Difference between revisions of "Zhikai Xu"
| (6 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
<p> | <p> | ||
The potential threats for FetchBook are "the big boys" in | The potential threats for <em>FetchBook</em> are "the big boys" in current online market, for example, Google. If specialized service is provided by such "big boys", the market will probably occupied by them because their existing popularity and technical & capical power. | ||
</p> | |||
==Learning Log== | |||
This short paper consists of two parts: personal learning log and academic thinking | |||
of scenario planning. The personal learning log can be put into three categories: | |||
a way of thinking, a way of persuading and a way of working. Within the “thinking” | |||
part, I combined my personal learning of scenario thinking with my previous professional | |||
working experience in IBM. | |||
<p><strong>Personal learning log</strong></p> | |||
<p><em>A way of thinking</em><br> | |||
Scenario thinking provides me a new way of thinking, which implies that uncertain | |||
future can be sought for by examining all possible influencing factors in current | |||
situation. The future solution to current problem need to balance both the demand | |||
and supply sides. All these learning reminds me the previous work project in | |||
IBM, in which scenario thinking can be applied to solve the supply chain issues. | |||
</p> | |||
<ul> | |||
<li>Uncertain future lays in certain current situation<br> | |||
Nothing comes from green ground. The future scenario is always based on the | |||
current situations. Holding an attitude of seeing the future from examining | |||
the current reality is important to explore and plan the future. Get rid of | |||
the thought that nobody knows the future matters a lot in scenario thinking.</li> | |||
<li>Digging out related factors<br> | |||
As soon as noticing the importance of looking at nowadays situation, I immediately | |||
find that it is not so easy to know the current situation. Because of the | |||
uncertainties and complexity of different factors in reality, the future scenario | |||
will probably be affected by something hidden from people’s eyes when we try | |||
to know what is happening now. Such hidden factors may grow so fast and strongly | |||
to largely influence the future that any details should be covered as much | |||
as possible when considering the driving forces.</li> | |||
<li>Balancing demand and supply<br> | |||
Every identity has its supply and demand sides. When intending to solve a | |||
problem, only considering taking action on supply or demand will not work, | |||
on the opposite, it will impose too much pressure on one side that the situation | |||
will probably go worse. Therefore, one key point to make potential solution | |||
to a problem is alleviating key driving factors both from the demand and supply | |||
sides of the problem.</li> | |||
<li>Looking back to the work in IBM<br> | |||
The process of doing our scenario planning project reminds me my work in IBM | |||
of improving IBM Supply Chain system in Great China Area. I researched to | |||
make working process reengineering and incorporate the human tasks more closely | |||
with information system. Even though the purpose of the project was to improve | |||
inner work efficiency, the outer environment would also influence the implementation | |||
of the new working process. At the time, I, with my colleagues, paid quite | |||
a lot of attention on pitfalls of previous working process and inner stakeholders | |||
but sometimes ignored the roles of other outsiders. Even the proposal is now | |||
working well in IBM, I am sure the all sided consideration would have benefited | |||
more to the organization.</li> | |||
</ul> | |||
<p><em>A way of persuading</em></p> | |||
<ul> | |||
<li> Inspiring story telling<br> | |||
Denial’s story telling skills impressed me a lot in the lectures of scenario | |||
planning. Obviously, the presenting type heavily depends on personal expression | |||
styles, which are hard to apply on everybody. However, story telling gives | |||
me a new sight of how to vividly show logic and science without explicitly | |||
presenting data and facts. It is indeed a charming way of persuading.</li> | |||
<li> Convincing Fact & logic<br> | |||
Underling all methods of persuading, it is fact & logic. Don’t be confused, | |||
I am not telling that story telling is exception. On the opposite, story telling | |||
also bears logic of story in the whole process of telling stories. My point | |||
of convincing fact & logic is more about formalizing a scenario. When | |||
complex group of factors crowded to contribute to a future scenario, how to | |||
incorporate all facts in a logical way that leads to the scenario accounts | |||
for a convincing effect. I felt confused when some groups gave their presentation | |||
of scenarios even they collected many data and facts, because it was hard | |||
to figure out logic.</li> | |||
</ul> | |||
<p><em>A way of working</em></p> | |||
<ul> | |||
<li> Teamwork<br> | |||
I am lucky to work in a united team. The experience of scenario project was | |||
not only a learning process, but more of making friends. Persistence to perfect | |||
and support was felt so commonly in my team. Besides the time in class and | |||
individual research, my team initiatively gathered together and totally spent | |||
around 32 hours to the team work of scenario thinking. To explore more truth | |||
and increase the coverage of driving forces’ influences in scenario planning, | |||
we picked the seemly most sophisticated method of matching different driving | |||
forces’ effects into a series of situations to formalize a scenario. I indeed | |||
enjoyed the hard working experience with my team members.</li> | |||
<li>Arguing<br> | |||
Argument can be way to reach to truth. Through debating, the correctness of | |||
a view point can be personally checked and rechecked by your opponent. Argument | |||
in a team helps explore the truth underlining the complex situation. It also | |||
nurtures the ability of reasoning and persuading.</li> | |||
</ul> | |||
<p><strong>Academic thinking: scenario planning in strategy thinking</strong><br> | |||
Unlike other methods in strategic thinking, scenario planning is famous for | |||
its ability to capture a whole range of possibilities and uncertainties to construct | |||
a series of scenarios, which escaped managers from biases in case of strategy | |||
thinking. From the futurists’ point of view, scenario planning is “An imagined | |||
sequence of events, esp. any of several detailed plans or possibilities.”(Webster’s | |||
Ninth New Collegiate Dictionary)</p> | |||
<p>In the past, scenario planning has been used in energy industry, military application | |||
, policy constitution, and gradually developed into the business world for strategy | |||
thinking. The best known creator of scenarios in the business community is Royal | |||
Dutch Shell, which for many years had developed new scenarios internally annually | |||
. Scenario planning is increasingly practiced to enable firms to cope with changing | |||
competitive environments. The effects of scenario planning on company performance | |||
were researched in contrasting industries in the UK: the water industry and | |||
the information technology (IT) consultancy industry, and improved financial | |||
performance were resulted from scenario planning in both industries .</p> | |||
<p>The popularity of scenario planning in business is largely because of the complexity | |||
in business situation, especially with the trend of globalization, in which | |||
many corporations are faced with multi stakeholders and sophisticated environment | |||
that they are unfamiliar with. Of course, it also lies on the way scenario works. | |||
</p> | |||
<p>In Paul J. H. Scheomaker’s paper of “Scenario Planning: A tool for Strategic | |||
Thinking”, the process of developing scenarios is divided into ten steps :<br> | |||
1. Define the scope<br> | |||
2. Identify the main stakeholders<br> | |||
3. Identify basic trends<br> | |||
4. Identify key uncertainties<br> | |||
5. Construct Initial Scenario Themes<br> | |||
6. Check for Consistency and Plausibility<br> | |||
7. Develop learning scenarios<br> | |||
8. Identify research needs<br> | |||
9. Develop quantitative models<br> | |||
10. Evolve toward decision scenarios. </p> | |||
<p>Through the working process of scenario planning, the most characteristics | |||
of scenario planning in strategy thinking can be abstracted and summarized into | |||
the following points:</p> | |||
<ul> | |||
<li> A wide coverage of factors<br> | |||
Besides considering qualitative factors in analyzing current situation, scenario | |||
planning include a wide range of factors as social changes, technological | |||
trends, business opportunities, shifts in values, political regulations or | |||
inventions into consideration. </li> | |||
<li> Flexibility<br> | |||
Any particular scenario is unlikely nor for sure. However, good analysts anticipate | |||
hidden weaknesses and inflexibilities in organizations and methods. By figuring | |||
out weaknesses in advance, most of the problems can be repaired or reduced | |||
more easily and more correctly than if a similar real-life problem should | |||
present as an emergency. Therefore, the flexible plans to cope with similar | |||
problems can have real future value .</li> | |||
<li>Planning<br> | |||
Scenario planning embodies the process of planning for future, which is a | |||
route how current situation will develop into the target scenario. The thinking | |||
of design this route leads more insight into the balancing of the variable | |||
influencing factors in process. </li> | |||
</ul> | |||
<p>Comparing scenario planning with other planning methods, we can find that scenario | |||
planning explores the mutual impact among multi uncertainties, while contingency | |||
planning and sensitivity analysis mainly focus on the change of one factor. | |||
Because the third and fourth steps of scenario planning (Identify basic trends | |||
and Identify key uncertainties) always incorporate subjective understandings | |||
and other factors that are hard to be modeled, scenario planning also extend | |||
the scope of computer simulations, and compensate it by all sided interpretation | |||
of a certain case .</p> | |||
<p>Now the application of scenario planning is leading into two directions: <br> | |||
1. strategy design<br> | |||
This is to design policy and the main usage of scenario planning. Most of the | |||
above discussion is concerned with designing a strategy or policy.<br> | |||
2. decision analysis <br> | |||
This is based on established strategy or policy to check the possible consequences | |||
of implementing the strategy or policy. Negative results may cause changes to | |||
the strategy, or contingency plans backing up into the previous strategy or | |||
policy.</p> | |||
<p>To sum up, as a strategic planning, scenario planning can be broadly used in | |||
various organizations use to make flexible long-term plans.</p> | |||
<p><br> | |||
<strong>Reference </strong></p> | |||
<p> 1.Joseph F. Coates, “From my perspective Scenario Planning” <br> | |||
2.P.J.H. Schoemaker and C.A.J.M. van de Heijden, “Integrating Scenarios into | |||
Strategic Planning at Royal Dutch/Shell,” Planning Review 20(1992):41-46<br> | |||
3.R. Phelps, C. Chan and S. C. Kapsalis, “Does scenario planning affect performance? | |||
Two exploratory studies” Journal of Business Research Volume 51, Issue 3 , March | |||
2001, Pages 223-232<br> | |||
4.P.J.H. Schoemaker, “Scenario Planning: A Tool for Strategic Thinking” Sloan | |||
Management Review; Winter 1995; 36, 2.<br> | |||
5.www.answer.com/scenarioplanning <br> | |||
6.P.J.H. Schoemaker, “Scenario Planning: A Tool for Strategic Thinking” Sloan | |||
Management Review; Winter 1995; 36, 2.<br> | |||
</p> | </p> | ||
| Line 34: | Line 206: | ||
===Industry Profit analysis=== | ===Industry Profit analysis=== | ||
<p> | <p>My research questions are about revenue analysis in TV industry, like some | ||
examples below:<br> | |||
-Advertisement <br> | |||
How does it work in normal TV? How will it work in Internet TV?<br> | |||
-Is possible to explore other profit sources?<br> | |||
-What else for future revenue?<br> | |||
-Interactive advertising</p> | |||
<p><br> | |||
I would like to first give a little insight of the recent years profit situation | |||
of TV industry through some data of Australia, EU and US market, and then analyze | |||
the advertisement and interactive trend in TV industry, finally concluded with | |||
thinking of profit in Internet TV.</p> | |||
<p><br> | |||
Generally, the television network market consists of advertiser spending on | |||
broadcast and cable networks plus other sources of revenue that vary by region. | |||
In North America, the television network market comprises license fees paid | |||
by cable systems and satellite providers to basic and premium cable networks. | |||
In Europe, Middle East, Africa (EMEA), and Asia/ Pacific, it includes public | |||
TV license fees. Net advertising figures—made up of spending minus agency commissions | |||
and discounts—are tracked in EMEA, Asia/Pacific, Latin America, and Canada. | |||
Advertising in the United States is customarily reported with agency commissions | |||
included. Let’s look at the situations in Australia, EU and US.<br></p> | |||
<p> | <p>Now we begin with Australia.</p> | ||
====Australia==== | ====Australia==== | ||
| Line 168: | Line 361: | ||
<p>Audience own full freedom and flexibility to choose and collect the information and programs they want through whatever medias available.</p> | <p>Audience own full freedom and flexibility to choose and collect the information and programs they want through whatever medias available.</p> | ||
====Experts==== | ====Experts==== | ||
No typical experts found | |||
====Timing==== | ====Timing==== | ||
<p>Audience habits are rapidely changing now. As long as property issues, technology and resource channels are avaible, audience will quickly adapt to the Internet TV.</p> | <p>Audience habits are rapidely changing now. As long as property issues, technology and resource channels are avaible, audience will quickly adapt to the Internet TV.</p> | ||
| Line 219: | Line 413: | ||
<p>It could be the best for the customers to have a large amount of available choices to get information and entertainment,meanwhile to be less limited by the time and location.</p> | <p>It could be the best for the customers to have a large amount of available choices to get information and entertainment,meanwhile to be less limited by the time and location.</p> | ||
====Experts==== | ====Experts==== | ||
<p> | <p>No typical experts found.</p> | ||
====Timing==== | ====Timing==== | ||
<p>The timeing of mixed up technology to replace TV heavily depend on whether the mixed innovation can be technically feasible, commertially profitable and fully acceptable in market.</p> | <p>The timeing of mixed up technology to replace TV heavily depend on whether the mixed innovation can be technically feasible, commertially profitable and fully acceptable in market.</p> | ||
====Web Resources==== | ====Web Resources==== | ||
<p>Please refer to my WIKI of profit research question in Internet TV. </p> | <p>Please refer to my WIKI of profit research question in Internet TV. </p> | ||
Latest revision as of 09:05, 17 May 2006
Object of the Future
FetchBook New & Used Books: Find the Lowest Price
http://www.fetchbook.info
I have found the website, FetchBook, which I thought most book buyers would benefit from.
When looking to buy a book on the web, this free service scans 126 bookstores and 60,000 sellers in just a few seconds, and finds the book stores with the lowest prices, usually at a discount of 30% - 80% off the list price.
FetchBook provides searching services for first, second hands books though most online book stores with high credit. It also enables third parties (individuals and vendors) to sell books on an online marketplace. Some book stores offer “Library” through FetchBook to the customers, which allow you to loan books instead of buying them. Customers can also get club memberships of some book stores through FetchBook, in which way more benefits including discounts and access to members’ only sections or activities are provided.
Like a broker and underwriter in financial market, FetchBook works on a higher level than the current online book stores and individual vendors. It provides the customers with an easy approach to book searching and purchasing on line. Book stores can also reach their potential customers more by FetchBook.
If FetchBook develops quite well in the future, I expect it to become
a rating and evaluating role in book sales besides just searching service provider.
What’s more, for other nondistinctive products, such as air plane tickets and
hotel booking, there is also possibility to establish one extra level above
individual online sales websites.
The potential threats for FetchBook are "the big boys" in current online market, for example, Google. If specialized service is provided by such "big boys", the market will probably occupied by them because their existing popularity and technical & capical power.
Learning Log
This short paper consists of two parts: personal learning log and academic thinking of scenario planning. The personal learning log can be put into three categories: a way of thinking, a way of persuading and a way of working. Within the “thinking” part, I combined my personal learning of scenario thinking with my previous professional working experience in IBM.
Personal learning log
A way of thinking
Scenario thinking provides me a new way of thinking, which implies that uncertain
future can be sought for by examining all possible influencing factors in current
situation. The future solution to current problem need to balance both the demand
and supply sides. All these learning reminds me the previous work project in
IBM, in which scenario thinking can be applied to solve the supply chain issues.
- Uncertain future lays in certain current situation
Nothing comes from green ground. The future scenario is always based on the current situations. Holding an attitude of seeing the future from examining the current reality is important to explore and plan the future. Get rid of the thought that nobody knows the future matters a lot in scenario thinking. - Digging out related factors
As soon as noticing the importance of looking at nowadays situation, I immediately find that it is not so easy to know the current situation. Because of the uncertainties and complexity of different factors in reality, the future scenario will probably be affected by something hidden from people’s eyes when we try to know what is happening now. Such hidden factors may grow so fast and strongly to largely influence the future that any details should be covered as much as possible when considering the driving forces. - Balancing demand and supply
Every identity has its supply and demand sides. When intending to solve a problem, only considering taking action on supply or demand will not work, on the opposite, it will impose too much pressure on one side that the situation will probably go worse. Therefore, one key point to make potential solution to a problem is alleviating key driving factors both from the demand and supply sides of the problem. - Looking back to the work in IBM
The process of doing our scenario planning project reminds me my work in IBM of improving IBM Supply Chain system in Great China Area. I researched to make working process reengineering and incorporate the human tasks more closely with information system. Even though the purpose of the project was to improve inner work efficiency, the outer environment would also influence the implementation of the new working process. At the time, I, with my colleagues, paid quite a lot of attention on pitfalls of previous working process and inner stakeholders but sometimes ignored the roles of other outsiders. Even the proposal is now working well in IBM, I am sure the all sided consideration would have benefited more to the organization.
A way of persuading
- Inspiring story telling
Denial’s story telling skills impressed me a lot in the lectures of scenario planning. Obviously, the presenting type heavily depends on personal expression styles, which are hard to apply on everybody. However, story telling gives me a new sight of how to vividly show logic and science without explicitly presenting data and facts. It is indeed a charming way of persuading. - Convincing Fact & logic
Underling all methods of persuading, it is fact & logic. Don’t be confused, I am not telling that story telling is exception. On the opposite, story telling also bears logic of story in the whole process of telling stories. My point of convincing fact & logic is more about formalizing a scenario. When complex group of factors crowded to contribute to a future scenario, how to incorporate all facts in a logical way that leads to the scenario accounts for a convincing effect. I felt confused when some groups gave their presentation of scenarios even they collected many data and facts, because it was hard to figure out logic.
A way of working
- Teamwork
I am lucky to work in a united team. The experience of scenario project was not only a learning process, but more of making friends. Persistence to perfect and support was felt so commonly in my team. Besides the time in class and individual research, my team initiatively gathered together and totally spent around 32 hours to the team work of scenario thinking. To explore more truth and increase the coverage of driving forces’ influences in scenario planning, we picked the seemly most sophisticated method of matching different driving forces’ effects into a series of situations to formalize a scenario. I indeed enjoyed the hard working experience with my team members. - Arguing
Argument can be way to reach to truth. Through debating, the correctness of a view point can be personally checked and rechecked by your opponent. Argument in a team helps explore the truth underlining the complex situation. It also nurtures the ability of reasoning and persuading.
Academic thinking: scenario planning in strategy thinking
Unlike other methods in strategic thinking, scenario planning is famous for
its ability to capture a whole range of possibilities and uncertainties to construct
a series of scenarios, which escaped managers from biases in case of strategy
thinking. From the futurists’ point of view, scenario planning is “An imagined
sequence of events, esp. any of several detailed plans or possibilities.”(Webster’s
Ninth New Collegiate Dictionary)
In the past, scenario planning has been used in energy industry, military application , policy constitution, and gradually developed into the business world for strategy thinking. The best known creator of scenarios in the business community is Royal Dutch Shell, which for many years had developed new scenarios internally annually . Scenario planning is increasingly practiced to enable firms to cope with changing competitive environments. The effects of scenario planning on company performance were researched in contrasting industries in the UK: the water industry and the information technology (IT) consultancy industry, and improved financial performance were resulted from scenario planning in both industries .
The popularity of scenario planning in business is largely because of the complexity in business situation, especially with the trend of globalization, in which many corporations are faced with multi stakeholders and sophisticated environment that they are unfamiliar with. Of course, it also lies on the way scenario works.
In Paul J. H. Scheomaker’s paper of “Scenario Planning: A tool for Strategic
Thinking”, the process of developing scenarios is divided into ten steps :
1. Define the scope
2. Identify the main stakeholders
3. Identify basic trends
4. Identify key uncertainties
5. Construct Initial Scenario Themes
6. Check for Consistency and Plausibility
7. Develop learning scenarios
8. Identify research needs
9. Develop quantitative models
10. Evolve toward decision scenarios.
Through the working process of scenario planning, the most characteristics of scenario planning in strategy thinking can be abstracted and summarized into the following points:
- A wide coverage of factors
Besides considering qualitative factors in analyzing current situation, scenario planning include a wide range of factors as social changes, technological trends, business opportunities, shifts in values, political regulations or inventions into consideration. - Flexibility
Any particular scenario is unlikely nor for sure. However, good analysts anticipate hidden weaknesses and inflexibilities in organizations and methods. By figuring out weaknesses in advance, most of the problems can be repaired or reduced more easily and more correctly than if a similar real-life problem should present as an emergency. Therefore, the flexible plans to cope with similar problems can have real future value . - Planning
Scenario planning embodies the process of planning for future, which is a route how current situation will develop into the target scenario. The thinking of design this route leads more insight into the balancing of the variable influencing factors in process.
Comparing scenario planning with other planning methods, we can find that scenario planning explores the mutual impact among multi uncertainties, while contingency planning and sensitivity analysis mainly focus on the change of one factor. Because the third and fourth steps of scenario planning (Identify basic trends and Identify key uncertainties) always incorporate subjective understandings and other factors that are hard to be modeled, scenario planning also extend the scope of computer simulations, and compensate it by all sided interpretation of a certain case .
Now the application of scenario planning is leading into two directions:
1. strategy design
This is to design policy and the main usage of scenario planning. Most of the
above discussion is concerned with designing a strategy or policy.
2. decision analysis
This is based on established strategy or policy to check the possible consequences
of implementing the strategy or policy. Negative results may cause changes to
the strategy, or contingency plans backing up into the previous strategy or
policy.
To sum up, as a strategic planning, scenario planning can be broadly used in various organizations use to make flexible long-term plans.
Reference
1.Joseph F. Coates, “From my perspective Scenario Planning”
2.P.J.H. Schoemaker and C.A.J.M. van de Heijden, “Integrating Scenarios into
Strategic Planning at Royal Dutch/Shell,” Planning Review 20(1992):41-46
3.R. Phelps, C. Chan and S. C. Kapsalis, “Does scenario planning affect performance?
Two exploratory studies” Journal of Business Research Volume 51, Issue 3 , March
2001, Pages 223-232
4.P.J.H. Schoemaker, “Scenario Planning: A Tool for Strategic Thinking” Sloan
Management Review; Winter 1995; 36, 2.
5.www.answer.com/scenarioplanning
6.P.J.H. Schoemaker, “Scenario Planning: A Tool for Strategic Thinking” Sloan
Management Review; Winter 1995; 36, 2.
