Difference between revisions of "The Waiting Game"
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
==Timeline Developments== | ==Timeline Developments== | ||
2006 – 2008 | ====2006 – 2008==== | ||
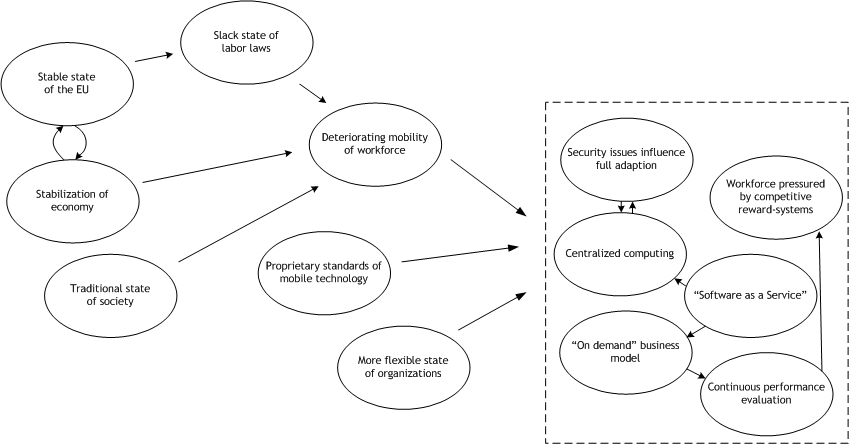
* Software as a service (SaaS) is taunted by most IT vendors as the future platform for doing business. | |||
* Exact, Best and Microsoft release online versions of their accounting software aimed at the small and medium size enterprises. Initial subscriptions in Europe show high interest due to low initial investment costs and increased number of entrepreneurships. | |||
* SaaS wins over major corporations. Companies realize that hosted solutions not only save costs but add value since vendors need to improve and maintain a strong offering throughout the subscription cycle. This is an opposing view of the current stand alone software, where a vendor will only need to renew the relationship when there is a new version of the software to sell. | |||
* Centralized computing is once again becoming the mainstream model as organizations utilize SaaS and embrace thin client computing. | |||
* The European mobile handset is highly saturated. This in turn drives handset manufacturers to constantly introduce new features. The white collar worker on the average owns two handsets. | |||
* Employee productivity is slipping as organizations slowly migrate to the new business model. Faced with increased competition, each provider offers proprietary solutions with customizable Service Level Agreements. | |||
* The European Union fails to arrive at an agreement for a unified workforce. Individual member governments set their own laws governing the employment of * Organizations are stressing importance on capturing the knowledge of their employees. Central storage of information for all divisions of the company, make it possible to visualize trends and forecast for the future with more accuracy. | |||
2008 - 2010 | ====2008 - 2010==== | ||
* Microsoft is hesitant in joining the SaaS bandwagon for enterprise software and continues to develop and market stand alone software solutions. In part because of reduced revenues which it can achieve using this model. | |||
* The proliferation of on demand software increases the demand for higher productivity from the employee. The integration of ERP, CRM, HR and Accounting software in one SaaS suite means that every action of an employee can be calculated into a monetary figure. | |||
* Employee pay rate, bonuses and benefits are calculated based on monthly productivity reports despite strong opposition by the workforce. | |||
* On demand access to organizational software and revised remuneration criteria, drive people to blur the 9 to 5 work day mentality. | |||
* Organizations set hiring requirements to include tangible productivity reports from previous employer. | |||
* Competition drives advances in technology, specifically in the knowledge management area. Organizations wish to retain as much information as possible from their employees since the current employee is only seen as a username. | |||
2010 - 2012 | ====2010 - 2012==== | ||
* A security breach in a data warehouse reigns panic across businesses. In Europe alone, one thousand businesses in various industries were affected by the breach. After two months, twelve companies go bankrupt as customers refuse to deal with them. | |||
* European government sets tougher regulation on IT security and data protection. | |||
* Organizations reevaluate their IT needs and some migrate their business specific applications in house. | |||
* Mobile operators continue to bundle their service offerings. Organizations are able to save significant costs in exchange for longer contracts with mobile operators. | |||
====2012 – 2015==== | |||
* Microsoft sees renewed sales as organizations migrate their IT infrastructure in house. | |||
* Significant gains in productivity over the recent years have stagnated. | |||
· Organizations choose hybrid approach to SaaS. Critical applications are hosted in house. | · Organizations choose hybrid approach to SaaS. Critical applications are hosted in house. | ||
* Knowledge capital value will be a requirement for stock listing in Europe | |||
* Mergers across SaaS software vendors. | |||
===The Waiting Game=== | ===The Waiting Game=== | ||
====2006 – 2008==== | |||
During this time period, Software as a service (SaaS) is taunted by most IT vendors as the future platform for doing business. Companies such as Salesforce.com and NetSuite gain more customers as they show off impressive ROI results from their current subscribers. Exact, Best and Microsoft release online versions of their accounting software aimed at the small and medium size enterprises. Initial subscriptions in Europe show high interest due to low initial investment costs and increased number of entrepreneurships. SaaS wins over major corporations. Companies realize that hosted solutions not only save costs but add value since vendors need to improve and maintain a strong offering throughout the subscription cycle. This is an opposing view of the current stand alone software, where a vendor will only need to renew the relationship when there is a new version of the software to sell. As a result of these developments, centralized computing is once again becoming the mainstream model as organizations utilize SaaS and embrace thin client computing. | |||
The European mobile handset market is highly saturated. This in turn drives handset manufacturers to constantly introduce new features in order to increase the customer base. On the average, the white collar worker owns two handsets. To add to this, mobile phone manufacturers have not been able to agree on standards to support. This ranges from the network protocol to operating software. | |||
