Difference between revisions of "Low cost of Technologies and appliances"
Bert.apperlo (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (11 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
''Economical driving force of [[ The Future of Secondary Education in 2020]]'' | ''Economical driving force of [[ The Future of Technology in Secondary Education in 2020]]'' | ||
== | == Description: == | ||
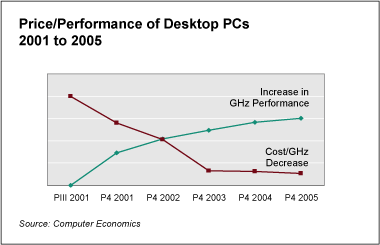
The decline in cost of technologies and appliances is an event that we have all realized the last couple of years; from Desktop Pc’s and Internet to mobile phones and GPS. Almost everyone can afford to have all these kind of technologies. A recent study of cost and performance trends for desktop computers from the major manufacturers indicates that. At the graph below you can see the continuous decline in prices of Desktop PCs, while the performance in GHz increases at the same time. | The decline in cost of technologies and appliances is an event that we have all realized the last couple of years; from Desktop Pc’s and Internet to mobile phones and GPS. Almost everyone can afford to have all these kind of technologies. A recent study of cost and performance trends for desktop computers from the major manufacturers indicates that. At the graph below you can see the continuous decline in prices of Desktop PCs, while the performance in GHz increases at the same time.<br><br> | ||
[[Image:Desktoppcstudy2005chart.gif]] | |||
Internet prices also decrease over the years-especially by using wireless access- and the same happens for several technologies and services. This allows technology to enter new industries and areas that hadn’t been entered before. | Internet prices also decrease over the years-especially by using wireless access- and the same happens for several technologies and services. This allows technology to enter new industries and areas that hadn’t been entered before. | ||
<br><Br> | |||
== | == Enablers: == | ||
<ul> | |||
<li>Economic development of countries</li> | |||
<li>Globalization</li> | |||
<li>Large investments in research</li> | |||
== | <li>More competitors in the technology industry</li> | ||
<li>Continued advancement in sillicon chip technology</li> | |||
</ul> | |||
<br> | |||
== Inhibitors: == | |||
== | <ul> | ||
<li>Economic instability</li> | |||
<li>Increase of Taxes</li> | |||
</ul> | |||
<br> | |||
== Paradigms: == | |||
As the cost of technology decreases over the years, people will start thinking about creating and using massively, inexpensive pieces of technology in several areas . One recent example is the $100 laptop project. The $100 Laptop is a proposed inexpensive laptop computer intended to be distributed to children around the world, especially to those in developing countries, to provide them with access to knowledge and modern forms of education. | As the cost of technology decreases over the years, people will start thinking about creating and using massively, inexpensive pieces of technology in several areas . One recent example is the $100 laptop project. The $100 Laptop is a proposed inexpensive laptop computer intended to be distributed to children around the world, especially to those in developing countries, to provide them with access to knowledge and modern forms of education. | ||
<br><Br> | |||
== Experts: == | |||
Where is Computing Headed? Ted G. Lewis <br> | |||
<br> | |||
== Timing: == | |||
<i>1940 – 1956</i><br> | |||
First generation: Vacuum tubes<br> | |||
<i>1956 – 1963</i><br> | |||
Second generation: Transistors<br> | |||
<i>1964 – 1971</i><br> | |||
Third generation: Integrated circuits <br> | |||
<i>1971 – Present</i><br> | |||
Fourth generation: Microprocessors Present and beyond Fifth generation: Artificial Intelligence <br> | |||
<br> | |||
== | == WEB Resources: == | ||
http://www.computereconomics.com/page.cfm?name=desktop2005<br> | http://www.computereconomics.com/page.cfm?name=desktop2005<br> | ||
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/One_Laptop_per_Child | http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/One_Laptop_per_Child<br> | ||
http://www.tcpd.org/Thornburg/Handouts/2020visions.html<br> | |||
http://csdl2.computer.org/persagen/DLAbsToc.jsp?resourcePath=/dl/mags/co/&toc=comp/mags/co/1994/08/r8toc.xml&DOI=10.1109/2.303615 <br> | |||
http://www.webopedia.com/DidYouKnow/Hardware_Software/2002/FiveGenerations.asp - http://www.jcmit.com/cpu-performance.htm<br> | |||
Latest revision as of 09:20, 27 March 2007
Economical driving force of The Future of Technology in Secondary Education in 2020
Description:
The decline in cost of technologies and appliances is an event that we have all realized the last couple of years; from Desktop Pc’s and Internet to mobile phones and GPS. Almost everyone can afford to have all these kind of technologies. A recent study of cost and performance trends for desktop computers from the major manufacturers indicates that. At the graph below you can see the continuous decline in prices of Desktop PCs, while the performance in GHz increases at the same time.
Internet prices also decrease over the years-especially by using wireless access- and the same happens for several technologies and services. This allows technology to enter new industries and areas that hadn’t been entered before.
Enablers:
- Economic development of countries
- Globalization
- Large investments in research
- More competitors in the technology industry
- Continued advancement in sillicon chip technology
Inhibitors:
- Economic instability
- Increase of Taxes
Paradigms:
As the cost of technology decreases over the years, people will start thinking about creating and using massively, inexpensive pieces of technology in several areas . One recent example is the $100 laptop project. The $100 Laptop is a proposed inexpensive laptop computer intended to be distributed to children around the world, especially to those in developing countries, to provide them with access to knowledge and modern forms of education.
Experts:
Where is Computing Headed? Ted G. Lewis
Timing:
1940 – 1956
First generation: Vacuum tubes
1956 – 1963
Second generation: Transistors
1964 – 1971
Third generation: Integrated circuits
1971 – Present
Fourth generation: Microprocessors Present and beyond Fifth generation: Artificial Intelligence
WEB Resources:
http://www.computereconomics.com/page.cfm?name=desktop2005
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/One_Laptop_per_Child
http://www.tcpd.org/Thornburg/Handouts/2020visions.html
http://csdl2.computer.org/persagen/DLAbsToc.jsp?resourcePath=/dl/mags/co/&toc=comp/mags/co/1994/08/r8toc.xml&DOI=10.1109/2.303615
http://www.webopedia.com/DidYouKnow/Hardware_Software/2002/FiveGenerations.asp - http://www.jcmit.com/cpu-performance.htm