Research questions
Industry Profit analysis
My research questions are about revenue analysis in TV industry, like some
examples below:
-Advertisement
How does it work in normal TV? How will it work in Internet TV?
-Is possible to explore other profit sources?
-What else for future revenue?
-Interactive advertising
I would like to first give a little insight of the recent years profit situation
of TV industry through some data of Australia, EU and US market, and then analyze
the advertisement and interactive trend in TV industry, finally concluded with
thinking of profit in Internet TV.
Generally, the television network market consists of advertiser spending on
broadcast and cable networks plus other sources of revenue that vary by region.
In North America, the television network market comprises license fees paid
by cable systems and satellite providers to basic and premium cable networks.
In Europe, Middle East, Africa (EMEA), and Asia/ Pacific, it includes public
TV license fees. Net advertising figures—made up of spending minus agency commissions
and discounts—are tracked in EMEA, Asia/Pacific, Latin America, and Canada.
Advertising in the United States is customarily reported with agency commissions
included. Let’s look at the situations in Australia, EU and US.
Now we begin with Australia.
Australia
The many ownership changes that occurred in the commercial television ector between the mid 1980s and the early 1990s caused abnormal losses during the period. However, the sector had returned to healthy levels of profitability by the end of that decade. In fiscal 2001 and 2002, profit margins were reduced due to an unexpected decline in advertising revenue in calendar 2001. 2004 saw a modest rise in revenues, profit and margins. We can see more from the picture below
Broadcast profit margin before tax of Australian commercial television stations 1958-2004
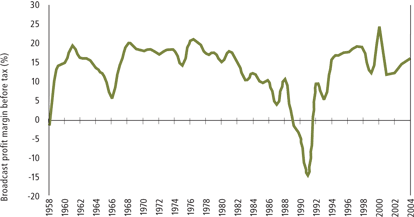
Data is collected from Australian Film Commission
EU
The meeting of experts on the reform of the instruments to encourage the European audiovisual industry addressed a profound research of financial situation in EU TV market.
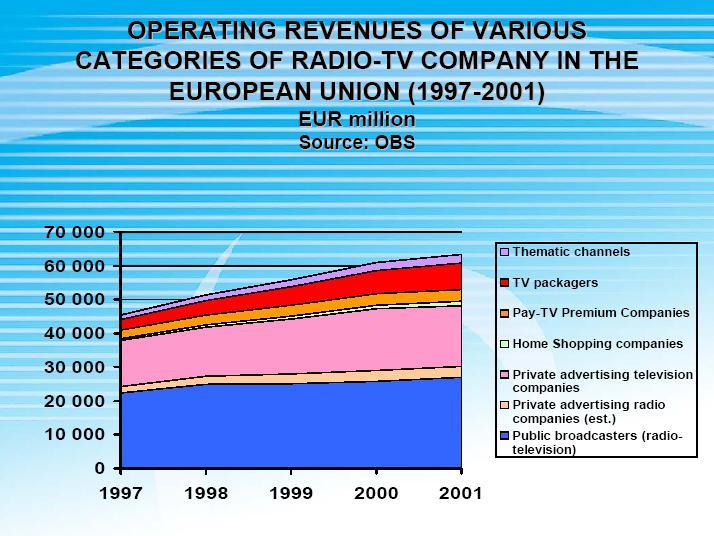
Operating Revenues of various categories of radio TV company in the European Union
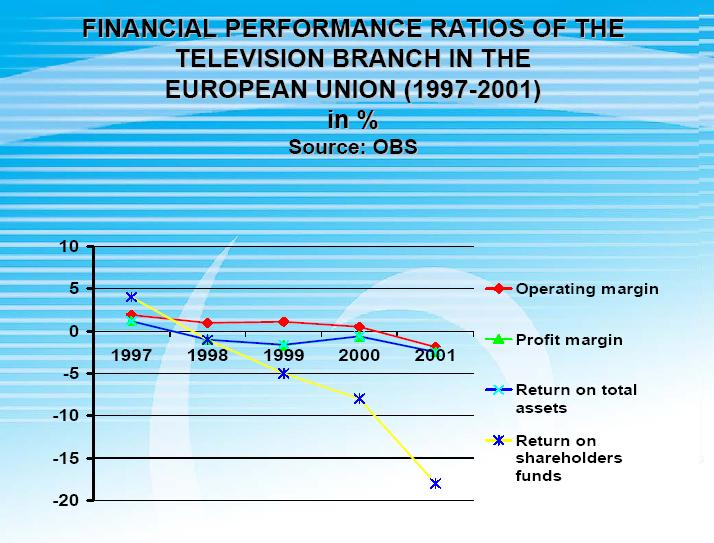
Financial Performance Ratios of the Television Branch in the European Union 1997-2001
Profit Margins of Television Companies in the European Union
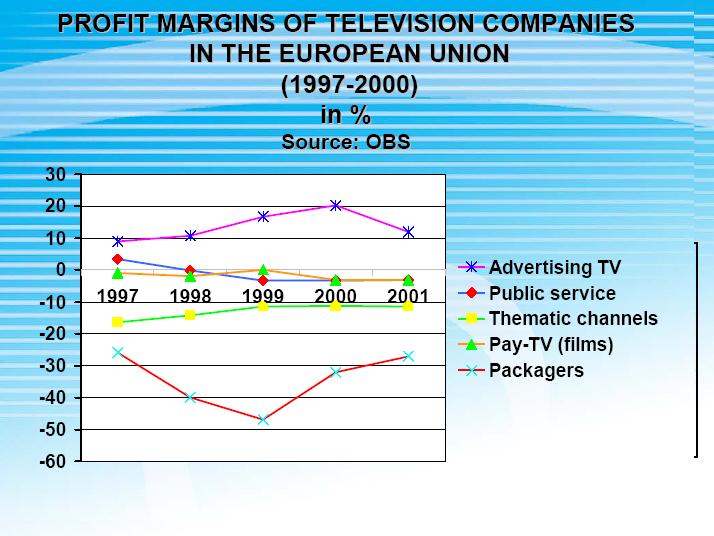
We can see here that even though the operating revenues were steadly increasing during the past few years, the important ratios were not optimistic enough at the same time. What was consistent in all the years was advertising's strong position of creating profits.
Data is collected from Meeting of Experts on the Reform of the Instruments to Encourage the European Audiovisual Industry. http://www.obs.coe.int
US
The PricewaterhouseCoopers business firm's Global Entertainment and Media Outlook: 2004-2008 report predicts that by 2008, the industry will reach $174 billion. The fastest growing market is, not surprisingly, the United States with an annual growth rate of 7.5%.
US's is composed of big four in Broadcast and big three in Cable
Big Four in Broadcast
CBS Television Network
2004 Revenue: $7.76 billion
Number of owned stations: 39
Number of affiliates: 200
NBC Television Network
2003 Revenue: $6.87 billion
Number of owned stations: 29
Number of affiliates: 230
Fox Broadcasting Company
2004 Revenue: $4.55 billion
Number of stations owned: 35
Number of affiliates: 200
ABC Inc.
2004 Revenue: $11.78 billion
Number of stations owned: 10
Number of affiliates: 225
Big Three in cable
QVC Inc.
2003 Revenue: $4.9 billion
Households reached: 86 million in the U.S.A., 13.1 million in the United Kingdom,
34 million in Germany, and 11.6 million in Japan.
ESPN Inc.
2004 Revenue: $3.2 billion
Corporate Owners: Walt Disney Co. owns 80% and The Hearst Corporation owns
20%.
Home Box Office Inc. (HBO) & Time Warner
2004 Revenue: $3 billion & 2004 Revenue: $42 billion
Data is collected from
http://www.turnoffyourtv.com/networks/revenueupdate04/revenue.html
Advertisement
In each case talked above, advertising has been among the most important sources of revenue during a long time in most locations of the world.
But currently the business of advertising is facing a variety of challenges and problems. Changes in the advertising industry practices has been slow. During the early '90s recession, advertisements were slumping. Especially given large shifts in TV technology, advertising and consumer lifestyles, advertisement is necessary to change.
Among major media, TV has no choice but to embrace change as well. It is the biggest advertising medium, accounting for more than $50 billion or about 23% of U.S. ad spending. TV revenue is booming, driven by strong demand from advertisers looking to spend to reach consumers looking to buy. But impending change is as clear as HDTV.
But how to change? Interactive TV came as the next big thing of the early '90s, but didn't attract enough eyes because the dot.com booming.
Interactive Trend
Interactive television, which will enable consumers to order products, compete in game shows, and pay bills via their TV sets, has so far shown more promise than profits. But companies that have invested heavily in the technology hope to see that change soon. Recent developments are:
Further down the line, interactive TV may offer consumers a much wider range of products. Entertainment, consumer electronics, and computer companies including Apple Computer, Sony, and Toshiba are exploring ways to mesh their capabilities. For example, IBM and Time Warner (which owns FORTUNE'S publisher) are discussing ways to combine Big Blue's data-transmitting expertise with the media giant's cable TV systems, TV shows, and movies.
Interactive more influences the revenues of TV industry. Traditional commercials are changing into interactive marketing and on line marketing.
