Taking on the Masses with Mobile Messaging TV
[2] Johna Till Johnson, Journal: Business Source Premier (BSP), Who wants their IPTV?
[3] Ellis, Leslie, Multi Channel News, 2/06/2006, Vol 27 issue 6, p23-24, AN 199642635 BSP, How IPTV differs from Cable TV
Driving Forces
Driving Forces 1
Name:
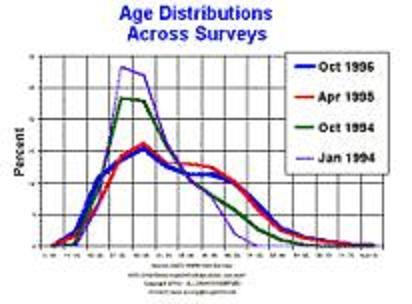
broadening age span of internet user
Description:
While internet where mainly used by teenagers and business man in the past 10 years. More and more individual knows how to use the internet now. Internet TV therfefore can reach much more people. The number of users has grown from an estimated 38 million in 1994 to 580 million in may 2002.
Enablers:
People now see internet more than just a medium to look for information, but as entertainment as well. New technology make internet faster and cheaper and therefore more people can afford internet
Inhibitors:
Increasing internet control by government for political reason as well as porn
Paradigms:
Internet is no longer seen as information retrieval alone. People use internet for all kind of stuff, like entertainment such as games, music and downloading.Due to the increasingly in use of the internet and the broadening of the age span, more and more new service will emerge.
Timing:
o In 1989, internet was mainly used by governmental agencies, with an estimate of 3900
o In 1999, extension like .com, .org, .net. .edu extension are becoming increasingly populiar. With an estimated totoal of more than 4 million. Country names has also becoming increasingly populair
Web Resources:
o basic net data, Richard T. Griffiths (Leiden University)
o http://www.let.leidenuniv.nl/history/ivh/chap5.htm
o http://ist-socrates.berkeley.edu/~zook/domain_names/Domains/international.html
o http://www.gvu.gatech.edu/user_surveys/survey-1998-10/graphs/general/q54.htm
Driving Forces 2
Name:
new technology which make internet faster and cheaper
Description:
Due to the continuosly improvement of internet technology, internet become much faster and cheaper than before.
Enablers:
A factors that strengthen this driving force is the increasing number of users of internet, because of the increasing awareness of the use of the importance of internet.
Inhibitors:
Increasing internet control by government for political reason.
Paradigms:
Internet is no longer seen as information retrieval alone. People use internet for all kind of stuff, like entertainment such as games, music and downloading.Due to the increasingly in use of the internet and the broadening of the age span, more and more new service will emerge.
Timing:
o In januari 1993, leased line was used with a speed of 56 kilobits per second
o In fall 1995, the technology of single T-1 was used. Internet can reach a speed of 1544 kilobits per second
o In fall 1998, multiple T-1 was introduced, speed is twice of the single T-1
o In fall 2002, Fractional DS-3, which can reach the speed of 15000 kilobits per second
Web Resources:
o http://ist-socrates.berkeley.edu/~zook/domain_names/Users/index.html
o http://www.nua.ie/surveys/how_many_online/index.html
o http://ist-socrates.berkeley.edu/~zook/domain_names/
o http://www.let.leidenuniv.nl/history/ivh/chap5.htm
o http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/History_of_the_Internet
o http://www.cedarville.edu/departments/compserv/historyinternet.htm