Ci'Num scenario 1: Collapse
Scenariothinking.org > Ci'Num 07 Homepage > The 2030 Scenarios
|
|
Position in the scenario tree
- Will we have the global organizational capacity to address the overshoot? - No
- What is the primary constraint of human activities? [irrelevant]
- What are the main mechanisms for organizing large scale systems? [irrelevant]
Initial Description
Despite having the necessary technologies at hand, we have collectively done little to reduce global warming and to plan for shortages in fossil energies, fresh water, arable land, etc. Crises occur in growing frequency and seriousness, severely damaging the world economy and producing human catastrophes, both natural and man-made, especially in developing countries. Hundreds of millions of refugees roam Asia and Africa, and migratory pressure on the North becomes insupportable. Borders close, local conflicts multiply and threaten to expand, mobility decreases, economies and societies retract and relocalize. Public spirit is low, spontaneously erupting in local conflicts. Alliances shift and solidarity can no longer be extended globally as each group fights for its own survival. Technology is used mostly to plan for and cope with current or coming difficulties, and to provide alternatives or escapes from an uninspiring daily life. Alternatives are found in frugal, hyperlocal community-building as well as in semi-autonomous, encrypted and somehow tolerated virtual networks.
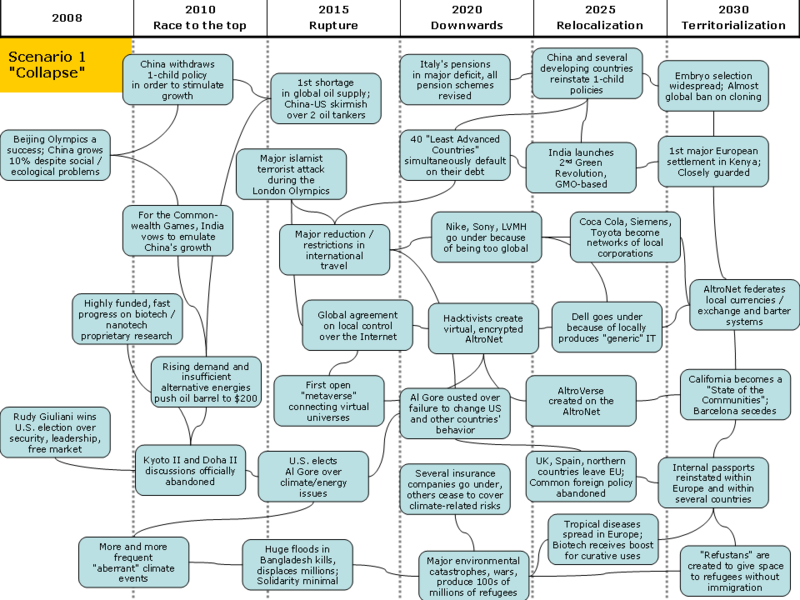
Timeline
(click image to see it full-size)
Full scenario
In retrospect, these seem like quiet, easy times, although of course they weren't. Everything seemed to work. As a symbol, the 2008 Beijing Olympics were an unprecedented success: Spectacular (205 records beaten!), grandiose, popular (4.5 billion viewers, all screentypes considered), safe and very profitable! China did justice to its new status as a world giant. Sure, doping ran rampant, especially in China's teams, and athletes and spectators alike came back to their own polluted metropolis feeling that nothing could really be worse than Beijing, Al Gore was touring the world with yet another frightening movie, but what the heck: We had fun; money, information and images flowed; innovation happened all over the place. The system worked.
Race to the top
That shared feeling gave Rudy Giuliani the U.S. presidency in November, 2008. Americans and others felt they needed leadership for growth and safety, not abstract, future-facing, planetary principles. "Clean" growth was fine, as long as it was fast growth. The fledgling discussions that should have led to a second Kyoto round by 2009 were soon abandoned when it became clear that neither Russia, nor the U.S. would sign, and when China, in its bid for greatness, announced it was giving up its "One child" policy.
Sure, we were aware of what was coming, although on an intellectual plane. TV news reported on extreme climate events, meters of rain in Britain while Eastern and Southern Europe suffered draughts and scorching heat. But most of it happened far away and was gone in a few weeks. It was hard to see the pattern clearly, however many blogs, prophets, reports and rockstars poked it right in your face.
But it was just too great a time. If you were into Web 2.0, 3.0, mobile or ubicomp, you could invent all you wanted and implement it, get funding and millions of users in a matter of weeks. With people interacting, cooperating, building things together online, it seemed like if the web's original vision was coming true, and this time, with viable business models. Biotech, neuroscience and nanotech were making fast progress, yielding new cures and diagnoses, better GMOs, spectacular new materials and a few less publicized drugs and methods that mostly soldiers, movie stars and aspiring champions took. New products came onto the market all the time, consumers liked them, emerging countries contributed to growing the market and keeping prices down, while their population got access to western affluence and asked for nothing better.
So we grew. India vowed that the 2010 Delhi Commonwealth Games would be even grander than Beijing, to which China responded by pumping more money into the Shanghai 2010 World Expo. The oil barrel hit $150, then $200, and that hurt, although not so much: There was plenty of money and besides, the careful planners knew there were always a few weeks each year when prices went sharply down, despite the clear upwards trend.
In many ways, we felt that global warming and the shortage of exhaustible resources such as oil and water would go away. We would discover inexhaustible energy sources, we would become able to control climate or recapture the CO2. Besides, we bought hybrid cars, we have 2 or 3 garbage cans for recycling, we almost gladly paid new taxes for our fuel and air travel, we videoconferenced a little, we worked from home most Fridays – enough, then, to let us feel entitled to oppose the wind turbine that would ruin the view from the back of our country house.
These were fun times, really. Until it hit us.
Rupture
It started on an Olympic year as well, 2012. In May, a skirmish between China's and the U.S. Navies over two supertankers that both countries wanted in their own ports, illustrated how depleted oil inventories were. This alone triggered a chain of events that sent oil prices to the roof, grounded 40% of UPS and Delta airplanes, caused several factories to shut down until oil supplies were regular again and led whole cities to forbid climatization despite the hot summers. Then, despite – or perhaps thanks to – the massive deployment of security and surveillance technology, 3 deadly and really cunning terrorist attacks created havoc just before the last day of London's Olympics. First, Wembley stadium's safety system was highjacked during the football final, and use to create panic while all doors were closed, electric fences were on and contradictory announcements were made. The second attack was biological, in the closed stadium where gymnastics took place. Meanwhile, a distributed denial of service attack disabled the city's communication networks, surveillance nodes and sensors as well as all geo-located information services, effectively preventing all kind of timely reaction.
At the end of August, an unusually stormy rainy season in the Gulf of Bengal resulted in flooding the Ganges-Brahmaputra Delta, killing and displacing millions of Bengalis and effectively destroying most of Bangladesh's infrastructure. But the rest of the world was so caught up in its own problems that, after the initial mobilization of media, NGOs and military assistance, solidarity was truly minimal.
These events had devastating ripple effects. Stock markets tumbled, of course. Air travel was hit hard, first by fear of other attacks and by security measures that made boarding planes a living hell and created total unpredictability in schedules, second by the price of fuel and last, by government air traffic restrictions. Heavy in debt due to their liberal purchase of new aircraft, several airlines filed for bankruptcy. Airbus only survived this blow by operating some of its own airplanes while finally agreeing for a 30% Russian investment. Public trust was shattered, savings went up, consumption, construction and investment plummeted. Security agencies at last succeeded in regulating the Internet, allowing national – and de facto U.S. – control over most of what circulated on the Net. In 2013, the world economy decreased by 2% and international trade by 22%.
Downwards
With his sometimes annoying "I told you so" attitude, Al Gore had no difficulty in winning the November 2012 presidential election in the U.S. He had more trouble in achieving anything of substance. Everybody was scrambling for his or her survival. Pension systems where crumbling down all over the western world, forcing radical changes in pension schemes: Full retirement age moved up to 70, sometimes 75; in some countries, the very idea of "full retirement" disappeared; family solidarity was strongly encouraged and sometimes made mandatory. Seizing the occasion, 40 "Least advanced countries" officially and simultaneously let it be understood that their foreign debt would not be honoured. Insurance companies revised their policies to exclude most climate-related risks. Border were closed tighter than ever in the West and Asia, effectively maintaining economic migrants and the growing number of refugees displaced by ecological catastrophes or local conflicts over natural resources in a permanent no-man's land.
Diplomatic relationships chilled notably among most countries. Multilateral diplomacy was entirely replaced by bilateral agreements dictated by the need for securing markets and energy supply channels.
Faced with tough and unforeseen budget problems, countries cut down on all non-essential spending, and even on some core activities such as education or R&D. Corporations did the same. Venture capital disappeared, except perhaps in the core of the Silicon Valley. R&D and innovation became almost clandestine activities, although they never ceased to take place.
A few hacktivists felt it their duty to protect the free flow of ideas that was such an important part of the pre-2012 era. On top of the physical and heavily controlled Internet, they set up an encrypted, dynamic virtual network which came to be called the Altronet. The Altronet successfully resisted a number of official and not-so-official attacks and then almost seemed to be left alone, perhaps because authorities and bad guys alike knew that it filled a gap and that they could use it for their own purposes as well. By 2020, most Internet users were de facto Altronet users.
Relocalization
Despite the Altronet, by 2020-2025, globalization was a thing of the past. Individuals, corporations, local communities, countries were all left to fend for themselves. International trade was half of what it was 10 years ago. Some financial markets chose to disconnect from real-time global trading networks. China, India and many developing countries reinstated "One-child" policies. After the UK, Spain and most Scandinavian countries had left it, the EU gave up all pretence of being anything else than an economic space – and even then, countries took to invoking safeguard clauses on all occasions and negotiated their own bilateral agreements. Local conflicts multiplied over access to water, trade routes, pipelines or even trade tariffs, although none have (yet) escalated to nuclear or biological warfare. On the other hand, terrorism was all but extinct, due to border closure and perhaps more importantly, to the departure of all western forces from the Middle East, Afghanistan and Pakistan. After striking a deal with the Palestinians, even Israel was left alone to manage its enormous economic problems.
The only thing on which developed countries could still agree was the protection of key infrastructures such as the Suez and Panama canals, network nodes and root servers, root identity providers, GPS satellites and, when they could, intercontinental pipelines.
Local communities slowly learned to cope with the new situation. Local currencies emerged, facilitated by electronic networks, contactless cards and simple, open software. After Nike, Sony and LVMH had shown what it cost to still operate as centralized multinationals, firms like Coca Cola, McDonald's, Siemens, Toyota and HSBC reinvented themselves as loose networks of local companies. Using knowledge accumulated by its engineers when they were subcontracting to western firms, plus its own brand of inventiveness, India launched and exported its own, GMO-based "2nd Green Revolution", despite well-grounded fear and protests over health and environmental risks. Many countries developed their own brands of "generic" IT equipments. India's generic or cheap "intelligent" drugs also came in handy when Eastern Europe was struck by a wave of tropical diseases, brought north by global warming and against which the local population had no natural defences.
Local values emerged or were rediscovered. Historical events, personalities, artefacts, works of art and places were revisited as the foundations of a new future. Designers, artists, fashion designers, learned to use these symbols in combination with recycled material to incarnate the values of their time. To compensate for the lack of funding and of international coordination, researchers and innovators built interdisciplinary local clusters, microfunding mechanisms and ultra-short innovation cycle mechanisms, yielding significant results in a number of areas: very low-powered IT, intelligent recycling, biomass and other renewable energy sources, revisitation of traditional medicine, resistant and frugal GMOs and genetically engineered livestock, advanced warning and crisis-management systems, polyresistance-enhancing drugs, etc. Of course, scientists and innovators used the Altronet heavily to interact with other people in the world, but their endeavours had difficulties reaching large enough markets, preventing some of their findings from making the difference they could have made.
People learned to do a lot of things together remotely; however, they could not remove a sense of emotional remoteness, and tended to give priority to their proximity links. The age of promethean science and technology was long gone. Science and technology had to be modest, problem-oriented, sensitive to the urgency of current problems and the fragility of local ecological, economic and political systems. Cloning, human enhancement and most nanotechnologies were mostly banned, although not everywhere. In fact, some mistrust could be felt about those technologists who, it was sometimes said, "led us to where we are".
Territorialization
By 2030, the world population was slightly under 8 billion, close to the bottom estimate of the UN's 2006 forecasts. Climate change had ruined the lives of hundred of millions and energy remained a major constraint, despite the halving of growth rates compared to the pre-2012 era. In fact, faced with constant emergencies, public entities and corporations had not taken many conscious steps to change their ways of producing and of doing business.
Individuals had gone a longer way, though, both out of economic constraints and because the millions of unemployed invented a number of local jobs: on-demand local taxis (often 2-wheeled), selective garbage collection, recycling management, repair-it-alls, etc. These individuals came to form an important part of the social fabric.
The many local equilibriums that originated from coping with the new, post-globalization situation, felt a strong need to define (and defend) the territories in which they operated. They wanted to assert and live by their newfound values, to define who was local and who was foreign, to protect their fragile activities from competition. After Catalonia, many European regions, as well as North American states or provinces, reached quasi-independent status. Cities like Barcelona also all but seceded. Internal passports were created within several countries and of course (as early as 2020), reinstated within the European Union.
Climate and conflict refugees also needed their territories. Through one of this period's rare major international initiative, they were directed towards three new "Refustans", bought from Russia, Australia and Tanzania and then viabilized. The story of these new countries remains to be written, but their initial years were clearly reminiscent of Australia's of the American West's histories.
"Territories" were not just geographic, though. Religious, ethnical, cultural and other kinds of communities also ended up forming their own borders, defining citizenship, forging rules and institutions and using the Altronet to effectively work as coherent territories. The quasi-independent State of California was the first to recognize their existence by revising its constitution to become a "State of Communities".
The Altronet played a large role in allowing new federated organizations to emerge. Local currencies and exchange systems use it for inter-system trade and compensation; several community disputes were settled on the Altroverse, the open-source federation of virtual universes that first emerged in the 2015s as the "Metaverse", and merged with the Altronet some years later. Some real popular trials were conducted in this 3D space, with judges, prosecutors and lawyers. In fact, the Altronet is generally credited for preventing many conflicts since it emerged, although of course, it has also helped spread forms of – less lethal – cyberwar. Some believe that the Altronet is the mechanism that will effectively bind these multiple and intertwined communities into a new, more open international community.
Amplify, comment and contribute!
You can do that, either by editing the above text, or by providing comments and ideas below.