Difference between revisions of "Penetration of Broadband"
| (13 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
- Supporting role of government | - Supporting role of government | ||
- High users transfer rate from dial-up to broadband | |||
- "Commoditisation" of broadband access in western countries, considered an utility | - "Commoditisation" of broadband access in western countries, considered an utility | ||
| Line 32: | Line 34: | ||
- Decrease in birth rate (largest users are youngest amongst population), countries with highest birth rate has lowest penetration | - Decrease in birth rate (largest users are youngest amongst population), countries with highest birth rate has lowest penetration | ||
- | - Learning curve limitation within the population | ||
- Accessiblity in rural areas | |||
- Viability of the broadband service providers | |||
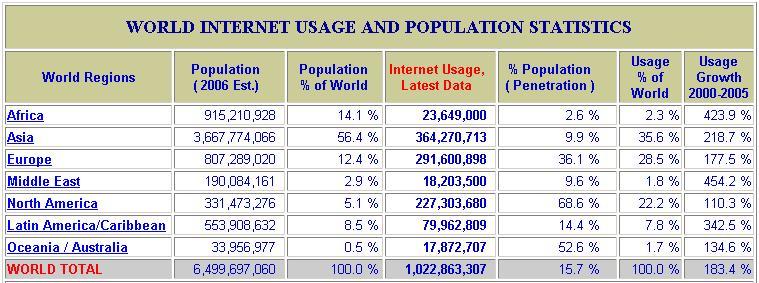
- questionable whether the demand for internet involves 100% penetration of the population or if full demand is at a lower level. currently, intenet penetration is: | |||
[[Image:penetstats.jpg]] | |||
source: http://www.internetworldstats.com/stats.htm | |||
==Paradigms:== | ==Paradigms:== | ||
With commoditization of broadband connections, increasing number of people make the amalgam between internet and broadband. | |||
==Experts:== | ==Experts:== | ||
www.balancingact.com | www.balancingact-africa.com | ||
http://www.oecd.org/document/39/0,2340,en_2649_34223_36459431_1_1_1_1,00.html | http://www.oecd.org/document/39/0,2340,en_2649_34223_36459431_1_1_1_1,00.html | ||
| Line 48: | Line 60: | ||
==Timing:== | ==Timing:== | ||
'''1997-1998:''' high speed home internet struggles to get off the ground with the cable modem. | |||
'''1999:''' introduction of DSL | |||
'''1999:''' Introduction of Napster and P2P application and the rise of Napster status at "most successful application of all times" creates the first public feeling of what can be "bandwith shortages". | |||
'''2001:''' home broadband growth rate becomes higher than dial-up, battlle between cable and DSL continues | |||
'''2003:''' Directways offer broadband over satelitte for rural and remote area | |||
'''2003:''' fiber optic cable used to develop broadband. the first service that offer consitant, high, and reliable performances | |||
'''2003:''' 3G allows ultimate broadband mobility | |||
'''2004:''' PC intergrate wi-fi | |||
'''2005:''' Current Communication, Cincinnati, introcduces broadband over power line | |||
'''2007:''' PC integrated wimax | |||
==Web Resources:== | ==Web Resources:== | ||
http://pcworld.about.com/news/Jun142005id121394.htm | |||
http://compnetworking.about.com/od/basicnetworkingconcepts/l/aa021403a.htm | |||
Latest revision as of 16:08, 21 May 2006
Description:
The current broadband penetration in OECD countries (December 2005) is 13.6% of the population. The growth rate of the penetration was 15% in 2005. The top 4 countries are Iceland, Korea, The Netherlands and Denmark with penetration rates over 25%. In real number, the country with the largest amount of subscriber is the USA. The lowest penetration rate is granted to Greece with 1.4%. The EU 15 averages at 14.2% penetration.
The growth of broadband penetration amongst OECD countries is supported by the different governments and enjoys exponential growth:
2001 2002 2003 2004 2005
OECD 2.9 4.9 7.3 10.2 13.6
EU15 1.6 3.4 5.9 9.7 14.2
Enablers:
- Supporting role of government
- High users transfer rate from dial-up to broadband
- "Commoditisation" of broadband access in western countries, considered an utility
- Disruptive technologies facilitates penetration in developing countries
- Increasing spending power
- Cultural embedding of internet usage ("I will Google that!")
- increased usage for elderly
Inhibitors:
- Security
- Privacy - government control
- Decrease in birth rate (largest users are youngest amongst population), countries with highest birth rate has lowest penetration
- Learning curve limitation within the population
- Accessiblity in rural areas
- Viability of the broadband service providers
- questionable whether the demand for internet involves 100% penetration of the population or if full demand is at a lower level. currently, intenet penetration is:
source: http://www.internetworldstats.com/stats.htm
Paradigms:
With commoditization of broadband connections, increasing number of people make the amalgam between internet and broadband.
Experts:
www.balancingact-africa.com
http://www.oecd.org/document/39/0,2340,en_2649_34223_36459431_1_1_1_1,00.html
http://www.internetworldstats.com/
Timing:
1997-1998: high speed home internet struggles to get off the ground with the cable modem.
1999: introduction of DSL
1999: Introduction of Napster and P2P application and the rise of Napster status at "most successful application of all times" creates the first public feeling of what can be "bandwith shortages".
2001: home broadband growth rate becomes higher than dial-up, battlle between cable and DSL continues
2003: Directways offer broadband over satelitte for rural and remote area
2003: fiber optic cable used to develop broadband. the first service that offer consitant, high, and reliable performances
2003: 3G allows ultimate broadband mobility
2004: PC intergrate wi-fi
2005: Current Communication, Cincinnati, introcduces broadband over power line
2007: PC integrated wimax
Web Resources:
http://pcworld.about.com/news/Jun142005id121394.htm
http://compnetworking.about.com/od/basicnetworkingconcepts/l/aa021403a.htm