Difference between revisions of "Security Policy"
| (7 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
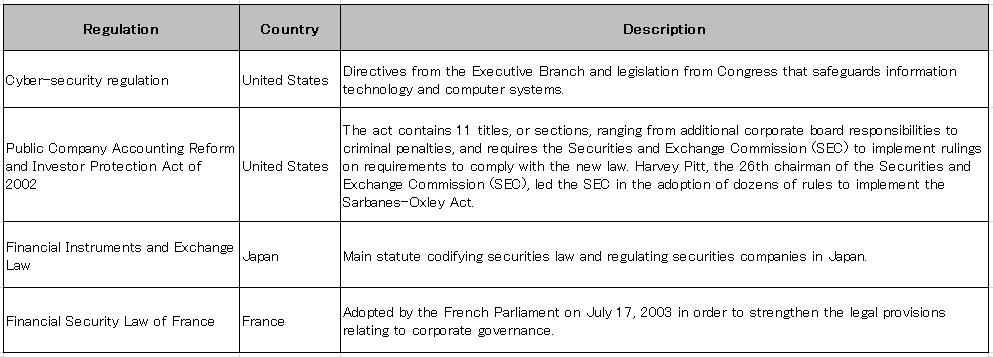
Undeveloped policy regarding personal information contributed to an enhancement in consumers’ sensitivity to the privacy. Against a back drop of some serious leak cases, governments established security regulations for corporations to protect their citizens from security risks. The table below shows the regulations that have been enacted in recent years. Following the Sarbanes-Oxley Act established in the United States, varied countries including Japan, Germany and France have developed the laws regarding security especially for cyber attacks. Such regulations have been inducing the development and prevalence of security technologies. | Undeveloped policy regarding personal information contributed to an enhancement in consumers’ sensitivity to the privacy. Against a back drop of some serious leak cases, governments established security regulations for corporations to protect their citizens from security risks. The table below shows the regulations that have been enacted in recent years. Following the Sarbanes-Oxley Act established in the United States, varied countries including Japan, Germany and France have developed the laws regarding security especially for cyber attacks. Such regulations have been inducing the development and prevalence of security technologies. | ||
[[Picture 3.jpg]] | [[Image:Picture 3.jpg]] | ||
In the United States, there are cyber-security regulations, for both federal and estate governments. For federal government cyber security regulations, they focus mainly on specific industries and fields, healthcare, organizations, financial institutions and agencies that work with systems and information. Unfortunately, this regulation do not reach and cover computer related industries like Internet Service Providers (ISP). | |||
The | The new J-Sox law obliges all listed companies in Japan to strengthen internal controls and to ensure full and accurate disclosure of financial information. The new laws will impact the 3,800 companies listed on Japanese stock exchanges and will also affect the subsidiaries of the listed companies, even if they operate in other parts of the world . | ||
Similar to the American Sarbanes-Oxley Act, the Financial Security Law of France rests mainly on an increased responsibility of leaders, a strengthening of internal control and a reduction in the sources of conflicts of interest. | Similar to the American Sarbanes-Oxley Act, the Financial Security Law of France rests mainly on an increased responsibility of leaders, a strengthening of internal control and a reduction in the sources of conflicts of interest. | ||
==Enablers:== | ==Enablers:== | ||
Leak cases | |||
People’s sensitivity to the personal information | |||
==Inhibitors:== | ==Inhibitors:== | ||
Excess financial damage to corporations due to a cost increase | |||
==Paradigms:== | ==Paradigms:== | ||
Strict security regulations convince corporations that they now have an additional area to invest in order to maintain their corporate activities. Consolidation of the security system used to be a corporate strategy that leads to an enhancement of the brand image, but it has become a commitment without which corporations cannot survive. The regulations also mitigate fear of the consumers who are reluctant to utilize the internet technology, consequently stimulating digital advertisement business. | |||
==Experts:== | ==Experts:== | ||
Security ministries for each country<br> | |||
Examples<br> | |||
*United States Department of Homeland Security | |||
*Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications | |||
==Web Source:== | ==Web Source:== | ||
Latest revision as of 09:57, 18 September 2009
Description:
Undeveloped policy regarding personal information contributed to an enhancement in consumers’ sensitivity to the privacy. Against a back drop of some serious leak cases, governments established security regulations for corporations to protect their citizens from security risks. The table below shows the regulations that have been enacted in recent years. Following the Sarbanes-Oxley Act established in the United States, varied countries including Japan, Germany and France have developed the laws regarding security especially for cyber attacks. Such regulations have been inducing the development and prevalence of security technologies.
In the United States, there are cyber-security regulations, for both federal and estate governments. For federal government cyber security regulations, they focus mainly on specific industries and fields, healthcare, organizations, financial institutions and agencies that work with systems and information. Unfortunately, this regulation do not reach and cover computer related industries like Internet Service Providers (ISP).
The new J-Sox law obliges all listed companies in Japan to strengthen internal controls and to ensure full and accurate disclosure of financial information. The new laws will impact the 3,800 companies listed on Japanese stock exchanges and will also affect the subsidiaries of the listed companies, even if they operate in other parts of the world .
Similar to the American Sarbanes-Oxley Act, the Financial Security Law of France rests mainly on an increased responsibility of leaders, a strengthening of internal control and a reduction in the sources of conflicts of interest.
Enablers:
Leak cases People’s sensitivity to the personal information
Inhibitors:
Excess financial damage to corporations due to a cost increase
Paradigms:
Strict security regulations convince corporations that they now have an additional area to invest in order to maintain their corporate activities. Consolidation of the security system used to be a corporate strategy that leads to an enhancement of the brand image, but it has become a commitment without which corporations cannot survive. The regulations also mitigate fear of the consumers who are reluctant to utilize the internet technology, consequently stimulating digital advertisement business.
Experts:
Security ministries for each country
Examples
- United States Department of Homeland Security
- Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications