Difference between revisions of "Quality of Broadband services"
(→Timing) |
|||
| (36 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
====Description==== | ====Description==== | ||
Quality of a broadband services refers to the measures of the broadband technical performance. These measures consists of the bandwidth available and the latency of the network at the end-user side, which are issues of major relevance in the Internet environment. Nowadays USA after being for almost a decade the leading country on Internet services, especially broadband, is facing a major debacle due to not properly planned investment which resulted in low quality services, such as the so called broadband subscription which offer a tiny 436Kb of bandwidth, while European average bandwidth is around 5MB up to the 100MB of the average Japanese household. | |||
Therefore, in order to support the increasing demand (see Figure 1) of services such as IPTV, Internet TV and mobile TV, the global infrastructure on which Internet is based will require large investments so that the final users will positively experience these services. Hence, a satisfied consumer will be willing to try more innovative services and will introduce it in his own life creating a so called network effect concerning the adaptation. | |||
[[image:USipTrafficProjection01.png]] | |||
<br>Figure 1 - US Internet data traffic projection. | |||
====Enablers==== | ====Enablers==== | ||
<ul> | |||
<li>Increasing use of new (high quality) type of connection: | |||
Fiber to the Home (FTTH) | |||
Hybrid fiber wire (HFW) | |||
WiFi | |||
Wi-Max | |||
</li> | |||
<li>Full implementation of IPv6 (Internet Protocol V6)<li> | |||
</ul> | |||
====Inhibitors==== | ====Inhibitors==== | ||
<ul> | |||
<li>Unexpected growth of the Internet traffic</li> | |||
<li>Slowdown of investment in infrastructure</li> | |||
</ul> | |||
====Paradigms==== | |||
Before: Up to couple of years ago Internet connections were often narrow-band, limiting the online experience to web-browsing, reading email and slow download through P2P software. | |||
After: The Internet has become a multimedia channel, through which is possible stream contents from audio to video. This is just the begin of what will be in the future internet through a progressive improvement of the quality of Broadband services in order to support HD video, high quality contents and real-time online storage. | |||
====Timing==== | |||
<b>Network technology milestones:</b><br> | |||
'80s-'90s: PSTN (2400bps - 56kb)<br> | |||
'90s: ISDN (64-128kb)<br> | |||
1998: WLAN (802.11) devices are introduced on consumer market <br> | |||
2000: Optical Fiber - FTTH, FTTB, FTTC (10 Mb) - Available for consumer market in Europe<br> | |||
2000: ADSL (256kb-8Mb)<br> | |||
2005: ADSL2 (up to 10Mb)<br> | |||
2006: Optical Fiber - FTTH, FTTB, FTTC (100 Mb) - Available for consumer market in Europe<br> | |||
2006: ADSL2+ (up to 25Mb) | |||
<br> | |||
<b>Mobile technology milestones:</b><br> | |||
1991: 2G - Digital cellular phones (Europe: GSM)<br> | |||
1993: 2G - First SMS sent <br> | |||
2000: 2.5G - GPRS data technology<br> | |||
2001: 3G - Ntt Docomo launches in Japan the first 3G service based on WCDMA<br> | |||
2003: 2.5G - EDGE data technology (widely diffuse in the USA)<br> | |||
2003: 3G - UMTS appears in Europe<br> | |||
2006: 3G - HDSPA (High-Speed Downlink Packet Access) is introduced | |||
<br> | |||
<b>Internet Protocols milestones:</b><br> | |||
1981: Introduction of IPv4<br> | |||
1992: Recognized an upcoming shortage of addresses with IPv4<br> | |||
1994: Begin of IPv6 deployment<br> | |||
2001: First experiment with IPv6<br> | |||
2004: Published Mobile IPv6 (RFC 3775)<br> | |||
2008: Deployment of IPv6 at Backbone level in USA<br> | |||
<br> | |||
[[image:IPv6History.gif]]<br> | |||
Figure 3: Adapted from Source: IPv6 Timeline - A pragmatic projection http://www.nanog.org/mtg-0302/ppt/hain.pdf | |||
====Web Resources==== | ====Web Resources==== | ||
<ul> | |||
<li>[[http://www.discovery.org/a/4428]]</li> | |||
<li>[[http://www.ipv6.com/articles/general/timeline-of-ipv6.htm]]</li> | |||
<li>[[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/3G]]</li> | |||
<li>[[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Broadband_Internet_access#DSL_.28ADSL.2FSDSL.29]]</li> | |||
</ul> | |||
<br> | |||
Go Back to [[The_future_of_television_%28moving_pictures%29_2015|The future of television 2015]] | |||
Latest revision as of 21:48, 18 May 2008
Description
Quality of a broadband services refers to the measures of the broadband technical performance. These measures consists of the bandwidth available and the latency of the network at the end-user side, which are issues of major relevance in the Internet environment. Nowadays USA after being for almost a decade the leading country on Internet services, especially broadband, is facing a major debacle due to not properly planned investment which resulted in low quality services, such as the so called broadband subscription which offer a tiny 436Kb of bandwidth, while European average bandwidth is around 5MB up to the 100MB of the average Japanese household.
Therefore, in order to support the increasing demand (see Figure 1) of services such as IPTV, Internet TV and mobile TV, the global infrastructure on which Internet is based will require large investments so that the final users will positively experience these services. Hence, a satisfied consumer will be willing to try more innovative services and will introduce it in his own life creating a so called network effect concerning the adaptation.
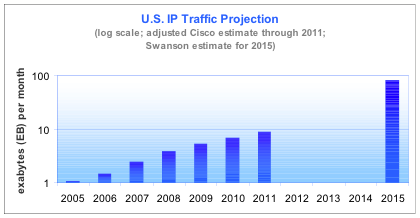
Figure 1 - US Internet data traffic projection.
Enablers
- Increasing use of new (high quality) type of connection: Fiber to the Home (FTTH) Hybrid fiber wire (HFW) WiFi Wi-Max
- Full implementation of IPv6 (Internet Protocol V6)
Inhibitors
- Unexpected growth of the Internet traffic
- Slowdown of investment in infrastructure
Paradigms
Before: Up to couple of years ago Internet connections were often narrow-band, limiting the online experience to web-browsing, reading email and slow download through P2P software.
After: The Internet has become a multimedia channel, through which is possible stream contents from audio to video. This is just the begin of what will be in the future internet through a progressive improvement of the quality of Broadband services in order to support HD video, high quality contents and real-time online storage.
Timing
Network technology milestones:
'80s-'90s: PSTN (2400bps - 56kb)
'90s: ISDN (64-128kb)
1998: WLAN (802.11) devices are introduced on consumer market
2000: Optical Fiber - FTTH, FTTB, FTTC (10 Mb) - Available for consumer market in Europe
2000: ADSL (256kb-8Mb)
2005: ADSL2 (up to 10Mb)
2006: Optical Fiber - FTTH, FTTB, FTTC (100 Mb) - Available for consumer market in Europe
2006: ADSL2+ (up to 25Mb)
Mobile technology milestones:
1991: 2G - Digital cellular phones (Europe: GSM)
1993: 2G - First SMS sent
2000: 2.5G - GPRS data technology
2001: 3G - Ntt Docomo launches in Japan the first 3G service based on WCDMA
2003: 2.5G - EDGE data technology (widely diffuse in the USA)
2003: 3G - UMTS appears in Europe
2006: 3G - HDSPA (High-Speed Downlink Packet Access) is introduced
Internet Protocols milestones:
1981: Introduction of IPv4
1992: Recognized an upcoming shortage of addresses with IPv4
1994: Begin of IPv6 deployment
2001: First experiment with IPv6
2004: Published Mobile IPv6 (RFC 3775)
2008: Deployment of IPv6 at Backbone level in USA
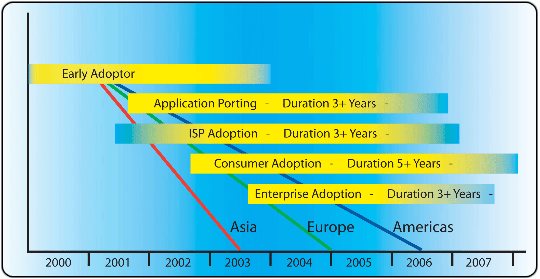
Figure 3: Adapted from Source: IPv6 Timeline - A pragmatic projection http://www.nanog.org/mtg-0302/ppt/hain.pdf
Web Resources
Go Back to The future of television 2015