Employee productivity is slipping as organizations migrate to the new business model of software as a service. Faced with increased competition, each provider offers proprietary solutions with customizable service level agreements. Contracts for these services are signed for a period of at least one year as software companies want to be sure that their investment is realized. On another front, the European Union fails to arrive at an agreement for a unified workforce. Individual member governments set their own laws governing the employment of cheaper eastern workers. | |||
====2008 – 2010==== | |||
Organizations are stressing importance of capturing the knowledge of their employees. Central storage of information for all divisions of the company, make it possible to visualize trends and forecast for the future with more accuracy. Microsoft is hesitant in joining the SaaS bandwagon for enterprise software and continues to develop and market stand alone software solutions. This is in part because of reduced revenues which it can achieve using this model. | |||
The proliferation of on demand software increases the demand for higher productivity from the employee. The integration of ERP, CRM, HR and Accounting software in one SaaS suite means that almost every action of an employee can be calculated into a monetary figure. Employee pay rate, bonuses and benefits are calculated based on monthly productivity reports despite strong opposition by the workforce. | |||
On demand access to organizational software and revised remuneration criteria, drive people to blur the 9 to 5 work day mentality. Organizations set hiring requirements to include tangible productivity reports from previous employer. During this period the competition continues to drive advances in technology, specifically in the knowledge management area. Organizations wish to retain as much information as possible from their employees. | |||
====2010 - 2012==== | |||
A security breach in a data warehouse reigns panic across businesses. In Europe alone, one thousand businesses in various industries were affected by the breach. After two months, twelve companies go bankrupt as customers refuse to deal with them. This is the result of incredible growth in this sector. Software companies neglected security concerns in order to add functionalities and meet and exceed delivery times to stay competitive. | |||
The European government sets tougher regulation on IT security and data protection. As one requirement, organizations need to reevaluate their IT policies and governance structure and add tangible measures to enforce them. Some organizations migrate their business specific applications in house. The telecom operators continue to bundle their service offerings in order to provide their clients with diverse features. Organizations are able to save significant costs in exchange for longer contracts with operators. This however does not add considerable value as the bundles often consist of seldom used features and increase complexity. | |||
====2012 – 2015==== | |||
Microsoft sees renewed sales as organizations migrate their IT infrastructure in house. The software giant’s Live initiative has evolved with enterprise needs in mind. Organizations are able to choose a hybrid approach to software as a service which increases security and confidence in the system. Significant gains in productivity over the recent years have stagnated. Stock markets around Europe set new requirements for inclusion. Public companies in certain industries will need to include their knowledge capital as an asset. | |||
Due to the lower growth rates, SaaS vendors enter a merger and acquisition period. This time however, it is not based on innovative functionality or synergies between companies. It is purely for market share. As a result only four major software vendors remain. | |||
Latest revision as of 13:09, 15 May 2006
Back to the workplace homepage
Conceptual Overview
Timeline Developments
2006 – 2008
- Software as a service (SaaS) is taunted by most IT vendors as the future platform for doing business.
- Exact, Best and Microsoft release online versions of their accounting software aimed at the small and medium size enterprises. Initial subscriptions in Europe show high interest due to low initial investment costs and increased number of entrepreneurships.
- SaaS wins over major corporations. Companies realize that hosted solutions not only save costs but add value since vendors need to improve and maintain a strong offering throughout the subscription cycle. This is an opposing view of the current stand alone software, where a vendor will only need to renew the relationship when there is a new version of the software to sell.
- Centralized computing is once again becoming the mainstream model as organizations utilize SaaS and embrace thin client computing.
- The European mobile handset is highly saturated. This in turn drives handset manufacturers to constantly introduce new features. The white collar worker on the average owns two handsets.
- Employee productivity is slipping as organizations slowly migrate to the new business model. Faced with increased competition, each provider offers proprietary solutions with customizable Service Level Agreements.
- The European Union fails to arrive at an agreement for a unified workforce. Individual member governments set their own laws governing the employment of * Organizations are stressing importance on capturing the knowledge of their employees. Central storage of information for all divisions of the company, make it possible to visualize trends and forecast for the future with more accuracy.
2008 - 2010
- Microsoft is hesitant in joining the SaaS bandwagon for enterprise software and continues to develop and market stand alone software solutions. In part because of reduced revenues which it can achieve using this model.
