Difference between revisions of "4 Developing standard of e-learning"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Description:== | ==Description:== | ||
Currently, most e-learning standards can be organized into some general categories: | Currently, most e-learning standards can be organized into some general categories:<br> | ||
'''Metadata.''' Many developers argue that metadata content is the heart of e-learning. Learning content and catalog offerings must be labeled in a consistent way to support the indexing, storage, discovery (search), and retrieval of learning objects by multiple tools across multiple repositories.<br> | |||
'''Content packaging.''' The goal of content packaging specifications and standards is to enable organizations to transfer courses and content from one learning system to another. This is crucial because content can potentially be created by one tool, modified by another tool, stored in a repository maintained by one vendor, and used in a delivery environment produced by a different supplier. Content packages include both learning objects and information about how they are to be put together to form larger learning units. They can also specify the rules for delivering content to a learner.<br> | |||
'''Metadata.''' Many developers argue that metadata content is the heart of e-learning. Learning content and catalog offerings must be labeled in a consistent way to support the indexing, storage, discovery (search), and retrieval of learning objects by multiple tools across multiple repositories. | '''Learner profiles.''' These standards allow different system components to share information about learners across multiple system components. Learner profile information can include personal data, learning plans, learning history, accessibility requirements, certifications and degrees, assessments of knowledge (skills/competencies). In addition, systems need to communicate learner data to the content, such as scores or completion status.<br> | ||
'''Content packaging.''' The goal of content packaging specifications and standards is to enable organizations to transfer courses and content from one learning system to another. This is crucial because content can potentially be created by one tool, modified by another tool, stored in a repository maintained by one vendor, and used in a delivery environment produced by a different supplier. Content packages include both learning objects and information about how they are to be put together to form larger learning units. They can also specify the rules for delivering content to a learner. | |||
'''Learner profiles.''' These standards allow different system components to share information about learners across multiple system components. Learner profile information can include personal data, learning plans, learning history, accessibility requirements, certifications and degrees, assessments of knowledge (skills/competencies). In addition, systems need to communicate learner data to the content, such as scores or completion status. | |||
'''A closer look at SCORM'''<br> | '''A closer look at SCORM'''<br> | ||
Because SCORM is the standard document with the most impact on the e-learning industry, it’s worth a closer look. | Because SCORM is the standard document with the most impact on the e-learning industry, it’s worth a closer look.<br> | ||
[[Image:scorm.jpg]] | [[Image:scorm.jpg]] | ||
Revision as of 04:35, 19 July 2006
Description:
Currently, most e-learning standards can be organized into some general categories:
Metadata. Many developers argue that metadata content is the heart of e-learning. Learning content and catalog offerings must be labeled in a consistent way to support the indexing, storage, discovery (search), and retrieval of learning objects by multiple tools across multiple repositories.
Content packaging. The goal of content packaging specifications and standards is to enable organizations to transfer courses and content from one learning system to another. This is crucial because content can potentially be created by one tool, modified by another tool, stored in a repository maintained by one vendor, and used in a delivery environment produced by a different supplier. Content packages include both learning objects and information about how they are to be put together to form larger learning units. They can also specify the rules for delivering content to a learner.
Learner profiles. These standards allow different system components to share information about learners across multiple system components. Learner profile information can include personal data, learning plans, learning history, accessibility requirements, certifications and degrees, assessments of knowledge (skills/competencies). In addition, systems need to communicate learner data to the content, such as scores or completion status.
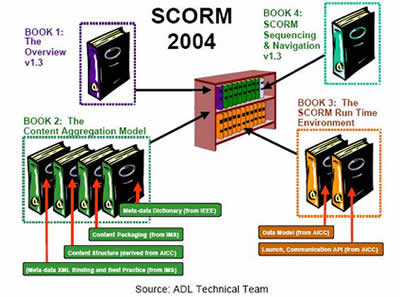
A closer look at SCORM
Because SCORM is the standard document with the most impact on the e-learning industry, it’s worth a closer look.