BMW's ongoing review for a new agency further highlights the central role interactive is playing for auto marketers. In a brief it sent to agencies in the review, the carmaker stated that "interactive represents a significant portion" of the account, and the winning agency would lead a redesign to make BMW's Web site "the best and most exciting automotive Web site."
Thinking of Profit in Internet TV
The Internet has progressed beyond being viewed as a purely direct-response channel to a key branding vehicle that can offer deeper consumer engagement than TV commercials — with more measurability. This has translated into a bigger role in client relationships.
With the fast-changing media landscape making consumers harder to reach through traditional methods, clients are involving interactive agencies earlier in the planning process and looking to them to take a more active role in setting strategy. As consumer habits shift, clients are in turn moving more money to digital initiatives, which in turn divert the main sources of traditional TV industry's profit into interactive on line advertisements.
Actually, Internet TV providers can be much more efficient in offering on line commercials to clients than traditional TV companies and creating up to date product of exploring innovative profit sources
The potential profits of Internet TV will not only come from the sources for old TV industry, but also variablility of mixed medias. For example, combining TV with blogs, on line shoppings, and etc.
Driving Forces
Sources of Profit are changing
Name
The sources of profit are changing in TV industry. As I analyzed in the research questions concerned with profit, the traditional ways of earning revenues in TV is advertisement, to be exactly, one way advertisement that audience in front of TV set passively accept whatever is showing on TV. Such kind of advertisement is confronted with a downside profit earning, that old TV industry can't back up itself with one way advertisement for a long time in the future. New profits may catch audience's eyes from television to other medias, like Internet TV, where the profits can be explored.
Enablers
Inhibitors
It could be other channels existing or potentially emerging that also provide interation with audience. For example, mobile TV is an alternative, which allows users to watch TV and provide fee of commertial services directly through mobiles. Even the enjoying feeling of watching TV can't be regarded the same as watching real TV through television set or PC, the convience and mature payment network exceed the situation in Internet TV. Whatever, mobile TV and Internet both need more technical maturity and market acceptance.
Paradigms
Innovative forms of profit are created based on more variable medias. Advertisements are diversified and audience participate and enjoy commertials while disclose their preference to ad makers and marketers to provide them more opportunities for new profit sources creation.
Experts
Supported by front edge advertisement makers, who are running interactive commertials to get large margin.
Timing
The change in profit resources is under way nowdays. It is probable within a few years that a quite larger amount of advertisements is distributed through more variable medias and in the form of two way communications.
Web Resources
Please refer to my WIKI of profit research question in Internet TV.
Habits of audience are changing
Name
The audience is exposed to whatever new technologies in the market, and they are approaching the most favourable way to collect the information they want. As long as TV can't meet their needs, they quickly resort to other media. That is exactly what is taking place or potentially emerging.
Enablers
Inhibitors
Paradigms
Audience own full freedom and flexibility to choose and collect the information and programs they want through whatever medias available.
Experts
No typical experts found
Timing
Audience habits are rapidely changing now. As long as property issues, technology and resource channels are avaible, audience will quickly adapt to the Internet TV.
Web Resources
Please refer to my WIKI of profit research question in Internet TV.
New competitors are edging in
Name
The range of competition in TV industry is enlarged out of the old empire. Active players in Internet business are stepping into TV area and biting the same cake.
Enablers
Inhibitors
Paradigms
For the audience, it could be the best that the functionalities provided be Internet and TV can be combined well with easy approach to reach and consistent payment methods
For the whole TV industry, the best value creatation channels will be utilized to create favourable profit and fulfill the task of public media.
Experts
Timing
Timing of prosperity of big players in Internet TV market, like Google, will largely depends on how to solve the problems mentioned in inhibitors.
Web Resources
Please refer to my WIKI of profit research question in Internet TV.
New media mix is forming
Name
Internet is actually not the only competitor to the traditional TV industry. New technologies even mix together to create new ways of information distribution. Whenever a market is appearing, new competitors are rushing in.
Enablers
Inhibitors
Business model structuring: the cooperation among other channels out of TV doesn't formalize a stable business model yet. Revenue distribution and power holding can be potential blocks that delays new mixed up to the market.
Paradigms
It could be the best for the customers to have a large amount of available choices to get information and entertainment,meanwhile to be less limited by the time and location.
Experts
No typical experts found.
Timing
The timeing of mixed up technology to replace TV heavily depend on whether the mixed innovation can be technically feasible, commertially profitable and fully acceptable in market.
Web Resources
Please refer to my WIKI of profit research question in Internet TV.