Difference between revisions of "The Future of E-learning in Korea 2020"
| (131 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
* Kang, Su Ik | * Kang, Su Ik | ||
* Heo, Yeub | * Heo, Yeub | ||
* Lee, Young Jae | * Lee, Young Jae | ||
== '''Introduction''' == | == '''Introduction''' == | ||
E-learning is now becoming a widely accepted method of training and education within schools, colleges and organisations. | |||
Of firms using e-learning already, 93% intend to increase its scope over the next year. Such surveys suggest the outlook is good, however there are crucial lessons to be learned from many of the early adopters which suggest that good e-learning is much more than just putting a program on a server. | |||
E-learning is here to stay, there’s no doubt about that. It will increasingly become a staple item in the training portfolio, however like all training media, we must learn how and when to use it to its best advantage. | |||
Wireless technology is beginning to appear in many more devices and this marks the start of a physically independent way of staying connected.The ability to access and participate in learning without the need for a physical connection will bring immeasurable benefits, with learners truly being able to learn at anyplace, anywhere. | |||
There is also the development of various peer-to-peer [p2p] approaches, aimed at providing a Napster-style solution for the training and development community. Whilst the technological issues are well understood, the practicality of sharing learning materials is still some way off. Issues such as copyright, quality, appropriateness and business sensitivity all need addressing before we can assemble courses from easily available online content. | |||
The type of training supported via e-learning is also changing. | |||
E-learning is here to stay, although it must be used correctly in order to ensure success. Emerging technologies such as wireless and 3G will certainly enhance the penetration and flexibility of the medium, and the quality of content must be of superior quality. | |||
It’s an exciting industry so that we draw the future of e-learning through scnario-thinking. | |||
== '''Research Questions''' == | == '''Research Questions''' == | ||
| Line 18: | Line 25: | ||
'''I. Technical Questions ''' | '''I. Technical Questions ''' | ||
1 What are the components of e-learning? | |||
'''Contents :''' Learning contents and materials(text, video, image, animation, etc.)<br> | |||
'''Delivery System :''' System infrastructure and solutions to deliver contents to learners<br> | |||
'''Management System :''' Support and manage activities of learners, instructors, administrators | |||
2 What will be the new technology for e-learning? | |||
[[Many different technologies support learning]] | |||
[[Image:emerging_tech.jpg]]<br> | |||
(source: SRI, 2004) | |||
[[Top 10 Technologies for E-Learning Infrastructure During the Next Three Years]] | |||
3. Who are the standard orginization of E-Learning? | |||
'''IEEE LTSC''' (Learning Technology Standards Committee) | |||
'''ISO/IEC JTC1/SC36''' (International Standards Organization: Information Technology Standards: Information Technology for Learning, Education and Training) | |||
'''CEN/ISSS/LTWS''' (European Committee for Standardization [Comite Europeen de Normalisation]: Information Society Standardization System: Learning Technology Workshop) | |||
'''II. Industrial Questions''' | '''II. Industrial Questions''' | ||
1 What are the contents of e-learning in industry? | 1 What are the contents of e-learning in industry? | ||
The intellectual property and knowledge to be imparted. It consists of the course outline, text based knowledge modules for | |||
learning, and multi-media. Content is the most important investment and asset of e-learning. Different types of e-learning content | |||
include text, audio, video, animation and simulation. | |||
The eLearning industry is comprised of three vendor segments: technology, content and services. | |||
'''Technology:''' This segment includes LMS, learning content management system (LCMS), authoring tools, training delivery systems, | |||
enterprise resource planning (ERP), application service provider (ASP), live eLearning tools, streaming video, EPSS, testing and | |||
assessment tools. | |||
'''Content:''' This segment includes third-party content providers, books and magazine publishers, enterprises, subject matter experts | |||
(SME), government agencies, colleges, universities, schools, training organizations, learning portals, IT firms, and system | |||
integrators. | |||
'''Services:''' This segment includes EIP, corporate universities, learning service providers (LSP), content aggregators, learning | |||
consultants, consulting, professional services, certification service providers, collaboration services, and online mentoring | |||
services. | |||
2 What is the role of the instructor in future e-learning? | |||