- The proliferation of on demand software increases the demand for higher productivity from the employee. The integration of ERP, CRM, HR and Accounting software in one SaaS suite means that every action of an employee can be calculated into a monetary figure.
- Employee pay rate, bonuses and benefits are calculated based on monthly productivity reports despite strong opposition by the workforce.
- On demand access to organizational software and revised remuneration criteria, drive people to blur the 9 to 5 work day mentality.
- Organizations set hiring requirements to include tangible productivity reports from previous employer.
- Competition drives advances in technology, specifically in the knowledge management area. Organizations wish to retain as much information as possible from their employees since the current employee is only seen as a username.
2010 - 2012
- A security breach in a data warehouse reigns panic across businesses. In Europe alone, one thousand businesses in various industries were affected by the breach. After two months, twelve companies go bankrupt as customers refuse to deal with them.
- European government sets tougher regulation on IT security and data protection.
- Organizations reevaluate their IT needs and some migrate their business specific applications in house.
- Mobile operators continue to bundle their service offerings. Organizations are able to save significant costs in exchange for longer contracts with mobile operators.
2012 – 2015
- Microsoft sees renewed sales as organizations migrate their IT infrastructure in house.
- Significant gains in productivity over the recent years have stagnated.
· Organizations choose hybrid approach to SaaS. Critical applications are hosted in house.
- Knowledge capital value will be a requirement for stock listing in Europe
- Mergers across SaaS software vendors.
The Waiting Game
2006 – 2008
During this time period, Software as a service (SaaS) is taunted by most IT vendors as the future platform for doing business. Companies such as Salesforce.com and NetSuite gain more customers as they show off impressive ROI results from their current subscribers. Exact, Best and Microsoft release online versions of their accounting software aimed at the small and medium size enterprises. Initial subscriptions in Europe show high interest due to low initial investment costs and increased number of entrepreneurships. SaaS wins over major corporations. Companies realize that hosted solutions not only save costs but add value since vendors need to improve and maintain a strong offering throughout the subscription cycle. This is an opposing view of the current stand alone software, where a vendor will only need to renew the relationship when there is a new version of the software to sell. As a result of these developments, centralized computing is once again becoming the mainstream model as organizations utilize SaaS and embrace thin client computing.
The European mobile handset market is highly saturated. This in turn drives handset manufacturers to constantly introduce new features in order to increase the customer base. On the average, the white collar worker owns two handsets. To add to this, mobile phone manufacturers have not been able to agree on standards to support. This ranges from the network protocol to operating software.
Employee productivity is slipping as organizations migrate to the new business model of software as a service. Faced with increased competition, each provider offers proprietary solutions with customizable service level agreements. Contracts for these services are signed for a period of at least one year as software companies want to be sure that their investment is realized. On another front, the European Union fails to arrive at an agreement for a unified workforce. Individual member governments set their own laws governing the employment of cheaper eastern workers.
2008 – 2010
Organizations are stressing importance of capturing the knowledge of their employees. Central storage of information for all divisions of the company, make it possible to visualize trends and forecast for the future with more accuracy. Microsoft is hesitant in joining the SaaS bandwagon for enterprise software and continues to develop and market stand alone software solutions. This is in part because of reduced revenues which it can achieve using this model.
The proliferation of on demand software increases the demand for higher productivity from the employee. The integration of ERP, CRM, HR and Accounting software in one SaaS suite means that almost every action of an employee can be calculated into a monetary figure. Employee pay rate, bonuses and benefits are calculated based on monthly productivity reports despite strong opposition by the workforce. On demand access to organizational software and revised remuneration criteria, drive people to blur the 9 to 5 work day mentality. Organizations set hiring requirements to include tangible productivity reports from previous employer. During this period the competition continues to drive advances in technology, specifically in the knowledge management area. Organizations wish to retain as much information as possible from their employees.
2010 - 2012
A security breach in a data warehouse reigns panic across businesses. In Europe alone, one thousand businesses in various industries were affected by the breach. After two months, twelve companies go bankrupt as customers refuse to deal with them. This is the result of incredible growth in this sector. Software companies neglected security concerns in order to add functionalities and meet and exceed delivery times to stay competitive.
The European government sets tougher regulation on IT security and data protection. As one requirement, organizations need to reevaluate their IT policies and governance structure and add tangible measures to enforce them. Some organizations migrate their business specific applications in house. The telecom operators continue to bundle their service offerings in order to provide their clients with diverse features. Organizations are able to save significant costs in exchange for longer contracts with operators. This however does not add considerable value as the bundles often consist of seldom used features and increase complexity.
2012 – 2015
Microsoft sees renewed sales as organizations migrate their IT infrastructure in house. The software giant’s Live initiative has evolved with enterprise needs in mind. Organizations are able to choose a hybrid approach to software as a service which increases security and confidence in the system. Significant gains in productivity over the recent years have stagnated. Stock markets around Europe set new requirements for inclusion. Public companies in certain industries will need to include their knowledge capital as an asset.
Due to the lower growth rates, SaaS vendors enter a merger and acquisition period. This time however, it is not based on innovative functionality or synergies between companies. It is purely for market share. As a result only four major software vendors remain.