The term instructor-led training is used synonymously with on-site training and classroom training. | |||
One-to-one training in on-line will be possible in future. | |||
3 Which e-learning system will be developed for each community? | |||
Community learning is an educational approach to teaching and learning that involves groups of | |||
students working together to solve a problem, complete a task, or create a product. | |||
[[4 How can we improve the quality of e-learning?]] | |||
5 What kinds of e-learning are supposed to be in the future? | |||
For a client in the automotive sector Learning on Demand created a series of learning technology roadmaps covering: | |||
[[learning objects]] | |||
simulation and games | |||
collaboration | |||
[[mobile learning]] | |||
application integration technologies | |||
[[6 How many substitutions are there in the e-learning?]] | |||
[[7 What is the most promising field in the lifetime learning?]] | |||
[[8 What about the prospect of e-learning compared to offline learning?]] | |||
'''III. Consumer Questions''' | '''III. Consumer Questions''' | ||
1 | [[1 Global market of e-learning?]] | ||
[[2 E-Learning legislation in Korea?]] | |||
[[3 How many foreigners come to Korea for learning?]] | |||
[[4 What's the average of the expenditure for learning in Korea?]] | |||
[[5 What do people want from e-learning?]] | |||
[[6 Which technologies are used for e-learning?]] | |||
[[7 Who is the principle subject?]] | |||
== '''Driving forces''' == | |||
[[1 Users' learning patterns]] | |||
[[2 Integration of knowledge management system and e-learning system]] | |||
[[3 Developing learning community]] | |||
[[4 Developing standard of e-learning]] | |||
5 Korean population | |||
About 56,000,000 people and 14% out of the popoulation will be loder than 65 yrs in 2020. | About 56,000,000 people and 14% out of the popoulation will be loder than 65 yrs in 2020. | ||
6 | 6 [[Reduction of e-learning infrastructure cost]] | ||
[[7 Development of online technology]] | |||
[[8 Digital Convergence]] | |||
9 [[The change of e-learning system to inhome system]] | |||
10 [[Increase of digital literacy]] | |||
11 [[Increasing mobility]] | |||
== '''Systems Diagram''' == | |||
[[Systems Thinking Workshop]]<br> | |||
[[Systems Diagram For E-Learning Content Providers]] | |||
== '''4 Scenarios in e-learning industry''' == | |||
[[Image:el_scenarios.jpg]] | |||
1) Scenario 1 - '''BMBP''' | |||
Big Market with Big Players | |||
2) Scenario 2 - '''BMSP''' | |||
Big Market with Small Players | |||
[[Scenario-1 and 2]] | |||
3) Scenario 3 - '''BM a few BP''' | |||
Big Market with a few Big Players | |||
[[Scenario-3]] | |||
4) Scenario 4 - '''SMSP''' | |||
Small Market with Small Players | |||
[[Scenario-4]] | |||
Latest revision as of 17:47, 29 July 2006
Group Composition
Our members are as below..
- Kang, Su Ik
- Heo, Yeub
- Lee, Young Jae
Introduction
E-learning is now becoming a widely accepted method of training and education within schools, colleges and organisations. Of firms using e-learning already, 93% intend to increase its scope over the next year. Such surveys suggest the outlook is good, however there are crucial lessons to be learned from many of the early adopters which suggest that good e-learning is much more than just putting a program on a server.
E-learning is here to stay, there’s no doubt about that. It will increasingly become a staple item in the training portfolio, however like all training media, we must learn how and when to use it to its best advantage. Wireless technology is beginning to appear in many more devices and this marks the start of a physically independent way of staying connected.The ability to access and participate in learning without the need for a physical connection will bring immeasurable benefits, with learners truly being able to learn at anyplace, anywhere. There is also the development of various peer-to-peer [p2p] approaches, aimed at providing a Napster-style solution for the training and development community. Whilst the technological issues are well understood, the practicality of sharing learning materials is still some way off. Issues such as copyright, quality, appropriateness and business sensitivity all need addressing before we can assemble courses from easily available online content.
The type of training supported via e-learning is also changing. E-learning is here to stay, although it must be used correctly in order to ensure success. Emerging technologies such as wireless and 3G will certainly enhance the penetration and flexibility of the medium, and the quality of content must be of superior quality. It’s an exciting industry so that we draw the future of e-learning through scnario-thinking.
Research Questions
I. Technical Questions
1 What are the components of e-learning?
Contents : Learning contents and materials(text, video, image, animation, etc.)
Delivery System : System infrastructure and solutions to deliver contents to learners
Management System : Support and manage activities of learners, instructors, administrators
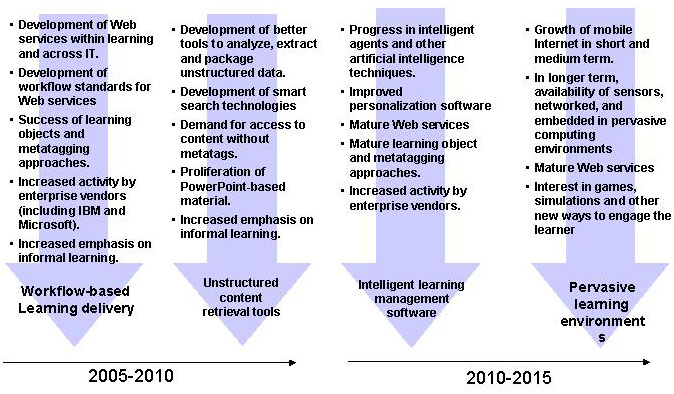
2 What will be the new technology for e-learning?
Many different technologies support learning
Top 10 Technologies for E-Learning Infrastructure During the Next Three Years
3. Who are the standard orginization of E-Learning?
IEEE LTSC (Learning Technology Standards Committee)
ISO/IEC JTC1/SC36 (International Standards Organization: Information Technology Standards: Information Technology for Learning, Education and Training)
CEN/ISSS/LTWS (European Committee for Standardization [Comite Europeen de Normalisation]: Information Society Standardization System: Learning Technology Workshop)
II. Industrial Questions
1 What are the contents of e-learning in industry?
The intellectual property and knowledge to be imparted. It consists of the course outline, text based knowledge modules for learning, and multi-media. Content is the most important investment and asset of e-learning. Different types of e-learning content include text, audio, video, animation and simulation. The eLearning industry is comprised of three vendor segments: technology, content and services. Technology: This segment includes LMS, learning content management system (LCMS), authoring tools, training delivery systems, enterprise resource planning (ERP), application service provider (ASP), live eLearning tools, streaming video, EPSS, testing and assessment tools. Content: This segment includes third-party content providers, books and magazine publishers, enterprises, subject matter experts (SME), government agencies, colleges, universities, schools, training organizations, learning portals, IT firms, and system integrators. Services: This segment includes EIP, corporate universities, learning service providers (LSP), content aggregators, learning consultants, consulting, professional services, certification service providers, collaboration services, and online mentoring services.
2 What is the role of the instructor in future e-learning?
The term instructor-led training is used synonymously with on-site training and classroom training. One-to-one training in on-line will be possible in future.
3 Which e-learning system will be developed for each community?
Community learning is an educational approach to teaching and learning that involves groups of students working together to solve a problem, complete a task, or create a product.
4 How can we improve the quality of e-learning?
5 What kinds of e-learning are supposed to be in the future?
For a client in the automotive sector Learning on Demand created a series of learning technology roadmaps covering: learning objects simulation and games collaboration mobile learning application integration technologies
6 How many substitutions are there in the e-learning?
7 What is the most promising field in the lifetime learning?
8 What about the prospect of e-learning compared to offline learning?
III. Consumer Questions
1 Global market of e-learning?
2 E-Learning legislation in Korea?
3 How many foreigners come to Korea for learning?
4 What's the average of the expenditure for learning in Korea?
5 What do people want from e-learning?
6 Which technologies are used for e-learning?
7 Who is the principle subject?
Driving forces
2 Integration of knowledge management system and e-learning system
3 Developing learning community
4 Developing standard of e-learning
5 Korean population
About 56,000,000 people and 14% out of the popoulation will be loder than 65 yrs in 2020.
6 Reduction of e-learning infrastructure cost
7 Development of online technology
9 The change of e-learning system to inhome system
10 Increase of digital literacy
Systems Diagram
Systems Thinking Workshop
Systems Diagram For E-Learning Content Providers
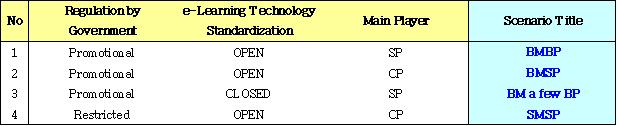
4 Scenarios in e-learning industry
1) Scenario 1 - BMBP
Big Market with Big Players
2) Scenario 2 - BMSP
Big Market with Small Players
3) Scenario 3 - BM a few BP
Big Market with a few Big Players
4) Scenario 4 - SMSP
Small Market with Small Players